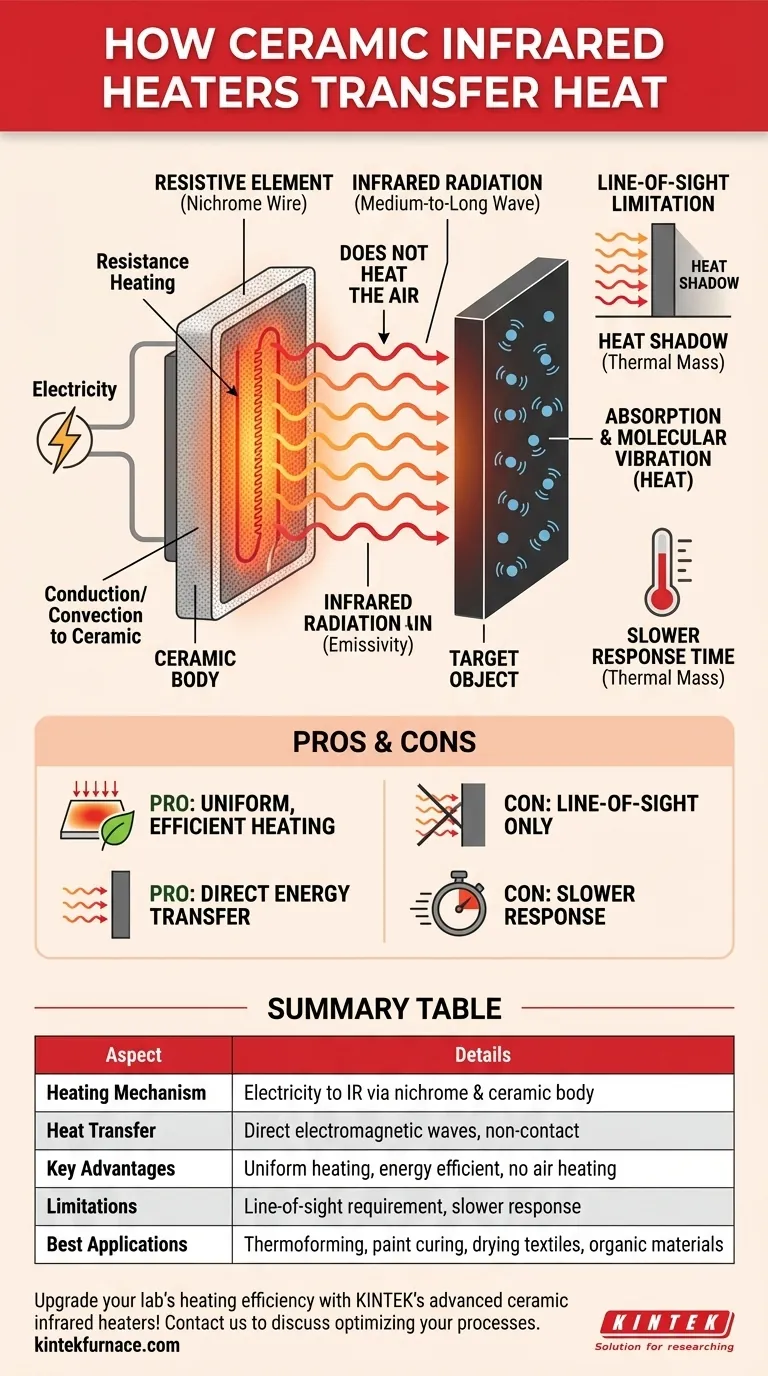
At its core, a ceramic infrared heater works by converting electricity into infrared radiation. A resistive element, typically a nichrome wire, heats a ceramic body, which then emits this energy as invisible infrared light that travels through the air and is absorbed directly by the target object.
The crucial distinction is that ceramic infrared heaters do not heat the air between the heater and the object. Instead, they transfer energy via electromagnetic waves, a process that is highly efficient for direct, line-of-sight surface heating.

The Core Mechanism: From Electricity to Radiation
To understand the process, it's best to break it down into its constituent parts. The magic isn't in one component but in how they work together as a system.
The Role of the Heating Element
The process begins with a simple principle: resistance heating. An electrical current is passed through a high-resistance wire, most commonly a nichrome (nickel-chromium) alloy.
This wire is embedded within or rests in grooves on the ceramic material. As electricity struggles to pass through the resistive wire, electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, causing the wire to become extremely hot.
The Function of the Ceramic Body
The ceramic component is far more than just a holder for the wire. It is the key to the heater's function and efficiency.
The hot nichrome wire transfers its heat to the surrounding ceramic material primarily through conduction and convection. The ceramic, chosen for its high emissivity, absorbs this energy and heats up uniformly. It effectively becomes a large, stable, and consistent radiating surface.
Emitting Infrared Waves
Once the ceramic body reaches its operational temperature (typically between 300°C and 700°C), it releases the majority of its thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
This energy is emitted predominantly in the medium-to-long wave infrared spectrum. These waves travel outwards from the heater's surface at the speed of light.
How the Target Object is Heated
The final step is the transfer of this radiated energy to the workpiece or object you intend to heat. This is where the unique properties of infrared become clear.
Radiation, Not Convection
Unlike a conventional heater that warms the surrounding air (convection), which then transfers its heat to the object, infrared waves travel through the air without significantly heating it. This is a form of direct, non-contact energy transfer.
Absorption by the Target
When the infrared waves strike the target object, they are either absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. The energy that is absorbed causes the molecules within the object to vibrate more rapidly. This increased molecular vibration is what we measure and feel as an increase in temperature.
The effectiveness of this absorption depends on the material, color, and surface finish of the target object. Dark, matte surfaces are generally better absorbers than bright, polished surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No heating technology is perfect for every scenario. Ceramic infrared heaters have distinct advantages and limitations rooted in their physical principles.
Pro: Uniform, Efficient Heating
Because the entire ceramic surface radiates evenly, these heaters are excellent for providing consistent heat over a broad area. This is ideal for applications like thermoforming plastic sheets, curing paint, or drying textiles. Energy is focused on the product, not wasted on heating the surrounding air.
Con: Line-of-Sight Limitation
Infrared energy travels in straight lines. Any object that blocks the path between the heater and the target will create a "heat shadow." This makes ceramic IR heaters less suitable for heating objects with complex geometries or hidden internal surfaces.
Con: Slower Response Time
The ceramic body has significant thermal mass, meaning it takes time to heat up to its operating temperature and also takes time to cool down. This thermal inertia makes them unsuitable for applications requiring rapid temperature cycling or instant on/off control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology requires matching the tool to the task.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of a flat surface: Ceramic IR heaters are an excellent, energy-efficient choice, especially for processes like thermoforming, paint curing, or pre-heating.
- If you need to heat organic materials, plastics, or water-based substances: The long-wave infrared energy from ceramic heaters is very effectively absorbed by these materials, making the process highly efficient.
- If your process requires rapid on/off cycles or instant heat: You should consider an alternative like a quartz or halogen heater, which has a much lower thermal mass and faster response time.
- If you need to heat the air in a space or an object with complex, hidden parts: A convection-based heating system will likely be a more effective solution.
By understanding the fundamental principle of radiant heat transfer, you can confidently determine where this technology provides a distinct advantage for your project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Converts electricity to infrared radiation via a nichrome wire and ceramic body |
| Heat Transfer | Direct, non-contact via electromagnetic waves in medium-to-long wave infrared spectrum |
| Key Advantages | Uniform heating, energy efficiency, no air heating, ideal for flat surfaces |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight requirement, slower response due to thermal mass |
| Best Applications | Thermoforming, paint curing, drying textiles, heating organic materials |
Upgrade your lab's heating efficiency with KINTEK's advanced ceramic infrared heaters! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you require uniform surface heating or specialized infrared applications, KINTEK delivers reliable, energy-efficient solutions. Contact us today to discuss how our heaters can optimize your processes and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision



















