At their core, rotary tube furnaces are specialized industrial tools for thermally processing granular, powdered, or pelletized materials in a continuous or batch fashion. They are indispensable for high-temperature operations like calcination, sintering, roasting, and pyrolysis, where achieving a highly uniform product is critical across industries ranging from metallurgy to chemical manufacturing and resource recovery.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace lies in its ability to combine high heat with constant, gentle tumbling. This unique motion ensures every particle of material is uniformly exposed to the heat and any controlled atmosphere, solving the challenge of achieving consistent quality in bulk material processing.

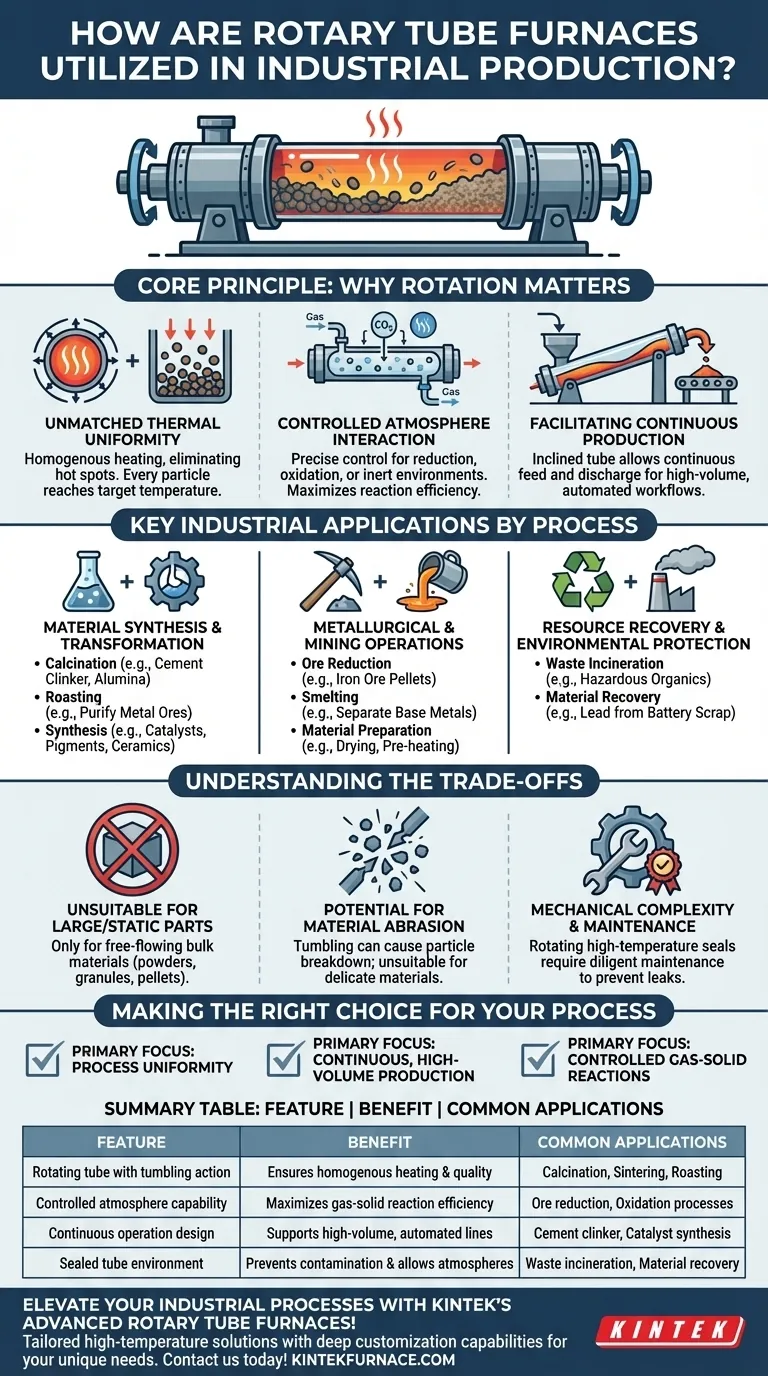
The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
The defining feature of this furnace is its slowly rotating process tube, often inclined at a slight angle. This design is not arbitrary; it is engineered to solve specific industrial challenges related to processing bulk solids.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
The primary benefit of rotation is homogenous heating. As the material tumbles, new surfaces are constantly exposed to the heat source, eliminating hot spots and ensuring the entire batch or flow reaches the target temperature uniformly.
Controlled Atmosphere Interaction
The sealed environment of the tube allows for precise control over the gas atmosphere. This is critical for processes like the gaseous reduction of ores, controlled oxidation of materials, or running reactions in an inert environment to prevent unwanted side effects. The tumbling action maximizes the surface area of the solid material exposed to the gas, increasing reaction efficiency.
Facilitating Continuous Production
For large-scale industrial operations, the ability to run continuously is a major economic driver. The slight inclination of the tube allows material to be continuously fed into the higher end and slowly travel to the lower end for discharge, creating an efficient, automated production line.
Key Industrial Applications by Process
While used across many sectors, the applications of rotary tube furnaces can be best understood by the thermal process being performed.
Material Synthesis and Transformation
This is the broadest and most common use case. It involves changing the chemical or physical properties of a material to create a new product.
- Calcination: Heating a solid to a high temperature to drive off volatile components, such as converting limestone to lime or producing cement clinker and alumina.
- Roasting: A metallurgical process involving gas-solid reactions, often used to purify metal ores.
- Synthesis: Creating new materials like industrial catalysts and pigments, or doping ceramics with rare earth metals to impart specific properties.
Metallurgical and Mining Operations
The ability to handle high temperatures and controlled atmospheres makes these furnaces vital in metallurgy.
- Ore Reduction: Using a reducing gas (like hydrogen) to remove oxygen from metal oxides, a key step in producing pure metals from ores like iron ore pellets.
- Smelting: Heating materials past their melting point to separate base metals from their impurities.
- Material Preparation: Drying and pre-heating raw materials before they enter a primary furnace, improving overall process efficiency.
Resource Recovery and Environmental Protection
Rotary furnaces provide a robust method for treating byproducts and waste streams.
- Waste Incineration: Safely destroying hazardous organic materials at high temperatures in a controlled environment.
- Material Recovery: Extracting valuable substances from waste, such as the recovery of lead from battery scrap or other metals from industrial byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. Understanding the limitations of a rotary tube furnace is key to its proper application.
Unsuitable for Large or Static Parts
These furnaces are designed exclusively for processing free-flowing bulk materials like powders, granules, and pellets. They cannot be used for heat-treating single, large, or static components.
Potential for Material Abrasion
The tumbling action, while ensuring thermal uniformity, can cause abrasion and particle breakdown. This makes it unsuitable for very delicate or friable materials where maintaining particle integrity is paramount.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating seals at the ends of the tube, which must maintain a tight seal at high temperatures, are complex mechanical components. They represent a critical point of failure and require diligent maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure operational safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal choice for ensuring that every particle of your bulk solid receives the exact same thermal and atmospheric treatment.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-volume production: The design of an inclined rotary furnace is inherently suited for integration into a 24/7 automated industrial workflow.
- If your primary focus is controlled gas-solid reactions: The combination of a sealed, atmosphere-controlled tube and the high surface area exposure from tumbling offers unmatched reaction efficiency.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace excels where process consistency and thermal uniformity are paramount for producing high-quality bulk materials at scale.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating tube with tumbling action | Ensures homogenous heating and uniform product quality | Calcination, sintering, roasting |
| Controlled atmosphere capability | Maximizes gas-solid reaction efficiency | Ore reduction, oxidation processes |
| Continuous operation design | Supports high-volume, automated production lines | Cement clinker production, catalyst synthesis |
| Sealed tube environment | Prevents contamination and allows inert/reactive atmospheres | Waste incineration, material recovery |
Elevate your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your calcination, sintering, or material synthesis workflows for superior quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules



















