A controlled atmosphere furnace prevents oxidation and decarburization by systematically replacing the reactive air inside its heating chamber with a carefully selected protective gas. This engineered environment, typically composed of inert gases like nitrogen or argon, creates a buffer that shields the heated material. By eliminating contact with oxygen and other reactive elements present in ambient air, the furnace halts the chemical reactions that degrade the metal's surface and compromise its integrity.
The fundamental principle is not just heating the material, but controlling the chemical environment in which it is heated. By removing reactive oxygen, you prevent oxidation (rusting) and decarburization (carbon loss), ensuring the material retains its desired surface properties and structural strength after treatment.

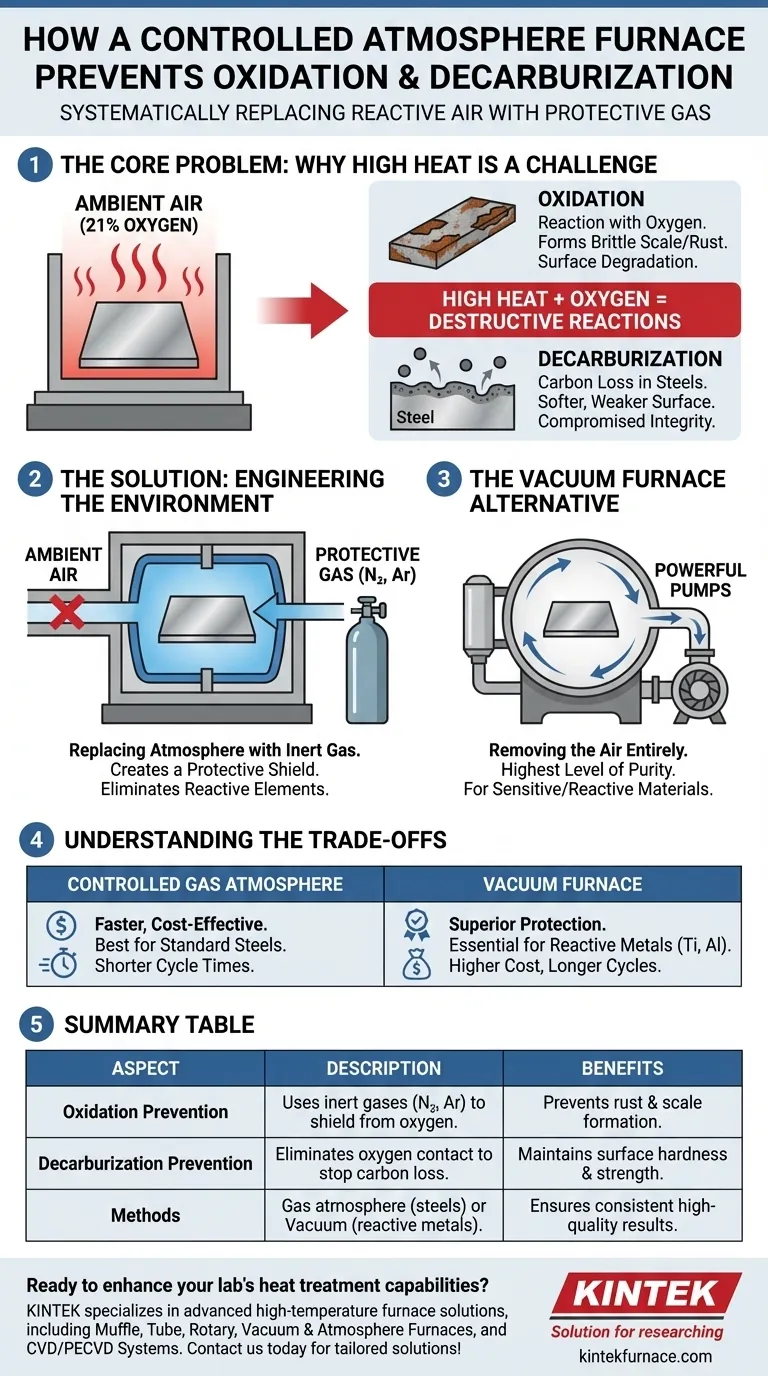
The Core Problem: Why High Heat Is a Challenge
When processing metals, high temperature is a necessary tool. However, when combined with normal air, it becomes a liability, triggering two primary destructive reactions on the material's surface.
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is the chemical reaction between a metal's surface and oxygen, a process that is massively accelerated by heat. This reaction forms a layer of oxides, commonly known as scale or rust. This scale is brittle, can flake off, and results in material loss and a poor surface finish.
What is Decarburization?
Decarburization is a specific issue for carbon-based steels. At high temperatures, the carbon atoms near the surface of the steel can react with oxygen in the air. This reaction pulls carbon out of the steel, leaving the surface layer softer and weaker than the core, which can be catastrophic for components that rely on surface hardness.
Why Ambient Air is the Enemy
Ambient air is approximately 21% oxygen. At room temperature, this poses a minimal threat. But in a furnace operating at hundreds or thousands of degrees, this oxygen becomes highly aggressive, actively seeking to react with the heated workpiece and degrade its quality.
The Solution: Engineering the Environment
To counteract these effects, furnaces are designed to remove and replace the air. This control over the internal atmosphere is what separates a simple oven from a precision heat treatment tool.
Replacing the Atmosphere with Protective Gas
The most common method is to purge the furnace chamber, flushing out the ambient air and replacing it with a protective gas. Gases like nitrogen (N2) and argon (Ar) are popular choices because they are inert, meaning they do not easily react with other elements, even at high temperatures.
This blanket of inert gas acts as a shield. It physically separates the hot metal surface from any residual oxygen, preventing oxidation and decarburization from ever starting.
The Vacuum Furnace Alternative
An even more effective method for eliminating reactive elements is the vacuum furnace. Instead of replacing the air, this type of furnace uses powerful pumps to remove it almost entirely. By creating a vacuum, there are virtually no oxygen molecules left to react with the material.
This approach offers the highest level of purity and is essential for processing extremely sensitive or reactive materials where even trace amounts of contamination are unacceptable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a gas atmosphere and a vacuum is a critical decision based on your material, desired outcome, and budget. There is no single "best" solution for all applications.
Controlled Gas vs. Vacuum
A furnace using a protective gas atmosphere is generally faster and more cost-effective for a wide range of common materials, such as standard steels. The equipment is often less complex and cycle times are shorter.
A vacuum furnace, while offering superior protection against contamination, typically involves higher equipment costs and longer process cycles due to the time required to pump down the chamber. However, for reactive metals like titanium or for medical implants and aerospace components, a vacuum is not optional—it is a requirement.
The Critical Role of Process Integrity
Regardless of the method, the effectiveness of the system depends on its integrity. A leak in a door seal or a contaminated gas supply can completely undermine the process, allowing oxygen to enter the chamber and ruin the workpiece.
Modern furnaces incorporate precise controls and thermal homogeneity to ensure the atmosphere remains stable and the temperature is uniform. This not only prevents oxidation but also reduces energy waste and improves the consistency of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of atmospheric control should be directly driven by the material you are processing and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of carbon steels: A controlled atmosphere of nitrogen or a nitrogen/hydrogen mix is typically the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or aluminum: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent the rapid oxidation that would occur in any other environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, perfectly clean surface with zero change: A high-purity vacuum environment offers the most reliable path to achieving a flawless, contamination-free finish.
By mastering the furnace environment, you gain direct control over the final quality and performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Uses inert gases like nitrogen or argon to shield materials from oxygen, preventing rust and scale formation. |
| Decarburization Prevention | Eliminates oxygen contact to stop carbon loss in steels, maintaining surface hardness and strength. |
| Methods | Gas atmosphere (cost-effective for steels) or vacuum (superior for reactive metals like titanium). |
| Benefits | Preserves material properties, improves surface finish, and ensures consistent results in high-temperature processes. |
Ready to enhance your lab's heat treatment capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—whether you're working with carbon steels or reactive metals. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can prevent oxidation and decarburization, ensuring superior material performance and efficiency in your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















