At their core, electric furnaces support environmental sustainability by completely eliminating on-site combustion. Unlike furnaces that burn natural gas, oil, or propane, electric models produce zero direct emissions, meaning no carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, or other harmful pollutants are released at your home or facility. This makes them an inherently cleaner technology at the point of use.
The true environmental value of an electric furnace is determined by two key factors: the cleanliness of the electrical grid that powers it and its role as an enabling technology for creating next-generation green solutions.

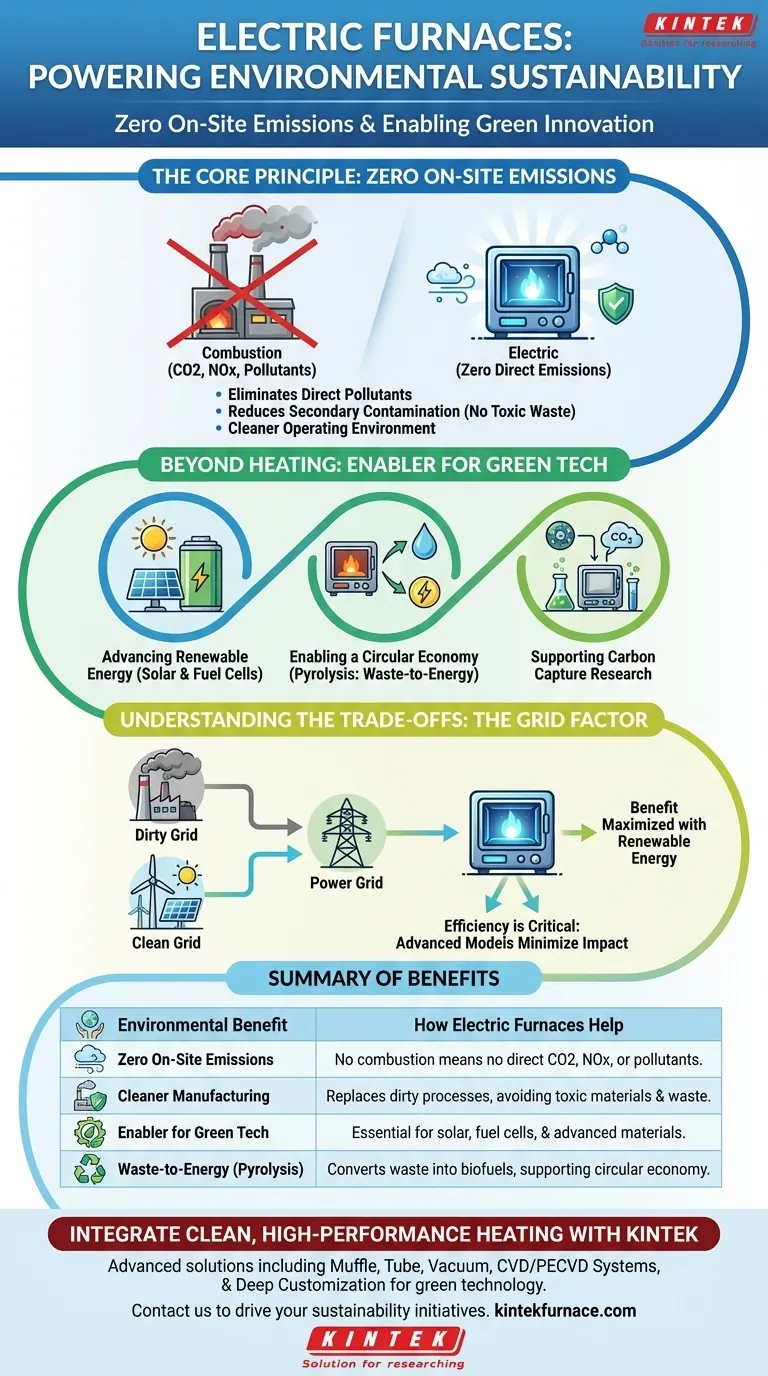
The Core Principle: Zero On-Site Emissions
An electric furnace's most significant environmental advantage is what it doesn't do. By using electricity to generate heat, it avoids the chemical process of combustion and its associated waste products entirely.
Eliminating Direct Pollutants
Because no fuel is burned, electric furnaces do not release greenhouse gases or other combustion byproducts into the atmosphere. This directly improves local air quality and eliminates the risk of carbon monoxide leaks.
Reducing Secondary Contamination
In industrial settings, specialized electric systems like vacuum furnaces replace older, dirtier methods. This avoids the use of toxic materials like cyanide salts and eliminates the challenge of disposing of contaminated waste, preventing land and water pollution.
Creating a Cleaner Operating Environment
The absence of combustion and hazardous materials results in a fundamentally cleaner, safer, and healthier environment for employees and residents.
Beyond Heating: An Enabler for Green Technology
Beyond their direct use, electric furnaces are a critical tool in the research and manufacturing of other sustainable technologies. Their precision and clean operation are often prerequisites for innovation.
Advancing Renewable Energy Production
The manufacturing of high-performance solar cells and the materials required for next-generation fuel cells often relies on the contaminant-free, high-temperature environment that only specialized electric furnaces can provide.
Enabling a Circular Economy
High-temperature electric furnaces are used for pyrolysis, a process that thermally decomposes materials like biomass or plastic waste in the absence of oxygen. This can convert waste into valuable biofuels and resources, turning a disposal problem into an energy solution.
Supporting Carbon Capture Research
The development of new materials and methods for capturing and storing carbon from the atmosphere often happens inside the precisely controlled environment of a laboratory-grade electric furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Grid Dependency Factor
While electric furnaces have zero direct emissions, their overall environmental footprint is tied to the source of their electricity. This is the most important trade-off to understand.
The Source of the Power Matters
An electric furnace is only as green as the grid that powers it. If your electricity is generated primarily by burning coal or natural gas, you are effectively outsourcing the emissions from your property to a power plant. The benefit is maximized when the grid is supplied by renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydropower.
Efficiency is a Critical Metric
Highly efficient electric furnaces use less electricity to produce the same amount of heat. Models with excellent thermal insulation, advanced controls, and waste heat recovery technology minimize energy consumption, reducing the overall environmental impact regardless of the power source.
The Rise of More Efficient Alternatives
For residential heating, it's important to note that a standard electric resistance furnace is not the most efficient electric option. An electric heat pump, which moves heat rather than creating it, can be three to four times more energy-efficient, offering a much lower overall environmental footprint for the same level of comfort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, consider what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is reducing your home's direct footprint: An electric furnace is an excellent choice, especially if you have access to a clean electricity grid or pair it with your own solar panels.
- If your primary focus is industrial process cleanliness: A specialized electric vacuum furnace is the superior environmental and operational choice for eliminating hazardous byproducts and achieving precise, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency: A modern electric heat pump will almost always be a better choice than a standard electric resistance furnace for heating and cooling a building.
Ultimately, electric furnaces are a powerful tool for decarbonization, whose full potential is unlocked by pairing them with efficient design and clean electricity.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | How Electric Furnaces Help |
|---|---|
| Zero On-Site Emissions | No combustion means no direct CO2, NOx, or carbon monoxide released at your facility. |
| Cleaner Manufacturing | Replaces dirty processes, avoiding toxic materials like cyanide salts and contaminated waste. |
| Enabler for Green Tech | Essential for manufacturing solar cells, fuel cells, and advanced materials for a sustainable future. |
| Waste-to-Energy (Pyrolysis) | Converts biomass and plastic waste into biofuels, supporting a circular economy. |
Ready to integrate clean, high-performance heating into your sustainable operations?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and industries with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions that align with environmental goals. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental and production requirements for green technology development.
Contact us today to discuss how our electric furnace solutions can help you achieve zero on-site emissions and drive your sustainability initiatives forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What ceramic materials are commonly used for heating elements? Discover the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications



















