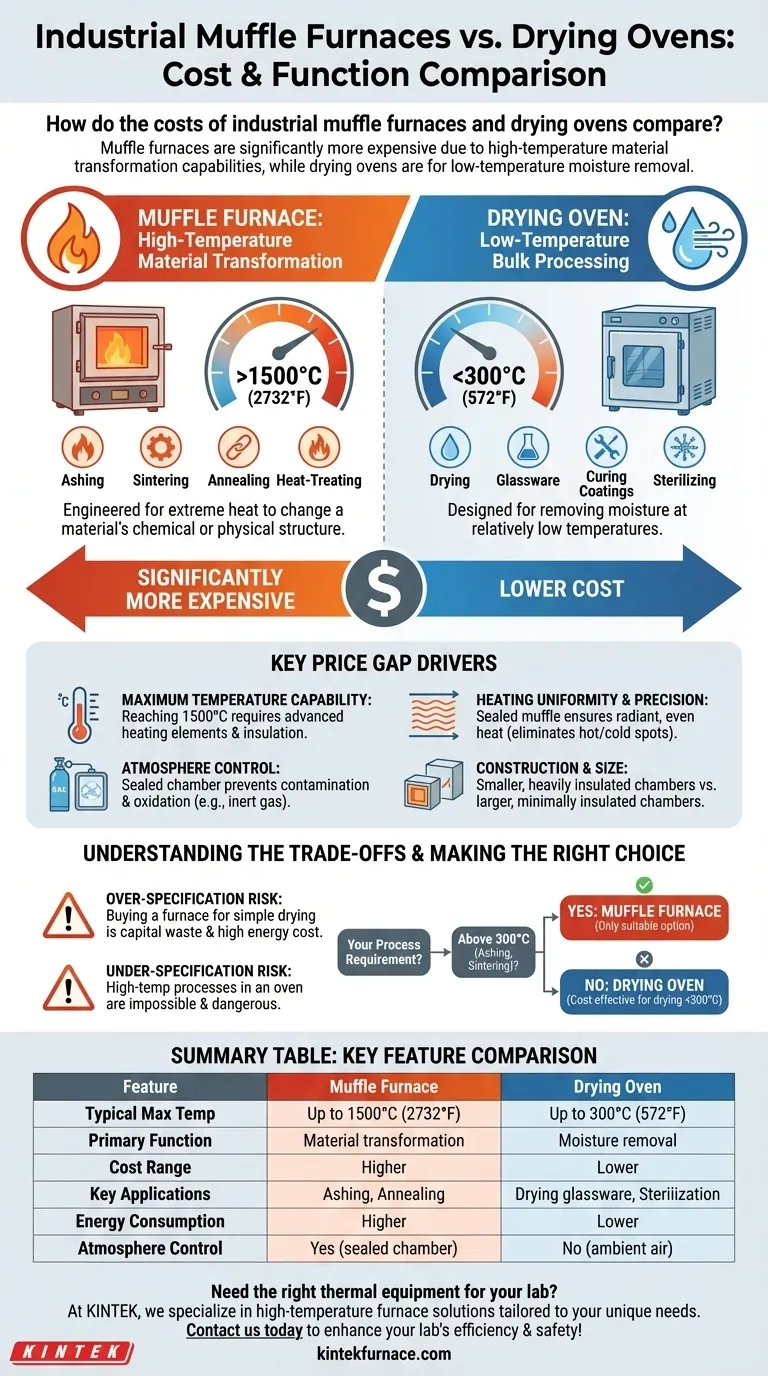
As a general rule, an industrial muffle furnace is significantly more expensive than an industrial drying oven. This price difference is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of the furnace's ability to achieve much higher temperatures, maintain precise thermal uniformity, and control the atmospheric conditions in which a material is processed. An oven removes moisture, but a furnace fundamentally transforms materials.
The cost difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven reflects their distinct purposes. A drying oven is a low-temperature tool for removing moisture, while a muffle furnace is a high-temperature, precision instrument designed for altering a material's fundamental properties.
The Core Difference: Function Defines Cost
The choice between these two pieces of equipment comes down to your technical goal. Their designs, and therefore their costs, are optimized for completely different tasks.
Drying Ovens: Low-Temperature Bulk Processing
A drying oven is designed for one primary purpose: removing moisture from materials at relatively low temperatures.
Typical applications include drying glassware, curing coatings, or sterilizing equipment. They are built for efficiency at temperatures that rarely exceed 300°C (572°F).
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Material Transformation
A muffle furnace is engineered for processes that require extremely high heat to change a material's chemical or physical structure.
This includes applications like ashing, sintering ceramics, annealing metals, and heat-treating. These processes demand precision and high thermal energy, often reaching 1500°C (2732°F) or more.
Key Technical Drivers of the Price Gap
The higher price of a muffle furnace is directly tied to the advanced components and engineering required to perform its function safely and reliably.
Maximum Temperature Capability
The most significant cost driver is temperature. Reaching 1500°C requires advanced heating elements, robust power systems, and specialized, dense insulation to contain the heat and protect the operator. A drying oven's simple construction is not capable of withstanding these thermal demands.
Heating Uniformity and Precision
Muffle furnaces are designed with a sealed inner chamber (the "muffle") that ensures radiant heat is distributed evenly. This eliminates hot and cold spots, which is critical for reliable process outcomes.
Drying ovens often rely on convection (circulating hot air), which can lead to uneven temperature distribution. This is acceptable for simple drying but unsuitable for sensitive thermal processes.
Atmosphere Control
The sealed chamber of a muffle furnace separates the material being heated from the heating elements and outside air. This prevents contamination and oxidation, allowing for processes to occur in a tightly controlled atmosphere (such as with inert gas). A drying oven simply circulates ambient air.
Construction and Chamber Size
To manage extreme heat, muffle furnaces have smaller, heavily insulated chambers. In contrast, drying ovens often feature larger chambers with minimal insulation, designed to accommodate more material for bulk drying operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong equipment has consequences beyond the initial purchase price.
The Cost of Over-specification
Purchasing a muffle furnace for a simple drying task is a significant waste of capital. The furnace's capabilities would be entirely unused, and its higher energy consumption would lead to unnecessarily high operational costs.
The Risk of Under-specification
Attempting a high-temperature process in a drying oven is not just ineffective—it is impossible and dangerous. The oven lacks the thermal capacity, and its materials would fail catastrophically, creating a severe safety hazard.
Operational Energy Costs
A muffle furnace's need to generate and contain extreme temperatures means it will consume substantially more energy per cycle than a drying oven operating at a lower temperature. This long-term operational cost must be factored into your decision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be based entirely on the requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is drying, curing, or sterilizing materials below 300°C: A drying oven is the correct and most cost-effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing, sintering, annealing, or any process requiring temperatures above 300°C: A muffle furnace is your only suitable and safe option.
- If your process requires high purity and avoiding oxidation is critical: The controlled atmosphere provided by a muffle furnace is non-negotiable.
Choosing the right thermal equipment is about aligning the tool's capabilities with your specific process requirements.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Max Temperature | Up to 1500°C (2732°F) | Up to 300°C (572°F) |
| Primary Function | Material transformation (e.g., ashing, sintering) | Moisture removal (e.g., drying, curing) |
| Cost Range | Higher | Lower |
| Key Applications | Ashing, annealing, heat-treating | Drying glassware, sterilization |
| Energy Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Atmosphere Control | Yes (sealed chamber) | No (ambient air) |
Need the right thermal equipment for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements, helping you avoid costly over- or under-specification. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and safety with advanced, cost-effective solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















