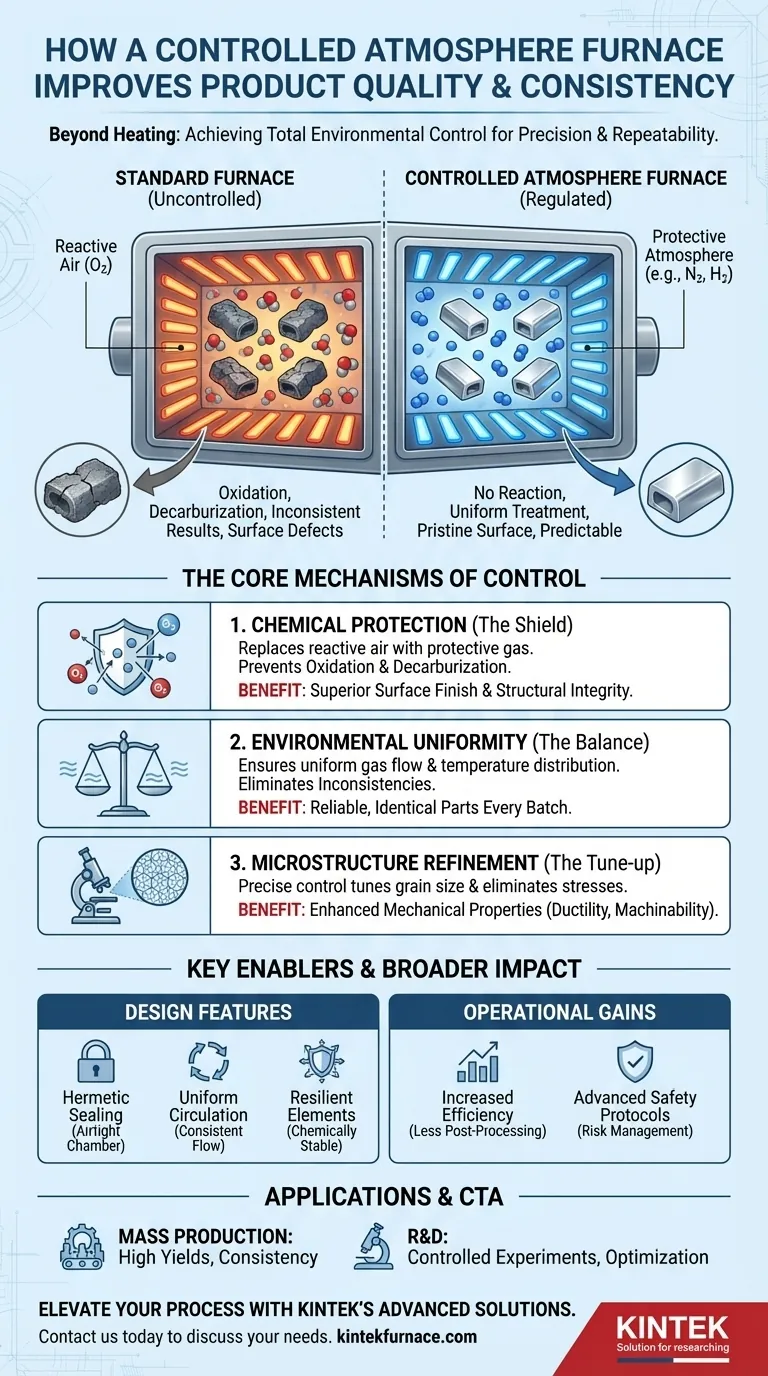
At its core, a controlled atmosphere furnace improves product quality and consistency by creating a highly regulated, predictable environment. Unlike a standard furnace that only controls temperature, it precisely manages the gaseous atmosphere surrounding the material, preventing unwanted chemical reactions and ensuring every part of every batch is treated identically.
The fundamental advantage is not just heat, but total environmental control. By isolating a material from reactive air and exposing it to a specific, uniform gas mixture, you move from merely heating a product to truly engineering its final properties with precision and repeatability.

The Core Mechanisms of Control
A controlled atmosphere furnace achieves superior results through two primary mechanisms: chemical protection and environmental uniformity. These principles work together to guarantee a predictable outcome.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
The most significant factor degrading material quality during heat treatment is reaction with the ambient air, particularly oxygen.
A controlled atmosphere furnace replaces the air with a specific gas or gas mixture. This protective or reducing atmosphere actively prevents destructive processes like oxidation (rusting or scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon content from steel), which can compromise a material's surface finish and structural integrity.
Ensuring Absolute Uniformity
Consistency is a direct result of uniformity. The furnace is engineered to eliminate variables that can cause deviations between batches or even within a single batch.
By ensuring a uniform flow and distribution of the atmosphere, the system guarantees that every surface of the material is exposed to the exact same gas concentration and temperature. This eliminates inconsistencies and ensures the entire product meets the required specifications.
Refining Material Microstructure
This precise control allows for targeted metallurgical improvements. Processes like annealing can be finely tuned to refine the material's grain size and eliminate residual stresses.
The result is a product with significantly improved mechanical properties, such as ductility and machinability, and a more reliable performance profile.
Key Design Features That Enable Control
The furnace's ability to maintain this precise environment is a function of its specialized engineering. Several key features are critical to its performance.
Tight Sealing and Gas Integrity
To maintain a pure internal atmosphere, the furnace chamber must be hermetically sealed. This prevents external air, with its reactive oxygen and moisture, from infiltrating and contaminating the process. This seal is the first line of defense in quality control.
Uniform Atmosphere Distribution
Advanced internal systems ensure the controlled atmosphere is not static. A consistent, uniform flow is maintained throughout the chamber, preventing pockets of stagnant gas or uneven temperature zones. This is crucial for treating large or complex-shaped parts evenly.
Resilient Heating Elements
The heating elements themselves are designed to operate reliably within specific chemical atmospheres. They are built from materials that will not degrade or react with the process gases, ensuring long-term stability and consistent thermal output.
Understanding the Broader Implications
While the primary goal is quality, the use of a controlled atmosphere has wider operational and safety consequences.
Efficiency and Throughput
By preventing the formation of scale and other surface defects, post-processing steps like cleaning or machining can often be reduced or eliminated. This improves production throughput and lowers overall operating costs. Modern furnaces are also designed for high energy efficiency.
Advanced Safety Protocols
Operating with potentially flammable or hazardous gases like hydrogen or ammonia requires robust safety systems. These furnaces are equipped with explosion protection devices and other safety mechanisms to manage these risks, demanding specialized operator training and strict adherence to protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a controlled atmosphere furnace depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is industrial mass production: The key benefit is the extreme consistency, which leads to higher yields, less scrap, and a more reliable final product.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: The furnace provides a perfectly controlled environment for conducting high-temperature experiments and optimizing new materials without a Voconfounding variable of atmospheric reaction.
By mastering the environment, you gain direct control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Key Benefit | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Protection | Prevents oxidation and decarburization | Improves surface finish and structural integrity |
| Environmental Uniformity | Ensures uniform gas and temperature distribution | Eliminates inconsistencies for reliable specifications |
| Microstructure Refinement | Controls grain size and reduces stresses | Enhances mechanical properties like ductility |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in industrial mass production or materials R&D, we deliver consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how our controlled atmosphere furnaces can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process



















