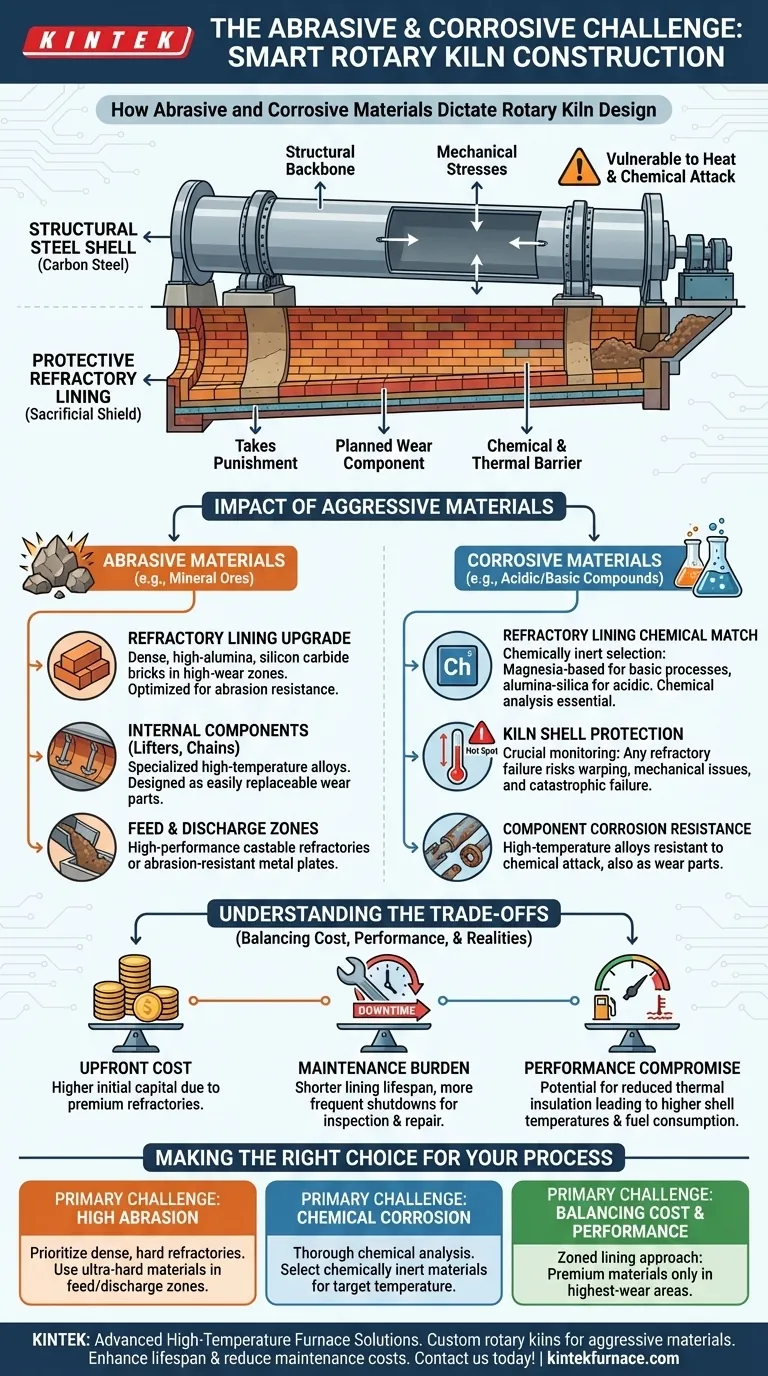
In short, abrasive and corrosive materials do not change the fundamental size or dimensions of a rotary kiln, but they completely dictate the selection of its internal materials. The primary strategy is to protect the structural steel shell by lining the kiln's interior with specialized, wear-resistant refractory materials designed to withstand the specific abrasive or chemical attack.
The core challenge is not about building a bigger kiln, but about building a smarter one. The steel shell provides the structure, but the internal refractory lining acts as a sacrificial shield, and its specification is the single most critical factor determining the kiln's operational lifespan and maintenance costs when processing aggressive materials.

The Core Principle: A System of Layers
A rotary kiln is best understood as a two-part system: a structural outer shell and a protective inner lining. Abrasive and corrosive materials force an explicit separation of these duties.
The Kiln Shell: The Structural Backbone
The outer cylinder of the kiln is almost always made of carbon steel. Its job is to provide the structural integrity to span between support piers, contain the material, and handle the immense mechanical stresses of rotation.
This steel shell, however, has poor resistance to high temperatures, direct abrasion, and chemical corrosion. It must be protected at all times.
The Refractory Lining: The Sacrificial Shield
The refractory is a brick or castable ceramic lining installed inside the steel shell. Its sole purpose is to take the punishment—heat, chemical attack, and abrasive wear—so the shell doesn't have to.
When processing aggressive materials, this lining is no longer just for thermal insulation; it becomes a planned wear component. The choice of refractory is the central engineering decision.
How Aggressive Materials Impact Key Components
The need for a robust refractory shield has a cascading effect on the kiln's design and long-term operation.
The Refractory Lining Itself
This is the most directly impacted component. Instead of a standard thermal brick, the material must be upgraded.
- For abrasion: Engineers select dense, high-strength refractories like high-alumina or even silicon carbide bricks in high-wear zones.
- For corrosion: The selection is a chemical matching game. For example, a basic process might require magnesia-based bricks, while an acidic one requires alumina-silica bricks. The goal is to choose a refractory that is chemically inert to the process material at operating temperature.
The Kiln Shell
While the shell material itself may not change, its operational risk increases dramatically. Any failure or breach in the refractory lining can lead to a "hot spot" on the steel shell.
This localized overheating can permanently warp the shell, causing severe mechanical issues and potentially leading to catastrophic failure. Therefore, monitoring shell temperature becomes a critical maintenance task.
Internal Components (Lifters, Chains, Dams)
Any internal hardware used to improve heat transfer or control material flow is directly exposed to the process. These components, such as metal lifters or chains, must be fabricated from specialized, high-temperature alloys chosen for abrasion and corrosion resistance.
Often, these internals are designed as wear parts, intended for frequent and relatively easy replacement compared to the refractory lining itself.
Feed and Discharge Zones
The points where material enters and exits the kiln experience extreme wear. These zones are often protected with specialized, high-performance castable refractories or abrasion-resistant metal plates that are easier to repair or replace than the main kiln brickwork.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a construction strategy for abrasive or corrosive materials involves balancing cost, performance, and operational realities.
The Upfront Cost
High-performance, abrasion-resistant, or chemically-resistant refractories are significantly more expensive than standard firebricks. This increases the initial capital cost of the kiln installation.
The Maintenance Burden
A lining designed to handle aggressive materials is still a consumable part. Its lifespan will be shorter, leading to more frequent kiln shutdowns for inspection, patching, or complete relining projects. This downtime represents a major operational cost.
The Performance Compromise
In some cases, the most durable refractory material may not have the best thermal insulation properties. This can lead to higher shell temperatures and greater fuel consumption, representing a direct trade-off between mechanical longevity and thermal efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material selection strategy must be guided by the primary challenge you face.
- If your primary focus is managing high abrasion: Prioritize dense, hard refractories (e.g., high-alumina) in the main body and consider ultra-hard materials like silicon carbide in the feed and discharge zones.
- If your primary focus is resisting chemical corrosion: Conduct a thorough chemical analysis of your process and consult with refractory experts to select a material that is chemically inert at your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance: Consider a zoned lining approach, using premium, high-cost refractories only in the highest-wear areas and more economical options in less critical sections.
Ultimately, accepting that the internal lining is a consumable component is the key to designing and operating a reliable and cost-effective rotary kiln for aggressive applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact on Rotary Kiln Construction |
|---|---|
| Refractory Lining | Upgraded to dense, high-strength materials (e.g., high-alumina, silicon carbide) for abrasion or chemically inert types (e.g., magnesia, alumina-silica) for corrosion resistance. |
| Kiln Shell | Remains carbon steel but requires protection; failure in lining can cause hot spots, warping, and potential catastrophic failure. |
| Internal Components | Made from specialized high-temperature alloys for abrasion and corrosion resistance, designed as easily replaceable wear parts. |
| Feed/Discharge Zones | Protected with high-performance castable refractories or abrasion-resistant plates for easier repair and replacement. |
| Trade-offs | Higher upfront costs, increased maintenance downtime, and potential thermal efficiency compromises due to refractory selection. |
Upgrade your rotary kiln for superior performance with KINTEK! We specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom rotary kilns designed to handle abrasive and corrosive materials. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental and industrial needs. Our product line features durable Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, ensuring long-lasting protection and efficiency. Don't let material challenges slow you down—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your kiln's lifespan and reduce maintenance costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















