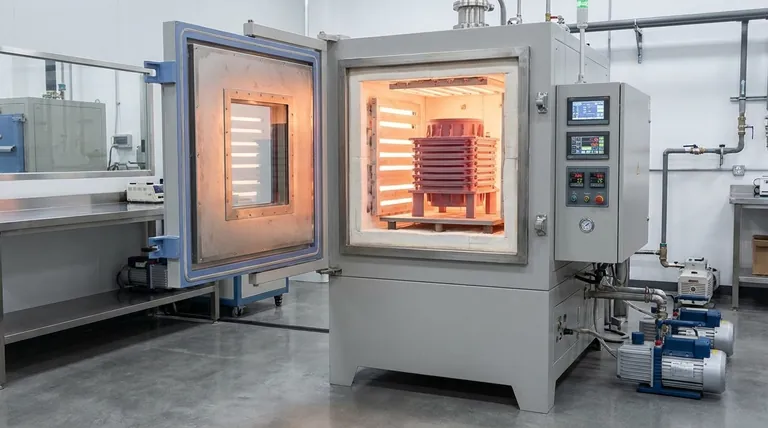
At its core, a vacuum brazing furnace eliminates part distortion by managing the entire thermal cycle with exceptional precision. It achieves this by ensuring the entire component heats and cools at a slow, controlled rate, which maintains a uniform temperature across the assembly and prevents the internal stresses that cause warping.
The key to preventing distortion is not just reaching the right temperature, but controlling the entire journey. Vacuum brazing excels by eliminating rapid, localized temperature changes—the primary cause of thermal stress in metal joining.

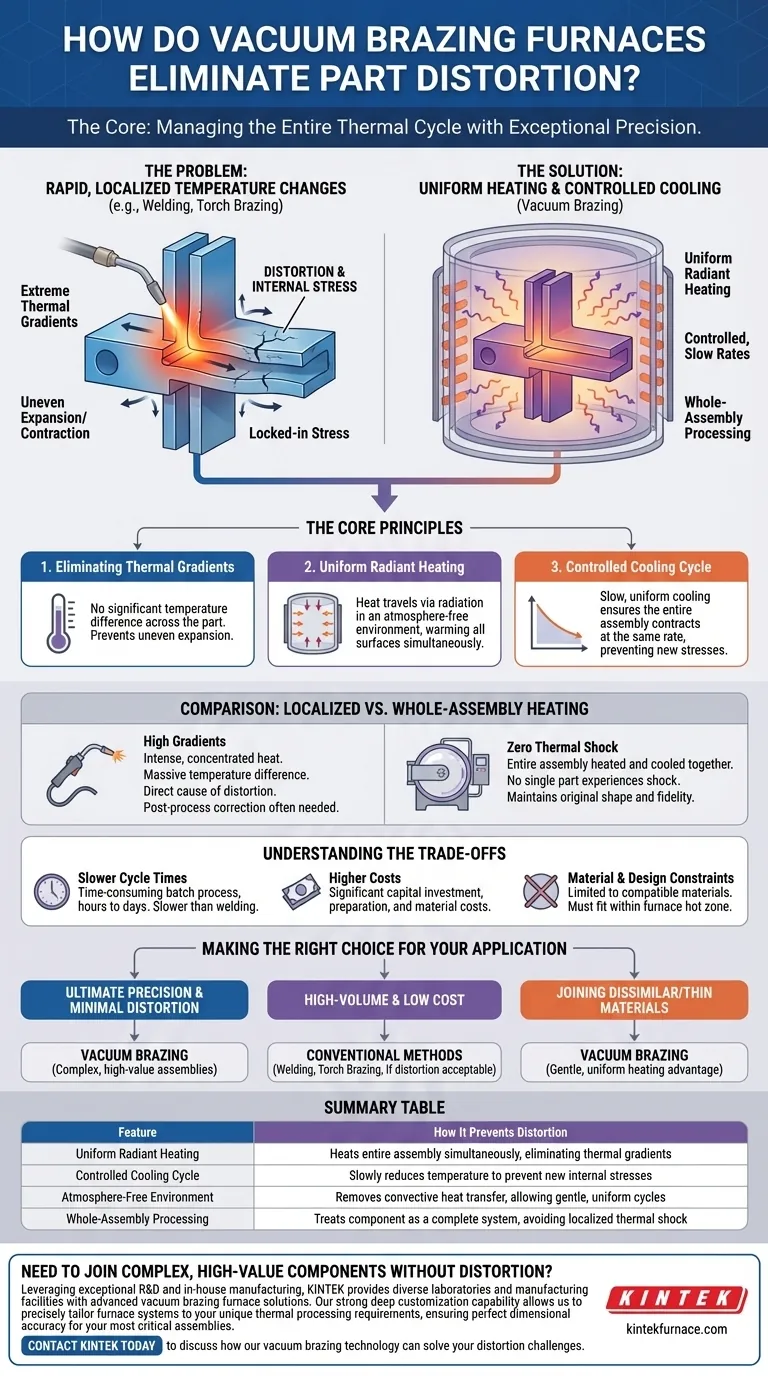
The Core Principle: Eliminating Thermal Gradients
The fundamental cause of distortion in any metal joining process is a thermal gradient, which is a significant difference in temperature between two areas of the same part. A vacuum furnace is specifically designed to minimize or eliminate these gradients.
What Causes Distortion?
When a section of metal is heated, it expands. When it cools, it contracts. If one part of a component is heated rapidly while another remains cool, the expanding section pushes against the cooler section, creating internal stress. When the part cools unevenly, this stress becomes "locked in," causing the component to warp, twist, or bend.
How Vacuum Furnaces Achieve Uniform Heating
A vacuum furnace removes almost all of the atmosphere. Without air molecules to transfer heat via convection, heat is transferred primarily through radiation.
Radiant heat travels in all directions from the furnace's heating elements, warming all surfaces of the component assembly simultaneously. This process is inherently more gentle and uniform than applying a concentrated flame or electric arc to a single joint line.
The Critical Role of Controlled Cooling
Preventing distortion is as much about cooling as it is about heating. Vacuum furnaces use programmed, multi-stage cooling cycles.
By slowly and uniformly reducing the temperature, the furnace ensures that the entire assembly contracts at the same rate. This prevents the formation of new stresses during the cooling phase, preserving the component's precise dimensions.
A Comparison with Other Joining Methods
The superiority of vacuum brazing for dimensional control becomes clear when compared to methods that rely on localized heat.
The High Gradients of Welding and Torch Brazing
Processes like welding and torch brazing apply intense, concentrated heat directly to the joint area. This creates a massive temperature difference between the molten joint and the surrounding cool base metal.
This extreme thermal gradient is the direct cause of significant distortion and residual stress, often requiring post-process straightening or stress-relieving operations.
The Advantage of Whole-Assembly Heating
Vacuum brazing treats the component as a complete system. The entire assembly is brought up to brazing temperature together, held at a uniform temperature (a "soak"), and then cooled together.
Because no single part of the component experiences a thermal shock, the original shape and dimensional tolerances are maintained with very high fidelity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While unmatched for precision, the vacuum brazing process involves clear trade-offs that make it unsuitable for every application.
Slower Cycle Times
Heating and cooling an entire assembly in a controlled manner is a time-consuming batch process. Cycle times can range from several hours to more than a day, depending on the mass of the parts and the complexity of the thermal profile. This is much slower than most welding processes.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The process also requires careful preparation, precise assembly, and the consumption of brazing alloys and "stop-off" materials, adding to the per-part cost.
Material and Design Constraints
The process is limited to materials that are compatible with the brazing filler metal and can withstand the required thermal cycle without undesirable metallurgical changes. The entire assembly must also fit within the furnace's usable hot zone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right joining process requires aligning the method's strengths with your project's most critical goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and minimal distortion: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for complex, high-value assemblies where dimensional accuracy is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and low cost: Conventional methods like automated welding or torch brazing are typically faster and more economical, provided some level of distortion is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or very thin materials: The gentle, uniform heating of vacuum brazing provides a significant advantage, reducing the risk of damage or cracking.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing provides an unparalleled level of thermal control, making it the superior solution for manufacturing dimensionally critical components.
Summary Table:
| Feature | How It Prevents Distortion |
|---|---|
| Uniform Radiant Heating | Heats entire assembly simultaneously, eliminating thermal gradients. |
| Controlled Cooling Cycle | Slowly reduces temperature to prevent new internal stresses from forming. |
| Atmosphere-Free Environment | Removes convective heat transfer, allowing for gentle, uniform thermal cycles. |
| Whole-Assembly Processing | Treats the component as a complete system, avoiding localized thermal shock. |
Need to join complex, high-value components without distortion?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and manufacturing facilities with advanced vacuum brazing furnace solutions. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely tailor furnace systems to your unique thermal processing requirements, ensuring perfect dimensional accuracy for your most critical assemblies.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our vacuum brazing technology can solve your distortion challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing



















