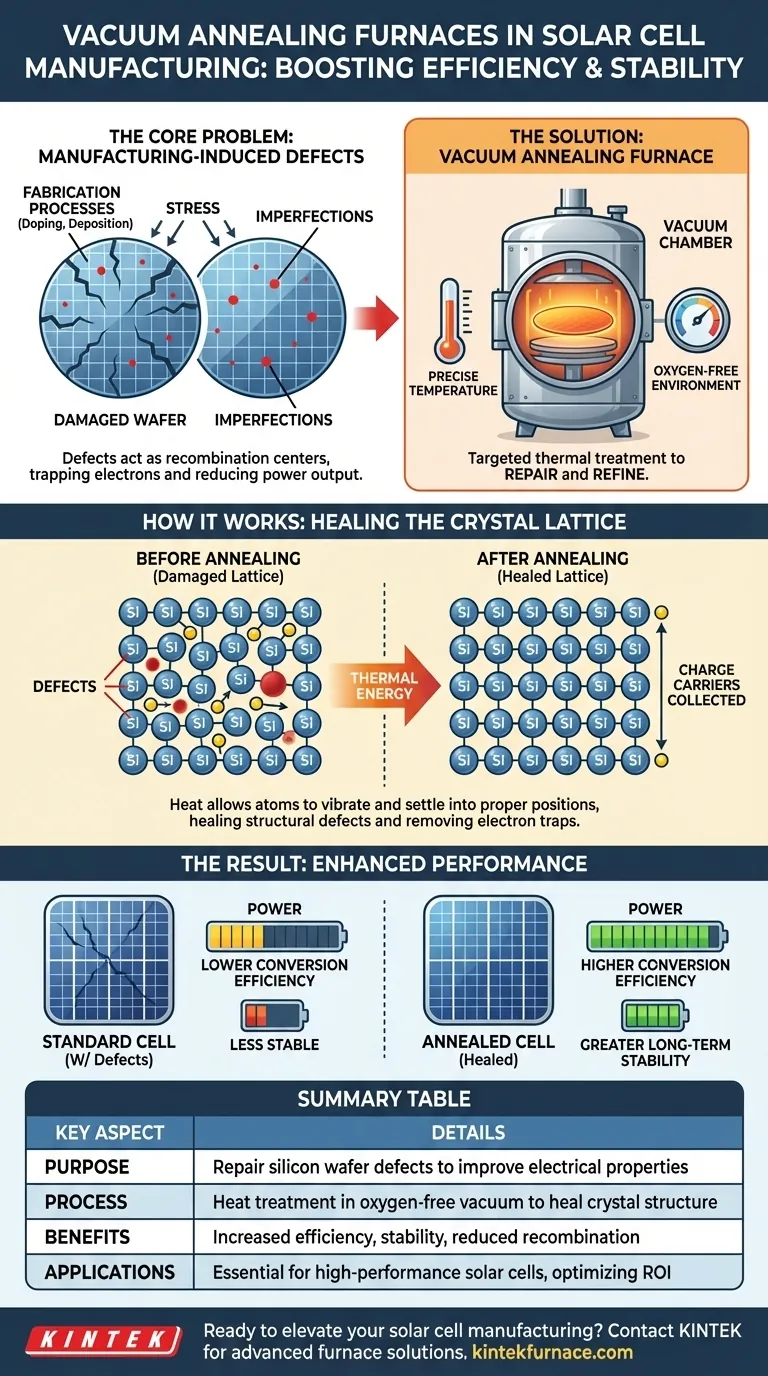
In solar cell manufacturing, a vacuum annealing furnace is a critical tool used to heat-treat silicon wafers in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. This process fundamentally repairs microscopic damage within the silicon's crystal structure that occurs during fabrication. By correcting these defects, annealing directly improves the wafer's electrical properties, leading to a solar cell with higher conversion efficiency and greater long-term stability.
The central purpose of vacuum annealing is not to add or build, but to repair and refine. Manufacturing processes inevitably create imperfections in the silicon wafer; annealing provides the controlled thermal energy needed to fix these flaws, allowing the finished solar cell to reach its maximum performance potential.

The Core Problem: Manufacturing-Induced Defects
To understand why annealing is necessary, we must first look at the imperfections created during the earlier stages of solar cell production.
How Defects are Created
The silicon wafers used for solar cells undergo several aggressive processes, such as ion implantation (doping) and the deposition of various films.
These steps, while essential, introduce significant stress and create point defects, dislocations, or impurities within the silicon's highly ordered crystal lattice.
The Impact of Defects on Performance
Each defect acts as a "recombination center"—a trap that can capture the electrons generated when sunlight strikes the cell.
When an electron is trapped, it cannot contribute to the electrical current. Widespread defects, therefore, create a major bottleneck, severely reducing the cell's overall power output and efficiency.
How Vacuum Annealing Solves the Problem
Vacuum annealing is a targeted thermal treatment designed specifically to reverse this damage and restore the integrity of the silicon crystal.
The Principle of Annealing
The process involves heating the wafer to a precise temperature, typically below the silicon's melting point. This heat provides thermal energy to the silicon atoms.
This energy allows the atoms to vibrate and move slightly, enabling them to settle back into their proper, low-energy positions in the crystal lattice. This effectively "heals" the structural defects.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Performing this process in a vacuum is non-negotiable. At high temperatures, silicon is highly reactive with oxygen and other atmospheric gases.
A vacuum prevents these contaminants from reacting with the wafer's surface, which would otherwise form an unwanted oxide layer or introduce new impurities, defeating the purpose of the repair.
The Result: Enhanced Efficiency and Stability
With the crystal lattice repaired, there are far fewer "traps" to capture electrons. More charge carriers are free to be collected as electrical current.
This directly translates to a measurable increase in the solar cell's conversion efficiency and ensures more reliable, stable performance over the lifetime of the cell.
Understanding the Alternatives and Trade-offs
Vacuum annealing is just one of several heat-treatment steps in solar cell manufacturing, each with a distinct purpose.
Annealing vs. Other Furnace Processes
It's important to distinguish annealing from other furnace applications. CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) furnaces are used to deposit new layers of material onto the wafer, such as anti-reflective coatings. Atmosphere furnaces might be used for processes like sintering, which bonds metallic contacts to the silicon.
In contrast, annealing is a refinement step. Its sole purpose is to improve the quality of the existing silicon wafer, not to add new materials to it.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
Adding an annealing step increases the complexity, time, and cost of the manufacturing line. This requires a capital investment in the furnace and adds to the operational expense per wafer.
However, for high-performance solar cells, this cost is easily justified. The significant gain in efficiency and the increased yield of top-tier cells provide a return on investment that outweighs the initial expense.
How to Apply This Knowledge
The decision to implement or optimize an annealing process depends entirely on your production goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum cell efficiency: A carefully controlled vacuum annealing step is essential to minimize recombination losses and unlock the wafer's full electrical potential.
- If your primary focus is minimizing production cost: You might investigate lower-temperature or shorter-duration annealing cycles that still provide a meaningful efficiency boost without maximizing process time and energy consumption.
Ultimately, vacuum annealing is the crucial link that transforms a physically stressed and imperfect wafer into a highly efficient and stable device for generating clean energy.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Repair silicon wafer defects from manufacturing to improve electrical properties |
| Process | Heat treatment in oxygen-free vacuum to prevent contamination and heal crystal structure |
| Benefits | Increased conversion efficiency, greater stability, reduced electron recombination |
| Applications | Essential for high-performance solar cell production, optimizing yield and ROI |
Ready to elevate your solar cell manufacturing with precision heat treatment? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored vacuum annealing furnaces can boost your efficiency and stability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















