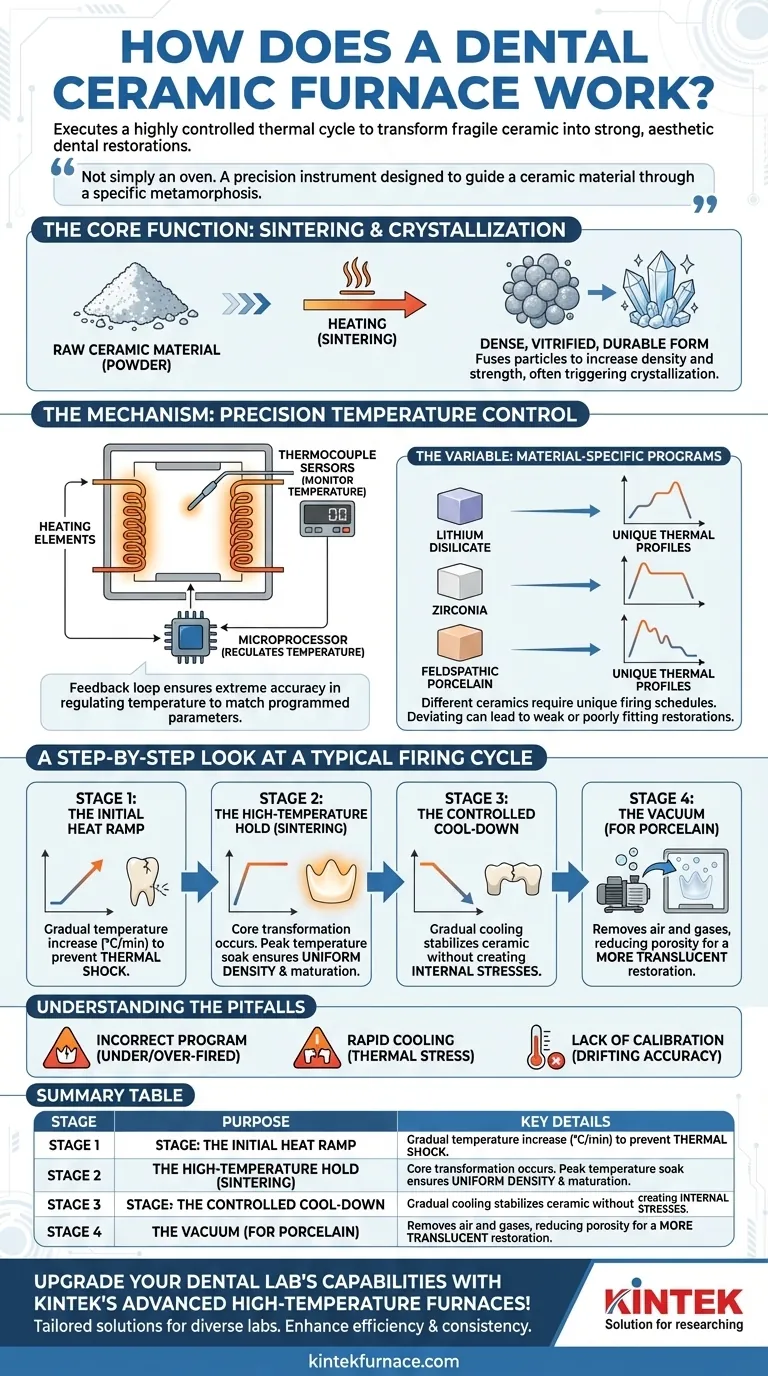
In essence, a dental ceramic furnace works by executing a highly controlled thermal cycle to transform a fragile ceramic material into a strong, aesthetic, and dimensionally stable dental restoration. This process involves precise heating to a specific peak temperature, holding it for a set duration, and then carefully cooling it back down. The entire cycle is programmed based on the exact type of ceramic being used.
A dental furnace is not simply an oven. It is a precision instrument designed to guide a ceramic material through a specific metamorphosis—from a chalky, weak state to a dense, vitrified, and durable final form. The success of a restoration depends entirely on the accuracy of this thermal journey.

The Core Function: Sintering and Crystallization
A furnace's primary job is to initiate and control the physical and chemical changes within dental ceramics. This is far more complex than simple heating.
The Goal: From Powder to Solid
The raw ceramic material, whether a milled block or applied porcelain powder, consists of individual particles. The firing process, known as sintering, heats these particles until their surfaces begin to fuse together.
This fusion reduces the space between particles, dramatically increasing the material's density and strength. For some materials, this process also triggers crystallization, forming an interlocking crystalline structure that provides exceptional durability.
The Mechanism: Precision Temperature Control
To achieve this transformation without flaws, the furnace relies on sophisticated components. Heating elements (often quartz or silicon carbide) generate the heat, while thermocouple sensors constantly monitor the internal temperature.
This feedback loop allows the furnace's microprocessor to regulate the temperature with extreme accuracy, ensuring the firing cycle matches the programmed parameters exactly.
The Variable: Material-Specific Programs
There is no universal firing program. Different ceramics like lithium disilicate, zirconia, and feldspathic porcelain have vastly different compositions and require unique thermal profiles.
Manufacturers provide specific firing schedules for their materials. Deviating from these schedules can lead to a weak, opaque, or poorly fitting restoration.
A Step-by-Step Look at a Typical Firing Cycle
Each stage of the firing cycle serves a distinct and critical purpose. Understanding each one is key to troubleshooting and achieving predictable results.
Stage 1: The Initial Heat Ramp
The furnace does not immediately jump to its peak temperature. Instead, it ramps up the heat at a controlled rate, often measured in degrees Celsius per minute (°C/min).
This gradual increase prevents thermal shock, where a sudden temperature change can cause the ceramic to crack before the firing process has even truly begun.
Stage 2: The High-Temperature Hold (Sintering)
This is where the core transformation occurs. The furnace reaches a programmed peak temperature and holds it for a specific duration.
During this "soak," the sintering or crystallization process reaches its intended completion. The length of the hold ensures the entire restoration, from the surface to its core, achieves uniform density and maturation.
Stage 3: The Controlled Cool-Down
Cooling is just as critical as heating. The furnace must lower the temperature gradually to allow the ceramic to stabilize without creating internal stresses.
Rapid cooling can cause microscopic (or visible) cracks that compromise the long-term integrity of the crown or bridge.
Stage 4: The Vacuum (For Porcelain)
When firing porcelain, many cycles include a vacuum phase. As the furnace heats up, a pump removes the air from the firing chamber.
This pulls the porcelain particles closer together and removes trapped gases, resulting in a less porous and more translucent restoration that mimics the vitality of a natural tooth. The vacuum is typically released before the high-temperature hold begins.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
A furnace is a powerful tool, but its misuse is the source of many common lab failures. Awareness of these issues is the first step toward prevention.
The Risk of an Incorrect Program
Using a firing schedule intended for a different material is a recipe for failure. This can result in an under-fired restoration (weak, chalky) or an over-fired one (slumped, glassy, discolored).
The Danger of Rapid Cooling
Opening the furnace muffle too early to speed up cooling is a common mistake. This introduces massive thermal stress and is a primary cause of delayed fractures that can occur even after the restoration is in the patient's mouth.
The Necessity of Calibration
Over time, the thermocouple sensor's accuracy can drift. A furnace that thinks it is at 920°C might actually be at 905°C, leading to under-firing.
Regular calibration using standardized kits is non-negotiable for any professional laboratory seeking consistent, high-quality results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you use the furnace should be tailored to the specific demands of the restoration you are creating.
- If your primary focus is strength (e.g., monolithic zirconia crowns): Ensure the furnace is perfectly calibrated to reach the full sintering temperature and that the hold time is strictly followed.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (e.g., layered porcelain veneers): Pay close attention to the firing program's vacuum levels and heat ramp to control the final translucency and surface texture.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and consistency: Invest in a furnace with highly repeatable programs and implement a strict protocol for calibration and maintenance.
Mastering your dental furnace is fundamental to mastering the art and science of ceramic restorations.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Heat Ramp | Prevent thermal shock | Controlled temperature increase (°C/min) |
| High-Temperature Hold | Sintering/crystallization | Peak temperature hold for uniform density |
| Controlled Cool-Down | Stabilize ceramic | Gradual cooling to avoid cracks |
| Vacuum Phase (Porcelain) | Reduce porosity | Removes gases for translucency |
Upgrade your dental lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and consistency in creating durable, aesthetic dental restorations. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your ceramic workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations



















