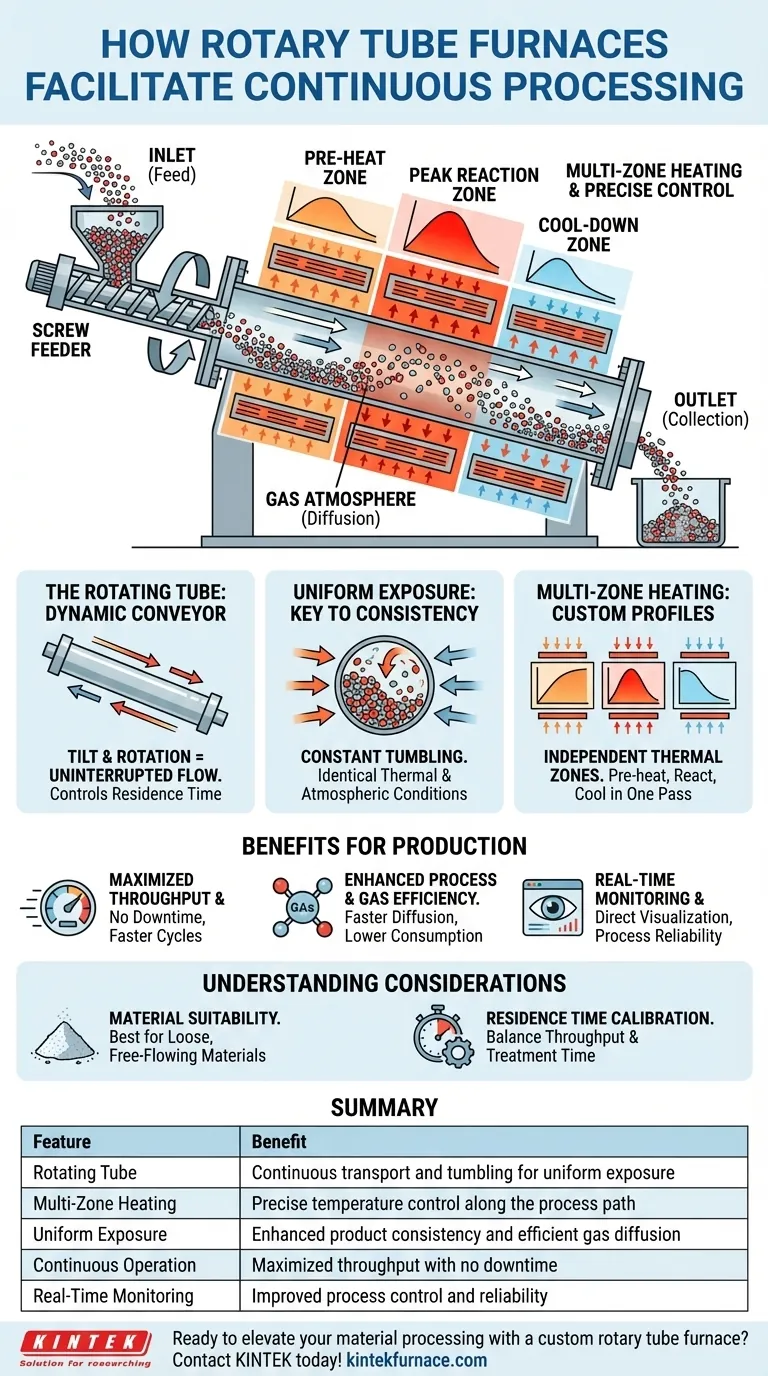
At its core, a rotary tube furnace facilitates continuous processing by using a slowly rotating, heated tube to simultaneously heat and transport material from an inlet to an outlet. This design transforms a static, batch-based operation into a dynamic, uninterrupted flow. The combination of controlled movement, precise heating, and atmospheric control allows for highly uniform and efficient processing of loose materials like powders and granules.
The true advantage of a rotary tube furnace lies not just in its ability to move material, but in its capacity to expose every particle to identical thermal and atmospheric conditions. This principle of uniform exposure is what unlocks significant gains in product consistency, efficiency, and scalability for industrial processes.
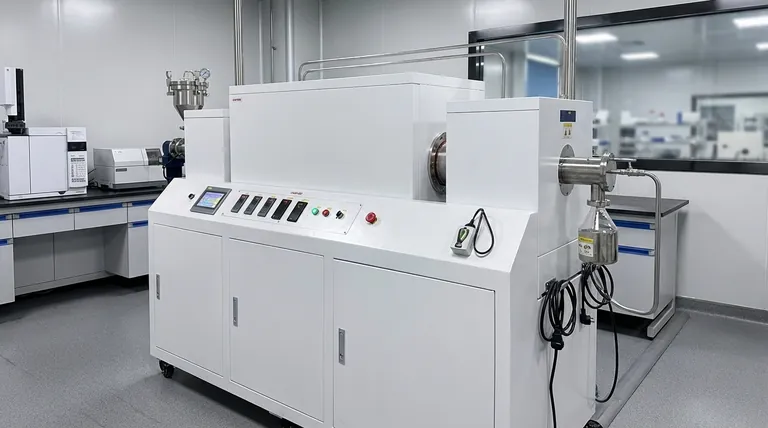

The Core Principles of Continuous Processing
To understand how these furnaces work, it's essential to break down their fundamental mechanics. The design is an elegant solution to the challenge of heating large volumes of particulate material uniformly and efficiently.
The Rotating Tube: A Dynamic Conveyor
The central component is the process tube, which is tilted at a slight angle and rotates slowly. Material is continuously fed into the higher end, and the rotation causes it to tumble and gradually travel down the length of the tube to a collection system at the lower end.
This mechanism acts as a self-regulating conveyor. The speed of rotation and the angle of inclination are critical parameters that control the residence time—how long the material spends inside the furnace being treated.
Multi-Zone Heating for Precise Control
Most industrial rotary tube furnaces are not heated uniformly along their entire length. Instead, they are divided into multiple, independently controlled thermal zones.
This allows you to create a precise temperature profile along the process path. For example, a material can be gradually pre-heated in the first zone, held at a peak reaction temperature in the middle zones, and then cooled in the final zone before exiting, all within a single, continuous pass.
Uniform Exposure: The Key to Consistency
In a static furnace, material at the bottom of a crucible is heated differently than material at the top. A rotary furnace solves this problem through constant tumbling.
This continuous movement ensures the entire surface area of the material is repeatedly exposed to the heat source and the furnace atmosphere. This leads to exceptionally uniform heat treatment and highly efficient gas diffusion, which is critical for processes like oxidation or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
The Tangible Benefits for Production
The principles of continuous transport and uniform exposure translate directly into significant operational advantages over traditional batch processing.
Maximized Throughput and Efficiency
Continuous operation eliminates the downtime inherent in batch systems—loading, heating, cooling, and unloading. By running without interruption, rotary furnaces achieve significantly shorter production cycles and maximize throughput, making them ideal for large-scale industrial applications.
Enhanced Process and Gas Efficiency
Because the material is constantly being mixed, the diffusion of process gases into the particles is much faster and more effective. This not only speeds up reactions but also reduces overall gas consumption compared to static processes where the gas must slowly penetrate a stationary pile of material.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Many modern rotary furnaces include features like an integrated quartz viewport. This allows for direct, real-time visual monitoring of the material as it undergoes processing. Paired with anti-clogging designs and automated feeding systems, it provides a high degree of process control without interruption.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool. Its benefits are only realized when applied to the right materials and processes.
Material Suitability is Crucial
These furnaces are specifically designed for loose, free-flowing materials such as powders, granules, or small pellets. They are not suitable for solid components, materials that can be damaged by tumbling, or substances that might melt and stick to the tube walls.
Residence Time Calibration
The throughput is directly tied to the material's residence time. Calibrating the tube's rotation speed and angle to achieve the desired processing time for your specific material is a critical step. A faster flow increases throughput but reduces treatment time, and vice versa.
System Complexity
Compared to a simple box or static tube furnace, a rotary system is mechanically more complex. It involves rotating seals, drive motors, and material feeding/collection systems that require proper installation and routine maintenance to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material, scale, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent production of powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice for maximizing throughput and ensuring product uniformity in processes like calcining, roasting, or sintering.
- If your primary focus is research and development with small, varied batches: A traditional static tube or batch furnace offers greater simplicity and flexibility for handling diverse materials and sample sizes.
- If your primary focus is processing materials that are sensitive to mechanical stress: You must carefully consider if the tumbling action is acceptable, as a static furnace or a mesh belt furnace might be a more suitable alternative.
By matching the furnace's unique capabilities to your specific goals, you can transform a series of discrete jobs into a highly efficient, continuous manufacturing operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Continuous transport and tumbling for uniform exposure |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Precise temperature control along the process path |
| Uniform Exposure | Enhanced product consistency and efficient gas diffusion |
| Continuous Operation | Maximized throughput with no downtime |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Improved process control and reliability |
Ready to elevate your material processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're handling powders, granules, or other loose materials, we can design a system to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can boost your efficiency and scalability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















