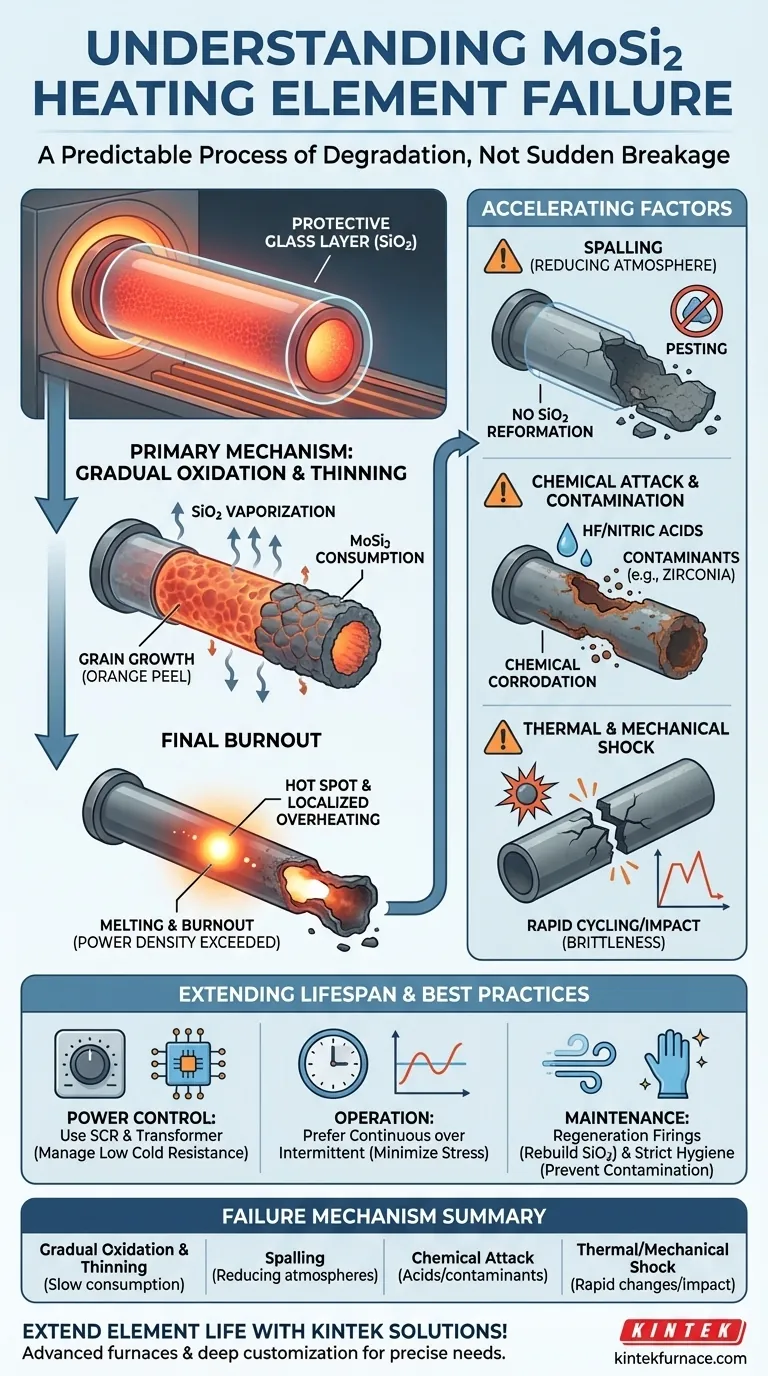
At their core, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements do not suddenly break but instead fail through a predictable process of degradation. The most common failure mechanism is a gradual thinning of the element due to oxidation. Over time, this thinning increases the element's electrical resistance to a point where its power density is exceeded, causing localized overheating and eventual burnout.
The key to understanding MoSi2 element failure is recognizing that it's a slow, aging process driven by oxidation. While these elements are designed for high-temperature oxidizing environments, the very process that protects them also gradually consumes them, and certain operating conditions can drastically accelerate this decay.

The Primary Failure Mechanism: Gradual Oxidation and Thinning
The fundamental reason MoSi2 elements have such a long service life is also the cause of their eventual failure. The process unfolds in a predictable sequence.
The Protective Glass Layer
When a MoSi2 element is heated in an oxidizing atmosphere (like air), a thin, protective layer of pure quartz glass (SiO2) forms on its surface. This layer is self-healing and protects the underlying material from further, rapid oxidation.
The Thinning Process
This protective SiO2 layer is not perfectly stable at very high temperatures. It slowly vaporizes and reforms, a process that consumes a small amount of the base MoSi2 material with each cycle. Over hundreds or thousands of hours, this leads to a measurable decrease in the element's diameter.
In addition, prolonged operation at high temperatures can cause grain growth within the element. This can make the surface appear rough, like an "orange peel," and contributes to the overall thinning and weakening of the material.
The Final Burnout
As the element becomes thinner, its electrical resistance increases. Since the power supply continues to deliver energy, this increased resistance in a smaller cross-sectional area causes the power density to rise dramatically. This creates "hot spots"—localized areas that become significantly hotter than the rest of the element—which ultimately lead to melting and burnout.
Accelerating Factors and Secondary Failure Modes
While gradual thinning is the default failure mode, several environmental and operational factors can cause MoSi2 elements to fail prematurely.
Spalling in Reducing Atmospheres
If operated in a reducing atmosphere (lacking sufficient oxygen), the protective SiO2 layer cannot reform if it gets damaged. This leads to a catastrophic failure known as spalling or "pesting," where the element rapidly disintegrates.
Chemical Attack and Contamination
MoSi2 elements are highly resistant to most chemicals but can be attacked and dissolved by hydrofluoric and nitric acids. More commonly in practice, failure is caused by contamination. Materials like colored zirconia that are not properly dried before firing can release compounds that aggressively attack the element's surface.
Thermal and Mechanical Shock
Like other ceramics, MoSi2 elements are brittle, especially at room temperature. They are susceptible to fracture from mechanical shock during installation or from significant stress induced by rapid heating or cooling cycles (thermal shock).
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Proper operation is critical to mitigating the risks of failure. Understanding the inherent characteristics of MoSi2 is the first step.
The Need for Sophisticated Power Control
MoSi2 elements have very low electrical resistance when cold, which increases dramatically as they heat up. This requires a specialized power control system, typically using a transformer and a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR), to manage the high initial startup current and precisely regulate power at operating temperature.
Intermittent vs. Continuous Operation
Although robust, frequent thermal cycling can induce mechanical stress on the elements and their support structures. For maximum lifespan, continuous operation at a stable temperature is generally preferable to intermittent use with frequent heating and cooling cycles.
The Risk of Contamination
The long life of MoSi2 elements depends entirely on maintaining the integrity of the protective SiO2 layer. Strict furnace hygiene and proper preparation of the items being fired are not optional—they are essential for preventing premature failure from chemical contamination.
How to Extend the Life of Your Elements
Your operational strategy should be directly informed by your primary application and furnace environment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan in a standard air atmosphere: Operate the elements within their recommended temperature range and avoid unnecessary, rapid thermal cycling to minimize stress.
- If your primary focus is operating in a reducing or reactive atmosphere: You must plan for periodic regeneration firings (heating the elements in air) to rebuild the protective SiO2 layer and prevent spalling.
- If your primary focus is preventing premature failure from contamination: Enforce strict protocols to ensure all materials entering the furnace are fully dried and that no reactive residues are present.
By understanding these mechanisms, you can shift from reacting to failures to proactively managing the health and longevity of your heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Failure Mechanism | Description | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Gradual Oxidation & Thinning | Slow consumption of material leading to increased resistance and burnout | High-temperature operation, time |
| Spalling | Rapid disintegration in reducing atmospheres | Lack of oxygen, no protective layer |
| Chemical Attack | Element damage from acids or contaminants | HF/Nitric acids, improper drying |
| Thermal/Mechanical Shock | Fracture from rapid temperature changes or physical impact | Brittleness, improper handling |
Extend the life of your heating elements with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, helping you prevent failures and maximize efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















