In essence, a muffle furnace provides an extremely hot, precisely controlled, and contamination-free environment. This unique capability allows researchers and quality control technicians to either analyze the fundamental composition of a material or test its durability under severe thermal stress.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a precision instrument designed to thermally decompose, test, or transform a sample by isolating it from the contaminants of direct combustion and providing an exact temperature profile.
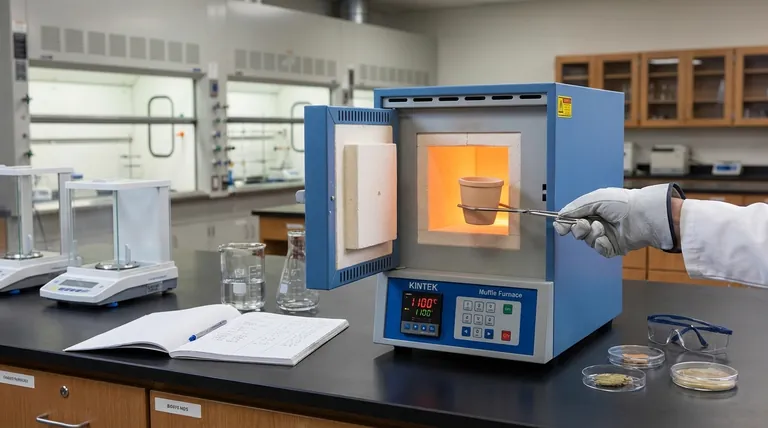

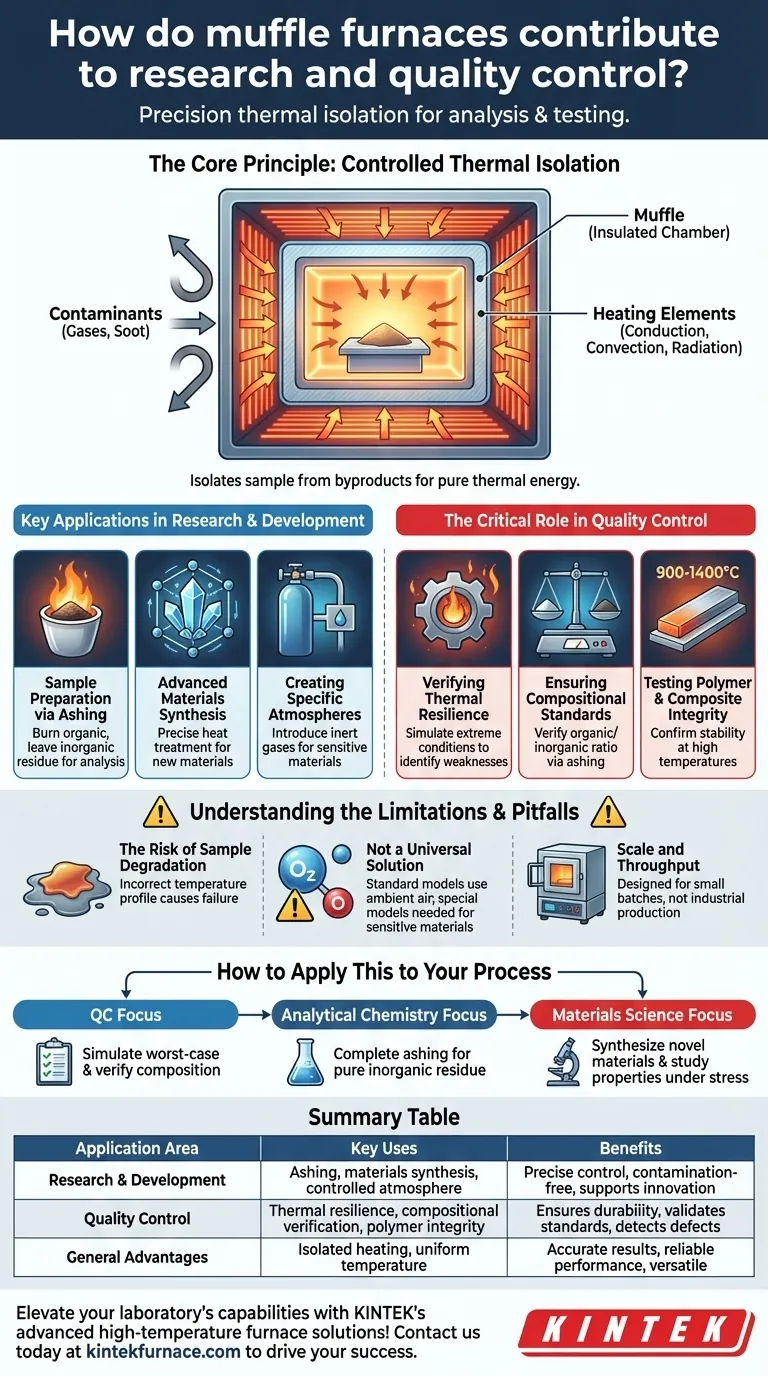
The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Isolation
A muffle furnace's primary function is to heat a material without letting the byproducts of heating (like gases or soot from fuel combustion) touch the sample. This is the key to its utility in both research and quality control.
How It Achieves High Heat
All muffle furnaces use a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation to generate and distribute heat. This is typically achieved using high-resistance electrical heating elements that surround the central chamber.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that contains the sample. This chamber separates the material being tested from the heating elements, ensuring the sample is heated only by pure thermal energy, not by direct flame or chemical reaction.
Why Isolation Is Critical
This isolation prevents contamination, which is essential for accurate analysis. For example, when determining the inorganic ash content of a sample, any soot from combustion would add to the final weight and corrupt the results.
Key Applications in Research & Development
In a research setting, the goal is often discovery—understanding a material's fundamental properties or creating something new. Muffle furnaces are indispensable tools for this work.
Sample Preparation via Ashing
In pharmaceutical or environmental analysis, a furnace is used for ashing. Organic materials in a sample are burned away at high temperatures (e.g., 500-600°C), leaving behind only the inorganic components (minerals, metals) for analysis with techniques like spectroscopy.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
The creation of new materials like technical ceramics, alloys, and composites often requires very specific heat treatment protocols. A muffle furnace provides the precise temperature control needed to achieve the desired crystalline structure or material phase.
Creating Specific Atmospheres
Some advanced models allow for the introduction of inert gases like argon or nitrogen. This creates a low-oxygen environment, which is critical for heat-treating materials that oxidize or tarnish easily when heated in normal air.
The Critical Role in Quality Control
In quality control (QC), the goal is validation—ensuring a product meets its design specifications. Muffle furnaces are used to test the thermal limits of manufactured goods.
Verifying Thermal Resilience
Furnaces simulate the most extreme thermal conditions a product might face. By subjecting components made of glass, ceramic, or metal to intense heat, manufacturers can identify potential weaknesses or defects before the product reaches the market.
Ensuring Compositional Standards
For many products, the ratio of organic to inorganic material is a critical quality standard. Ashing a sample from the production line and measuring the remaining residue is a direct way to verify that the product composition is correct.
Testing Polymer and Composite Integrity
Testing polymer-based compounds often requires temperatures from 900°C to 1400°C. A muffle furnace can confirm the material's stability and behavior at these temperatures, ensuring product safety and performance in high-stress applications.
Understanding the Limitations and Pitfalls
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with operational constraints that must be respected to ensure reliable results.
The Risk of Sample Degradation
Using an incorrect temperature profile is the most common pitfall. Setting the temperature too high can cause the sample to disintegrate or even melt, destroying the test. Setting it too low can result in incomplete ashing or transformation, leading to inaccurate data.
Not a Universal Solution
A standard muffle furnace operates with ambient air. If your work involves materials sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures, you must use a model specifically designed for controlled or inert atmospheres.
Scale and Throughput
Muffle furnaces are laboratory instruments, not industrial production ovens. They are typically small and designed for processing a limited number of samples at a time, making them unsuited for high-volume manufacturing itself.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your approach to using a muffle furnace should be dictated by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is Quality Control: Use the furnace to simulate worst-case thermal scenarios and verify the thermal resilience and compositional makeup of your finished product.
- If your primary focus is Analytical Chemistry: Use the furnace for complete sample combustion (ashing) to ensure you are left with a pure, non-contaminated inorganic residue for accurate elemental analysis.
- If your primary focus is Materials Science Research: Use the furnace's precise temperature and atmospheric controls to synthesize novel materials or to carefully study how a material's properties change under specific thermal stress.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a tool to reveal the fundamental truth of a material, either by stripping it down to its core components or by pushing it to its absolute limit.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Research & Development | Ashing, materials synthesis, controlled atmosphere studies | Precise temperature control, contamination-free environment, supports innovation |
| Quality Control | Thermal resilience testing, compositional verification, polymer integrity checks | Ensures product durability, validates standards, detects defects |
| General Advantages | Isolated heating, uniform temperature distribution | Accurate results, reliable performance, versatile for various materials |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in research and quality control. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















