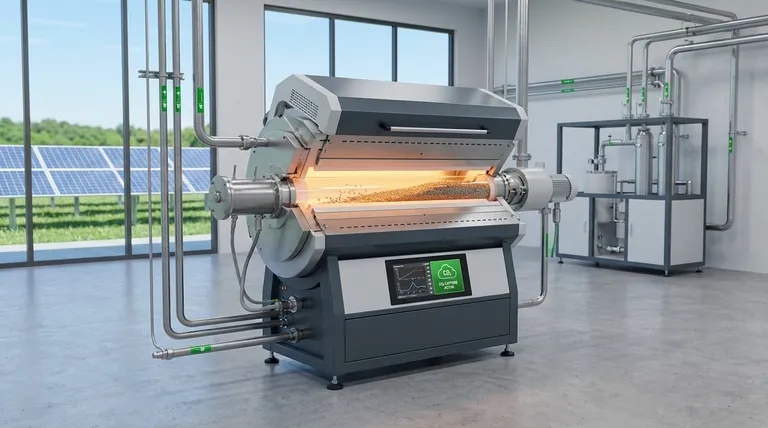
At their core, indirectly heated rotary kilns contribute to environmental goals by fundamentally separating the heating source from the material being processed. This separation prevents the mixing of combustion flue gases with the gases released from the process itself, enabling high-purity carbon capture and offering a clear pathway for using low-carbon energy sources for heat.
The single most important environmental advantage of an indirectly heated kiln is its ability to isolate the process gas stream. This makes capturing process-specific CO2 emissions vastly more efficient and economical than with direct-fired systems.

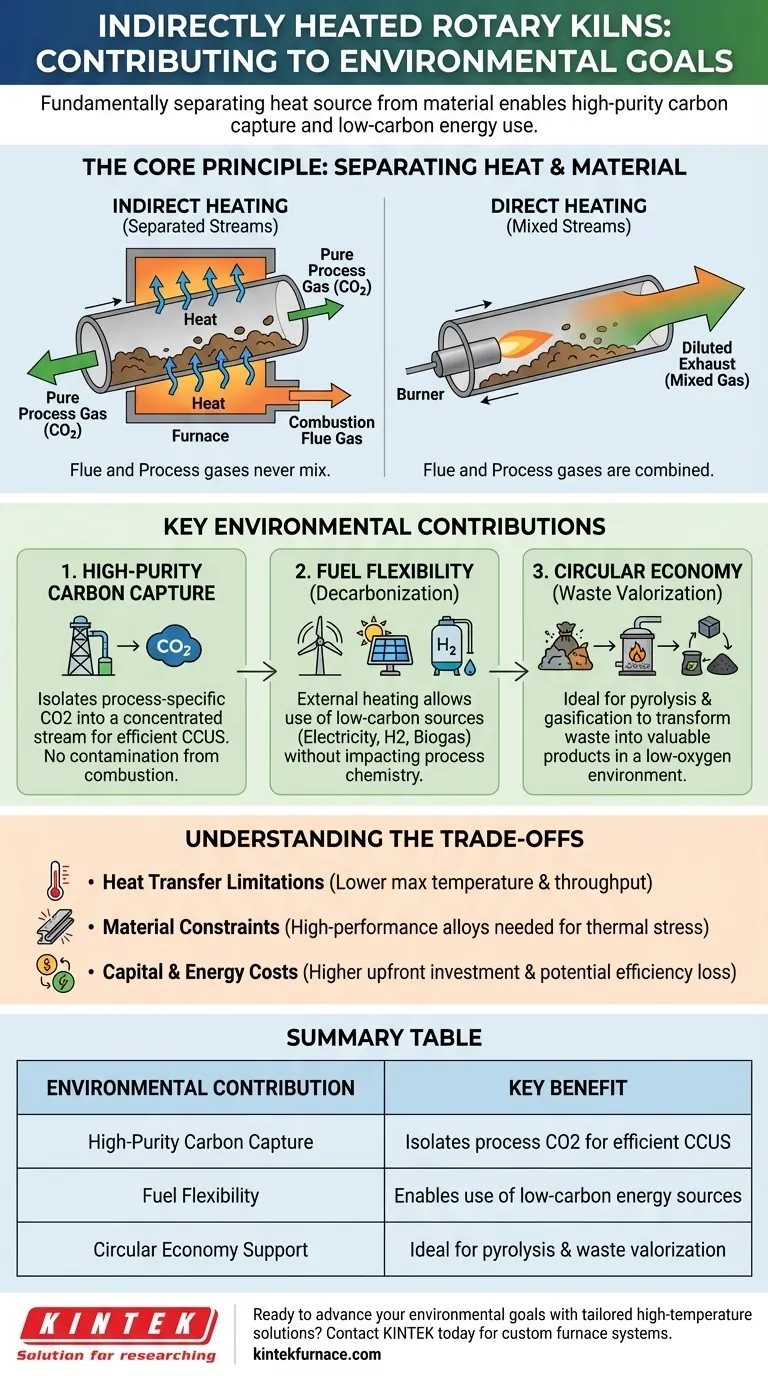
The Core Principle: Separating Heat from Material
To understand the environmental benefits, you must first grasp the fundamental design difference between indirect and direct heating. This distinction is the source of all subsequent advantages.
How an Indirectly Heated Kiln Works
An indirectly heated rotary kiln is essentially a rotating tube housed within a larger, stationary furnace or heating chamber.
Heat is applied to the outside of the rotating tube. This heat is then conducted through the tube wall to the material tumbling inside.
Crucially, the gases from the heating source (flue gas) never come into contact with the material or the gases released by the material (process gas).
The Direct-Fired Kiln Contrast
In a direct-fired kiln, a burner shoots a flame directly into the rotating drum, and the hot combustion gases flow over the material.
While often more thermally efficient for high-volume applications, this design mixes the flue gas (from burning fuel) with the process gas (from the material). The result is a single, high-volume, diluted exhaust stream.
Key Environmental Contributions
The separation of gas streams in an indirect kiln unlocks several powerful strategies for decarbonization and environmental management.
Enabling High-Purity Carbon Capture
This is the most significant advantage. Many industrial processes, like the calcination of minerals, release CO2 as a direct result of the chemical reaction.
In an indirect kiln, this process CO2 exits the system as a concentrated, pure stream, uncontaminated by the nitrogen and other products of fuel combustion.
Capturing CO2 from a pure stream is dramatically simpler and less energy-intensive than trying to scrub it from the massive, diluted exhaust of a direct-fired system. This makes carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) a practical and economic reality.
Reducing Footprint with Fuel Flexibility
Because the heat source is external, indirect kilns are exceptionally flexible. They can be heated with a variety of energy sources without impacting the process chemistry.
This allows for the use of low-carbon or zero-carbon energy, such as:
- Renewable electricity (resistance heating)
- Green hydrogen
- Biogas
This provides a direct path to eliminating the carbon footprint associated with heating the kiln, a step that is far more complex in direct-fired systems.
Advancing the Circular Economy
Indirect kilns are ideal for advanced thermal treatment processes like pyrolysis and gasification, which decompose materials in a low-oxygen environment.
This capability is used to transform waste materials—such as plastics, biomass, or sludge—into valuable products like synthetic gas (syngas), oils, or biochar. By avoiding direct combustion, the process focuses on material conversion rather than simple incineration, supporting circular economy goals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the indirect heating method is not a universal solution. It comes with specific engineering and operational trade-offs that must be considered.
Heat Transfer Limitations
The rate of heat transfer is limited by the thermal conductivity of the rotating kiln's metal shell.
This can result in lower maximum operating temperatures and reduced throughput compared to direct-fired kilns, where heat is transferred more directly to the material.
Material of Construction Constraints
The rotating kiln shell is subjected to extreme thermal stress. This demands the use of high-performance metal alloys that can maintain their strength at high temperatures.
The choice of alloy can limit the maximum temperature and may be a factor when processing chemically aggressive or abrasive materials that could damage the shell.
Capital and Energy Costs
The design, featuring an outer furnace and a high-alloy inner tube, can lead to a higher upfront capital cost than a simpler direct-fired kiln.
Furthermore, depending on the design, some heat can be lost from the outer furnace, potentially making it less energy-efficient in certain applications if not properly engineered and insulated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an indirectly heated kiln should be driven by your primary process and environmental objectives.
- If your primary focus is high-purity carbon capture: An indirectly heated kiln is the superior and often only viable choice for isolating process CO2.
- If your primary focus is electrifying your process or using hydrogen: The design of an indirect kiln is perfectly suited for integrating electric heaters or hydrogen burners.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput at very high temperatures (e.g., cement manufacturing): A traditional direct-fired kiln may still be the more established technology, though it comes with greater decarbonization challenges.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization via pyrolysis: The oxygen-free environment of an indirectly heated kiln is essential for this process.
Choosing the right thermal processing technology is a strategic decision that directly impacts your ability to meet future environmental and operational targets.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Contribution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Purity Carbon Capture | Isolates process CO2 for efficient CCUS |
| Fuel Flexibility | Enables use of low-carbon energy sources |
| Circular Economy Support | Ideal for pyrolysis and waste valorization |
Ready to advance your environmental goals with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping industries achieve efficient carbon capture and sustainability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your decarbonization journey!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















