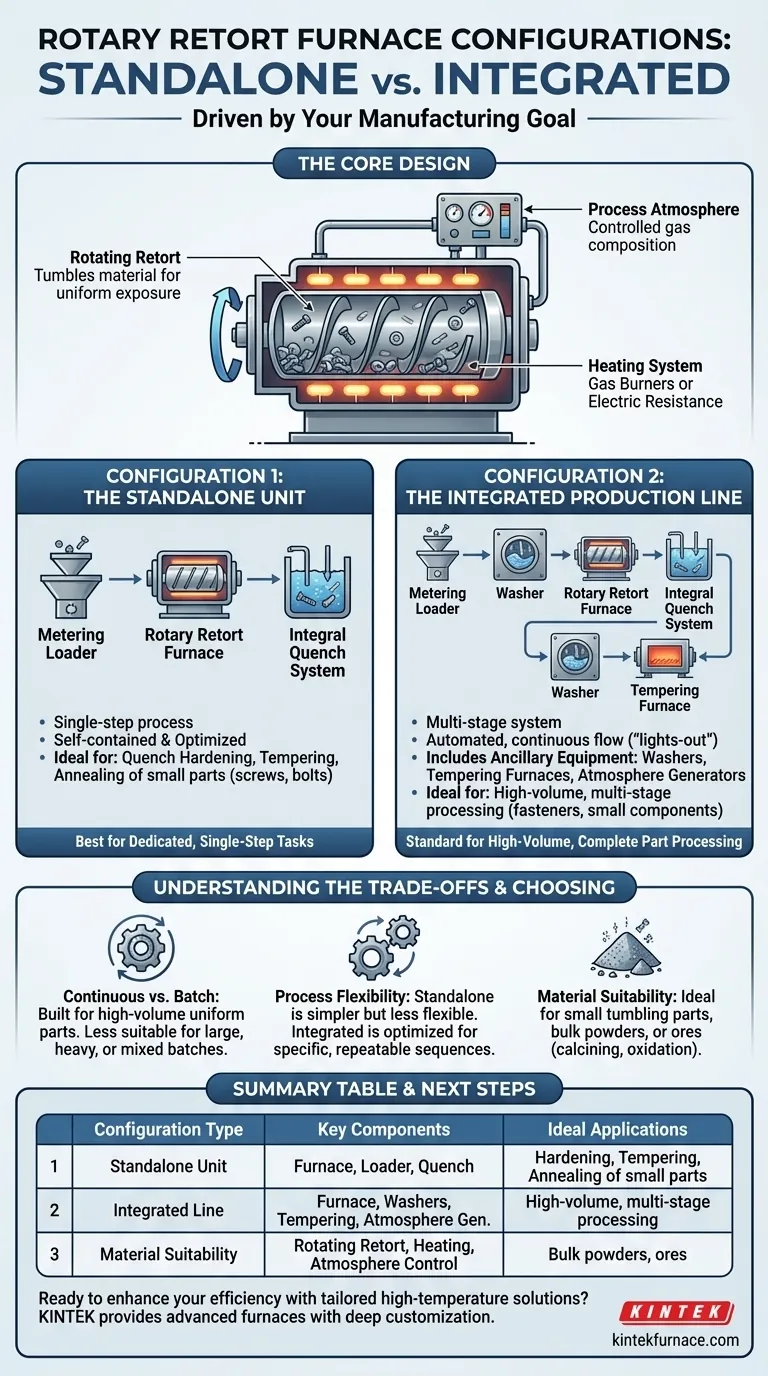
At its core, a rotary retort furnace can be configured in two fundamental ways. It can be implemented as a self-contained, standalone unit for a single process step or as a fully integrated component within a larger, multi-stage production line for complete part processing.
The choice of configuration is not about the furnace itself, but about the manufacturing goal. A simple, single-step process requires a standalone unit, while a complex, continuous production flow demands a fully integrated line with ancillary equipment.

The Core Design of a Rotary Retort Furnace
Before exploring configurations, it's essential to understand the furnace's fundamental components. The system's effectiveness relies on the interplay between its mechanics, heating, and atmosphere.
The Rotating Retort
The central feature is a long, cylindrical retort, or barrel, which is slightly inclined. This barrel rotates slowly, ensuring that the material inside tumbles and moves continuously from the entry to the exit point.
This constant motion guarantees that every part is exposed to the heat uniformly, which is critical for consistent product quality.
The Heating System
The furnace can be heated using two primary methods: gas burners or electric resistance heaters. External heating elements surround the retort, providing the thermal energy needed for the process.
The choice between gas and electric heating impacts operational cost, efficiency, and the level of temperature control achievable. Electric heat often provides more precise control, while gas may offer lower energy costs.
The Process Atmosphere
For metallurgical processes like hardening, the atmosphere inside the retort must be carefully controlled to prevent oxidation and achieve the desired material properties. This requires atmosphere generators and analyzers to maintain a specific gas composition.
Configuration 1: The Standalone Unit
A standalone configuration is designed for a single, well-defined heat treatment task. It is a self-contained system optimized for one part of a larger manufacturing process.
What It Includes
This setup typically consists of the rotary retort furnace itself, a metering loader to feed parts at a consistent rate, and an integral quench system. The quench system allows for rapid cooling of parts as they exit the furnace, which is essential for hardening.
Ideal Applications
This configuration is ideal for dedicated, single-step processes. Common applications include the quench hardening, tempering, or annealing of small, uniform parts like screws, bolts, nuts, and washers.
Configuration 2: The Integrated Production Line
For high-volume manufacturing that requires multiple sequential steps, the rotary retort furnace becomes a central component in a complete, automated production line.
A Multi-Stage System
This configuration connects the furnace with other essential equipment to create a continuous flow from raw parts to finished goods. It is designed for "lights-out" manufacturing with minimal manual intervention.
Key Ancillary Equipment
An integrated line includes the core furnace but adds several other modules:
- Washers: To clean and prepare parts before heating or to remove quench oils after.
- Tempering Furnaces: A secondary furnace to perform tempering, a lower-temperature process that reduces brittleness after hardening.
- Atmosphere Generators & Analyzers: To supply and monitor the precise protective atmosphere for the entire line.
When This Configuration Is Necessary
This setup is required for complex manufacturing where parts must be hardened, quenched, cleaned, and tempered in a continuous, uninterrupted sequence. It is the standard for high-volume production of fasteners and other small metal components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a configuration requires balancing capability with complexity and cost. A rotary retort is not a universal solution, and its benefits are specific to certain applications.
Continuous vs. Batch Processing
Rotary retorts are built for a continuous throughput of loose, small parts. They excel at processing a high volume of uniform items. They are less suitable for very large, heavy components or small, mixed batches, where a traditional batch furnace would be more practical.
Process Flexibility
While a standalone unit is simpler, an integrated line offers less flexibility for one-off jobs. It is optimized for a specific, repeatable production sequence. Changing the process often requires reconfiguring multiple stages of the line.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are ideal for small metal parts that can tumble without damage. They are also highly effective for processing bulk materials like alumina, iron ore pellets, or powders in processes such as calcining, where uniform heating and constant mixing are critical.
Choosing the Right Configuration for Your Process
Your final decision must be driven by your specific production requirements, material type, and desired end-state.
- If your primary focus is a single heat treatment step (like annealing): A standalone unit with a loader and appropriate cooling system offers the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, multi-stage fastener manufacturing: An integrated line with washers and tempering furnaces is the only way to achieve a complete, automated process.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders or ores: Your configuration will center on the retort design and heating system to ensure precise temperature control for processes like oxidation or calcining.
Ultimately, understanding these configuration options allows you to design a system that delivers consistent quality and high throughput for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Configuration Type | Key Components | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standalone Unit | Rotary retort furnace, metering loader, integral quench system | Quench hardening, tempering, annealing of small parts like screws and bolts |
| Integrated Production Line | Furnace, washers, tempering furnaces, atmosphere generators | High-volume, multi-stage processing of fasteners and small metal components |
| Material Suitability | Rotating retort, heating system (gas/electric), atmosphere control | Bulk powders, ores for calcining, oxidation processes |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced rotary retort furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for standalone processes or integrated production lines. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment and material processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















