In short, the choice between a vacuum and an atmosphere furnace is dictated by whether your application requires the complete removal of reactive gases or the controlled introduction of specific gases. Vacuum furnaces are chosen for their purity and ability to process highly sensitive materials without oxidation, while atmosphere furnaces are used to actively change a material's surface chemistry or provide a cost-effective protective environment.
The decision is not about which furnace is "better," but which environment is correct for the desired outcome. A vacuum furnace creates a near-perfectly clean slate by removing the atmosphere, whereas an atmosphere furnace uses a specific gas or gas mixture to create a purpose-built, reactive, or protective environment.
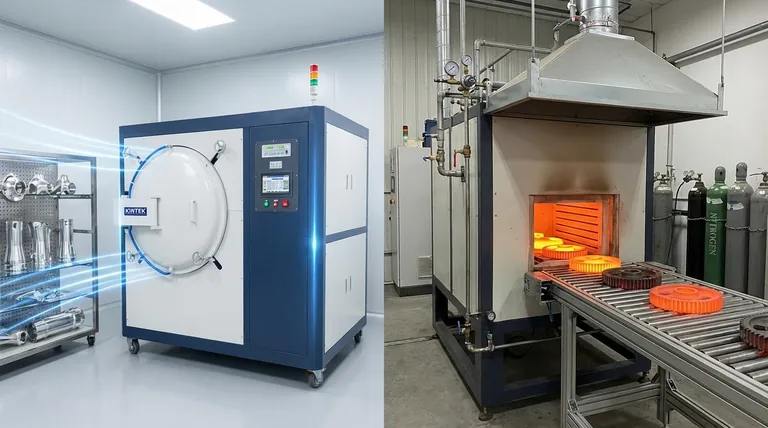

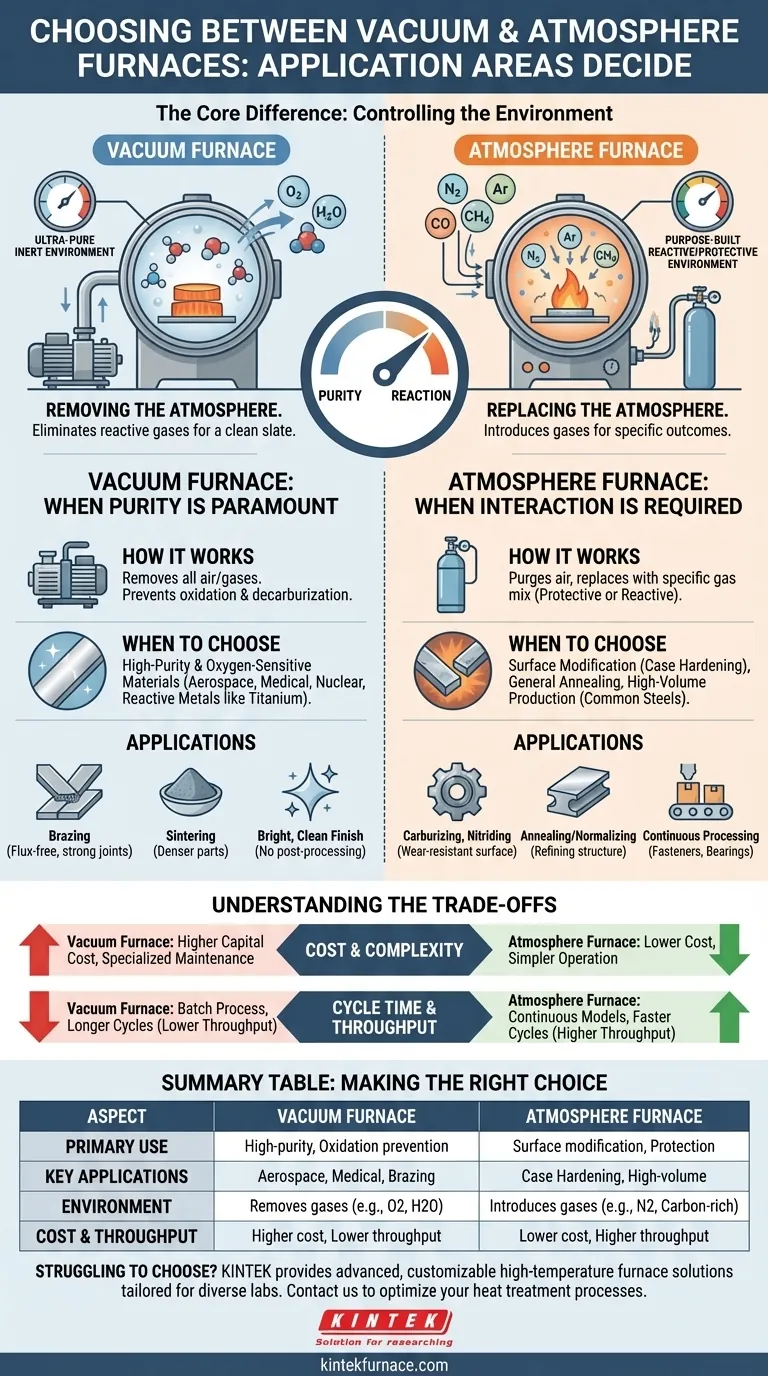
The Core Difference: Controlling the Environment
The fundamental distinction between these two furnace types is how they manage the environment surrounding the part being processed. This control is the single most important factor in achieving the desired metallurgical properties.
How Vacuum Furnaces Work: Removing the Atmosphere
A vacuum furnace uses a system of pumps to remove virtually all of the air and other gases from a sealed heating chamber. This is not about creating "suction" but about eliminating molecules—primarily oxygen and water vapor—that can react with the material at high temperatures.
The result is an ultra-pure, inert environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and decarburization, ensuring the material's integrity is preserved or enhanced.
How Atmosphere Furnaces Work: Replacing the Atmosphere
An atmosphere furnace works by purging the chamber of ambient air and replacing it with a carefully controlled gas or mixture of gases. This introduced atmosphere serves a specific purpose.
It can be protective, using inert gases like nitrogen or argon to displace oxygen and prevent scaling. Or, it can be reactive, using gases like carbon monoxide, methane, or ammonia to intentionally diffuse elements into the part's surface to change its properties.
When to Choose a Vacuum Furnace
Vacuum heat treatment is essential for applications where purity, cleanliness, and the prevention of any surface reaction are paramount.
For High-Purity and Oxygen-Sensitive Materials
Applications in aerospace, medical, and nuclear industries often involve reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, and high-strength superalloys. Any surface oxidation can compromise their mechanical properties, making the purity of a vacuum environment non-negotiable.
For Brazing and Sintering
Brazing (joining metals with a filler metal) in a vacuum produces exceptionally strong, clean joints without the need for flux, which can leave corrosive residues. Similarly, sintering (fusing powdered metal) in a vacuum helps pull out trapped gases, resulting in a denser, stronger final part.
For a Bright, Clean Finish
Parts processed in a vacuum furnace emerge bright, clean, and free of discoloration. This eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing steps like acid pickling or bead blasting, which are often required after atmosphere processing.
When to Choose an Atmosphere Furnace
Atmosphere furnaces are the workhorses of the industry, excelling in high-volume applications and processes that require a specific chemical interaction with the material's surface.
For Surface Modification (Case Hardening)
This is the primary domain of atmosphere furnaces. Processes like carburizing, nitriding, and carbonitriding require a carbon- or nitrogen-rich atmosphere to diffuse these elements into the surface of steel parts. This creates a hard, wear-resistant outer case while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
For General Annealing and Normalizing
For common carbon and alloy steels, the goal of annealing (softening) or normalizing (refining grain structure) is simply to heat and cool the part correctly. A simple, inert nitrogen or endothermic gas atmosphere is sufficient to prevent heavy scaling and is far more cost-effective than a vacuum cycle.
For High-Volume, Continuous Processing
Atmosphere furnaces are often designed for continuous operation, using conveyor belts or pusher mechanisms to move parts through the heat zones. This makes them ideal for high-volume production of parts like fasteners, bearings, and automotive components where throughput is a key economic driver.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a universal solution. The choice involves balancing process requirements with operational and economic realities.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces have a higher upfront capital cost due to their complex sealing, pumping systems, and controls. They also require more specialized maintenance. Atmosphere furnaces, particularly for simpler processes, are generally less expensive to build and operate.
Process Control and Repeatability
Vacuum furnaces offer superior process control and repeatability. Starting from a near-perfect vacuum ensures that every cycle is identical and free from contamination. Atmosphere furnaces can have more variability due to gas flow dynamics, leaks, and an inability to completely purge all contaminants.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Atmosphere furnaces, especially continuous models, generally offer higher throughput. Vacuum furnaces are batch-process tools, and cycles can be longer due to the time required to pump down the chamber and cool the load (often with a high-pressure gas quench).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the material and the desired outcome dictate the correct furnace environment.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and a "bright" finish: Choose a vacuum furnace to eliminate any risk of oxidation, especially for sensitive alloys or complex brazed assemblies.
- If your primary focus is intentionally changing the surface chemistry of a part: Choose an atmosphere furnace for case hardening processes like carburizing or nitriding.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective heat treatment of common steels: An atmosphere furnace provides a suitable protective environment with much higher throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium or medical implants: A vacuum furnace is the only choice to guarantee the required material integrity.
Understanding the fundamental purpose of the environment—to remove or to add—is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-purity processing, oxidation prevention | Surface modification, cost-effective protection |
| Key Applications | Aerospace, medical, brazing, sintering | Case hardening, annealing, high-volume production |
| Environment Control | Removes gases (e.g., oxygen, water vapor) | Introduces specific gases (e.g., nitrogen, carbon-rich) |
| Cost & Throughput | Higher cost, lower throughput (batch process) | Lower cost, higher throughput (continuous process) |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you need ultra-pure environments for sensitive materials or cost-effective solutions for high-volume processing, we're here to help. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















