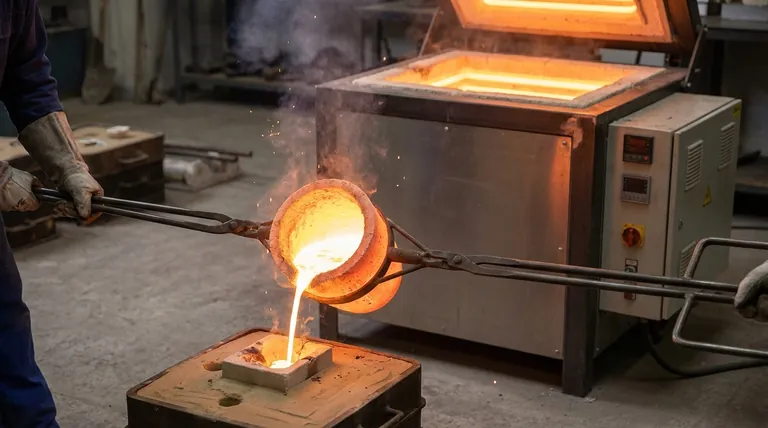
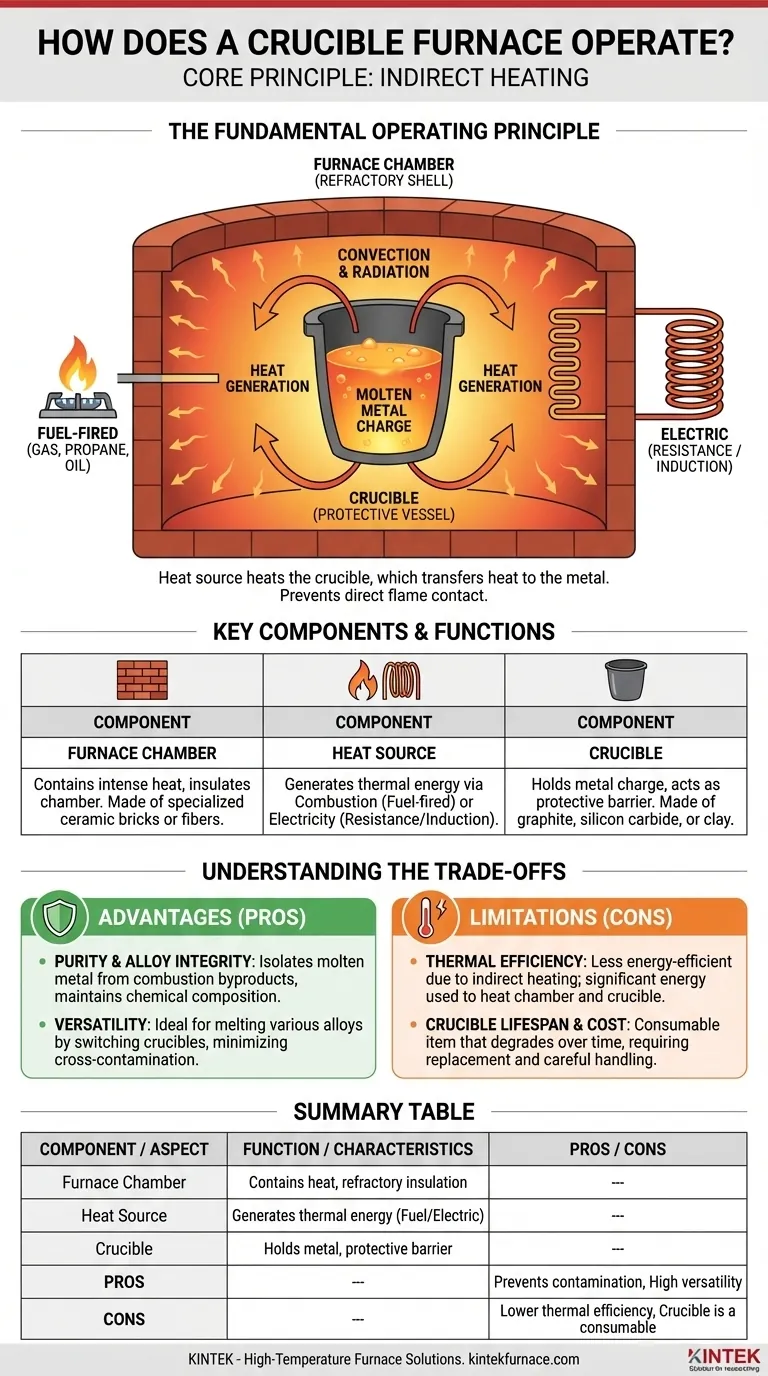
At its core, a crucible furnace operates by using an external heat source to heat a durable container, the crucible, rather than heating the metal directly. This high-temperature furnace chamber heats the crucible through convection and radiation, and the crucible, in turn, transfers that heat to the metal charge inside until it becomes molten. Once melted, the metal can be safely poured for casting.
The fundamental principle of a crucible furnace is indirect heating. Its design intentionally separates the metal from the direct flame or heating elements, which prevents contamination and allows for the precise melting of a wide variety of alloys.

The Fundamental Operating Principle
A crucible furnace's operation can be broken down into three key components: the chamber that contains the heat, the source that generates it, and the vessel that holds the metal.
The Furnace Chamber (The Refractory Shell)
The outer body of the furnace is built from refractory materials, such as specialized ceramic bricks or fibers.
These materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures without breaking down. Their primary job is to contain the intense heat and insulate the chamber, concentrating the thermal energy onto the crucible.
The Heat Source (Generating Thermal Energy)
Heat is generated by one of two primary methods: combustion or electricity.
Fuel-fired furnaces use a burner to combust natural gas, propane, or oil. The resulting hot gases circulate within the chamber, transferring heat to the crucible.
Electric furnaces use either resistance heating elements lining the chamber walls or, in more advanced systems, induction. Induction furnaces use a powerful electromagnetic field to induce an electric current directly within the crucible or the metal itself, generating rapid and efficient heat.
The Crucible (The Protective Vessel)
The crucible is the heart of the system. It's a pot made from materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or clay that can handle extreme thermal shock.
Its critical role is to hold the metal and act as a barrier, shielding it from impurities that could be introduced by direct flame contact. This is essential for maintaining the purity and specific properties of the alloy.
The Heat Transfer Mechanism
Heat moves from the source to the metal primarily through convection and radiation. The hot gases or glowing electric elements radiate heat to the crucible walls and the furnace interior.
Simultaneously, the air or gases inside the chamber circulate via convection, further ensuring the crucible is heated evenly from all sides. This comprehensive heating is what melts the metal charge inside the crucible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the crucible furnace design comes with inherent advantages and limitations that are critical to understand for any application.
Advantage: Purity and Alloy Integrity
The single greatest benefit is preventing contamination. By isolating the molten metal from combustion byproducts, the chemical composition of the alloy remains unaltered. This is crucial for metals where even minor impurities can drastically change their mechanical properties.
Advantage: Versatility
Crucible furnaces are ideal for foundries that need to melt many different types of alloys. Since the metal is contained, switching from melting aluminum to bronze simply requires using a different, dedicated crucible, minimizing cross-contamination.
Limitation: Thermal Efficiency
Indirect heating is inherently less energy-efficient than direct melting methods. A significant amount of energy is used to heat the furnace chamber and the crucible itself before the metal begins to melt. Some heat is always lost through the furnace structure.
Limitation: Crucible Lifespan and Cost
Crucibles are consumable items. They degrade over time due to thermal stress and chemical reactions with molten metal. Their replacement represents a recurring operational cost and requires careful handling to avoid catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific design of a crucible furnace is always tied to its intended application. Selecting the right type depends entirely on the metal you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is casting common non-ferrous metals (like aluminum or bronze): A standard fuel-fired or electric resistance crucible furnace is the most practical and widespread solution.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or reactive alloys (like titanium or specialty steels): An induction furnace using a hermetically sealed crucible is necessary to prevent any atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility for small batches: A "lift-out" furnace, where the crucible is physically removed for pouring, offers a simpler workflow than a larger, fixed "tilting" furnace.
Understanding this core principle of indirect, contained heating is the key to mastering the use of a crucible furnace for any metallurgical task.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Chamber | Contains heat | Made of refractory materials (ceramic bricks/fibers) for insulation |
| Heat Source | Generates thermal energy | Fuel-fired (gas, propane, oil) or Electric (resistance, induction) |
| Crucible | Holds the metal charge | Made from graphite, silicon carbide, or clay; acts as a protective barrier |
| Pros | Cons | |
| :--- | :--- | |
| Prevents contamination, ensuring alloy purity | Lower thermal efficiency (indirect heating) | |
| High versatility for different alloys | Crucible is a consumable, adding to operational cost |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace Solution Tailored to Your Lab?
Understanding the precise operation of a crucible furnace is key to achieving pure, uncontaminated melts. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, custom high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you're melting common non-ferrous metals or producing high-purity reactive alloys.
Let us help you optimize your metallurgical processes. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover the perfect furnace solution for your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















