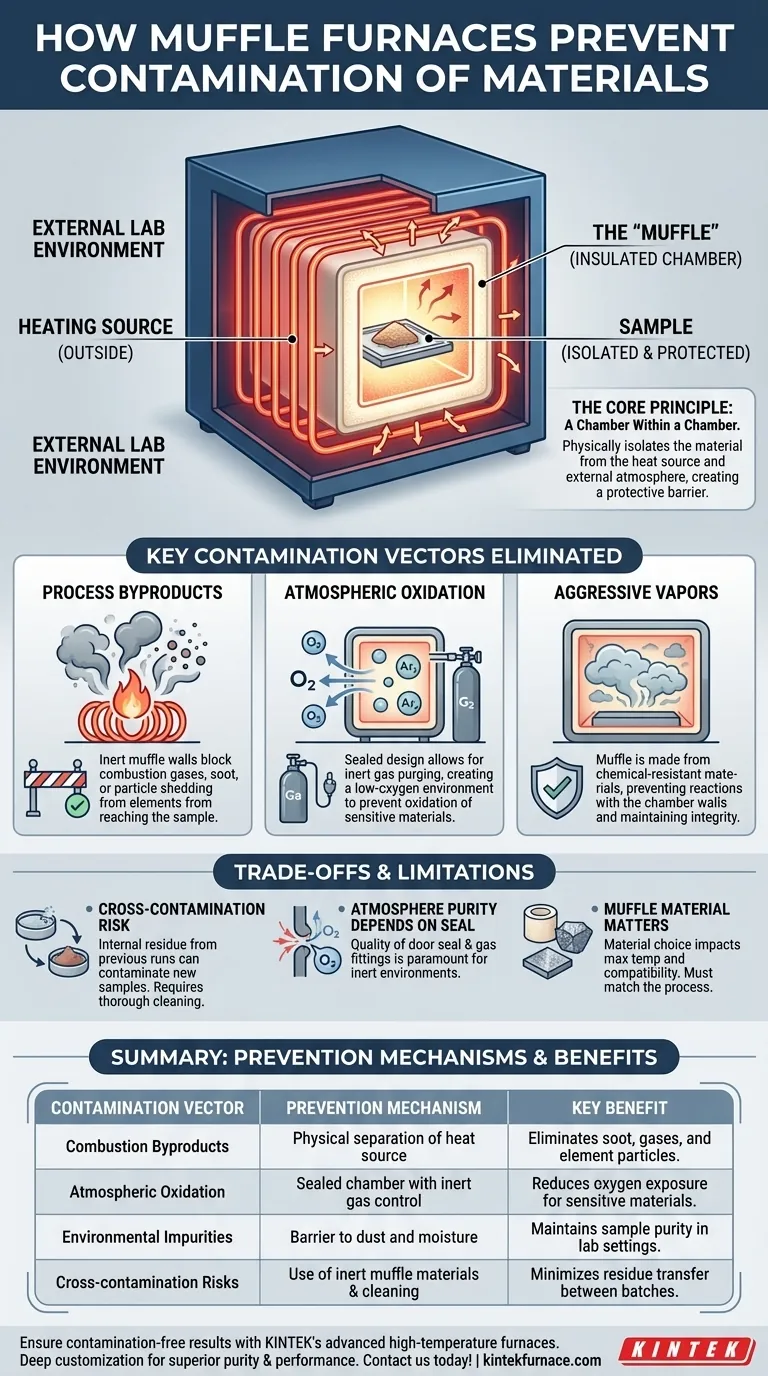
At its core, a muffle furnace prevents contamination by physically isolating the material being heated inside a separate, sealed chamber—the "muffle." This design creates a protective barrier that separates the sample from the furnace's heating source and the outside atmosphere, ensuring that impurities, combustion byproducts, and unwanted gases cannot interfere with the process.
The defining principle of a muffle furnace is not just its high heat capability, but its "chamber-within-a-chamber" design. This fundamental separation is what protects sensitive materials from contamination, ensuring process purity and reliable results.

The Core Principle: A Chamber Within a Chamber
The effectiveness of a muffle furnace comes down to its unique architecture, which creates a highly controlled internal environment.
What is the "Muffle"?
The muffle is an insulated inner box or tube that holds the sample. It is typically made from inert materials like high-purity ceramics or specialized metal alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures without reacting or degrading.
Separation from the Heat Source
The heating elements (in an electric furnace) or flame (in a fuel-fired one) are located outside the muffle. Heat is transferred through the muffle's walls to the sample via radiation and convection.
This separation is critical. It guarantees that byproducts from combustion (like soot or gases) or microscopic particles shed from aging electric coils never come into direct contact with your material.
Isolation from the External Environment
The sealed design of the muffle also acts as a barrier to the external lab environment. This prevents airborne dust, moisture, and other atmospheric contaminants from entering the chamber and compromising the purity of the sample.
Key Contamination Vectors a Muffle Furnace Eliminates
Understanding how a muffle furnace protects your materials requires knowing what it is protecting them from.
Protection from Process Byproducts
In fuel-fired furnaces, combustion creates a host of chemical byproducts. The muffle ensures these gases cannot reach the sample. In electric furnaces, it prevents any potential outgassing or particle shedding from the heating elements themselves.
Control Over Chemical Reactions (Oxidation)
Many materials, especially metals, will readily oxidize at high temperatures when exposed to oxygen. A muffle furnace's sealed chamber allows for precise atmospheric control.
By purging the chamber and introducing an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, you can create a low-oxygen environment. This is essential for processes like bright annealing or sintering sensitive alloys where oxidation must be prevented.
Resistance to Aggressive Vapors
During some processes, the material itself may release corrosive gases or vapors. The muffle is constructed from materials specifically chosen for their resistance to chemical attack, ensuring the furnace's integrity and preventing reactions between the chamber walls and the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a muffle furnace is not a magical solution. Its performance depends on proper use and understanding its inherent characteristics.
Cross-Contamination is a Real Risk
The muffle prevents external contamination, but it cannot prevent internal cross-contamination. If you heat different materials in the same muffle without thorough cleaning, residue from a previous run can vaporize and contaminate your current batch.
Atmosphere Purity Depends on the Seal
For applications requiring an inert atmosphere, the quality of the door seal and gas fittings is paramount. Any leaks will allow oxygen from the ambient air to enter the chamber, compromising the controlled environment.
The Muffle Material Matters
The choice of muffle material (e.g., high-purity alumina ceramic vs. a metal alloy) has a direct impact on the maximum temperature and the types of materials you can process. A material that is inert for one application may not be for another, so matching the muffle to your process is critical for ensuring purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage a muffle furnace effectively, align its capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination from fuel combustion: Any standard muffle furnace is perfectly designed for this, as the physical barrier is its defining feature.
- If your primary focus is protecting materials from atmospheric oxidation: You must select a furnace specifically designed with gas ports and a high-integrity seal to enable inert atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material purity: Pay close attention to the muffle's material composition and implement a strict cleaning protocol between runs to eliminate any risk of cross-contamination.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace offers precise control over the heating environment, empowering you to protect the integrity of your materials with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Contamination Vector | Prevention Mechanism | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion byproducts | Physical separation of heat source | Eliminates soot and gases from fuel or elements |
| Atmospheric oxidation | Sealed chamber with inert gas control | Reduces oxygen exposure for sensitive materials |
| Environmental impurities | Barrier to dust and moisture | Maintains sample purity in lab settings |
| Cross-contamination risks | Use of inert muffle materials and cleaning protocols | Minimizes residue transfer between batches |
Ensure contamination-free results in your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs for superior purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















