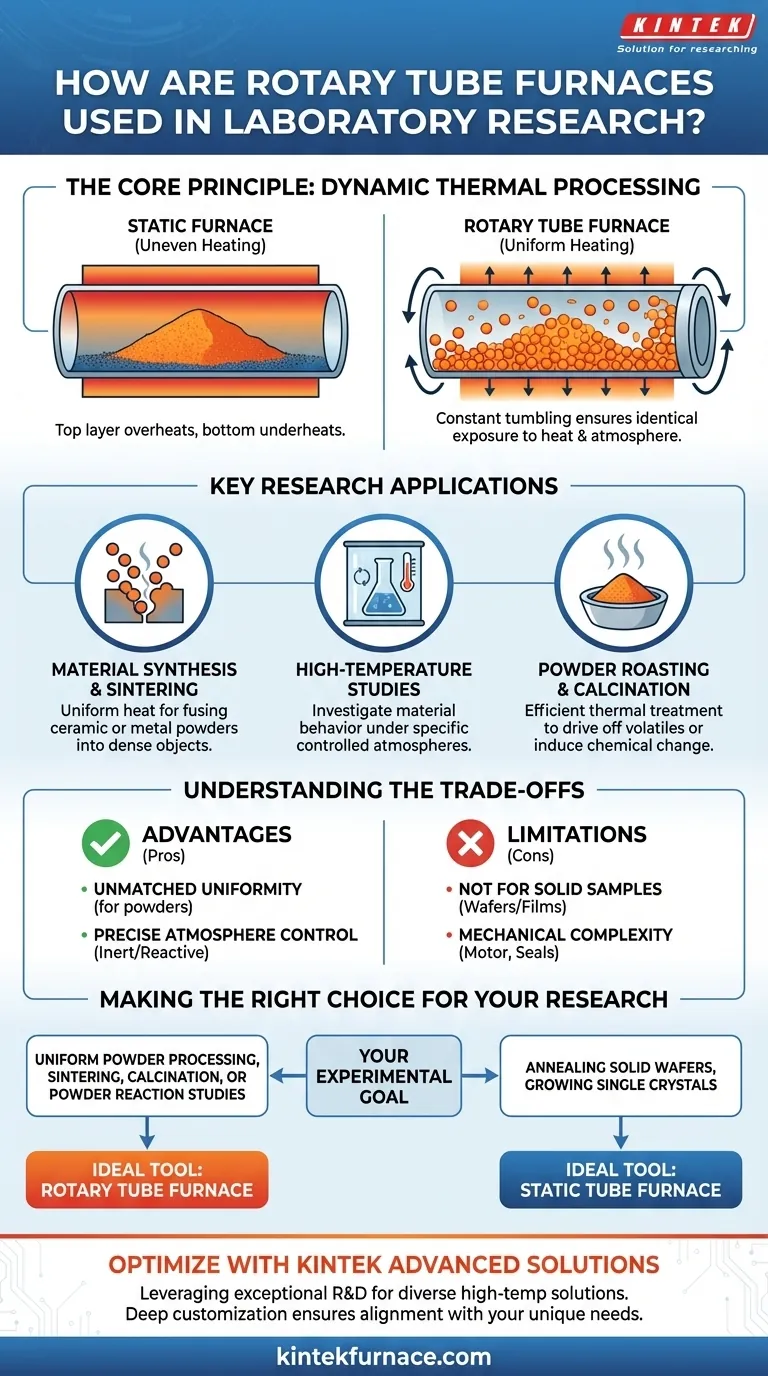
In laboratory research, rotary tube furnaces are specialized instruments used for continuous, high-temperature thermal processing of free-flowing materials like powders and granules. They excel at applications such as ceramic sintering, powder roasting, and synthesizing advanced materials where uniform heating and atmospheric control are critical for achieving consistent results.
The core challenge in processing powders at high temperatures is ensuring every particle is treated identically. A rotary tube furnace solves this by constantly tumbling the material, guaranteeing uniform exposure to both heat and the controlled atmosphere, which is something a static furnace cannot achieve.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Thermal Processing
The defining feature of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to apply heat to a sample that is in motion. This dynamic approach is fundamentally different from static box or tube furnaces and provides unique advantages for specific research goals.
How It Works: The Rotating Tube
A rotary tube furnace consists of a cylindrical tube, which holds the sample material, placed inside a heating chamber. An external motor slowly rotates this tube along its horizontal axis. As the tube rotates, the loose material inside tumbles and mixes continuously while being heated.
The Critical Advantage of Rotation
This constant tumbling is the key to the furnace's effectiveness. In a static furnace, a powder sample would sit still, leading to uneven heating—the top layer gets hotter than the bottom, and only the surface interacts with the furnace atmosphere.
Rotation eliminates this problem. It ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source and any introduced gases, preventing agglomeration and leading to a far more homogenous final product.
Key Research Applications
The unique capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them indispensable for several areas of materials science and chemical research.
Material Synthesis and Sintering
These furnaces are commonly used to synthesize advanced materials like ceramics or nanomaterials. The uniform heat distribution is essential for sintering metal or ceramic powders, where individual particles must be heated precisely to fuse together into a solid, dense object without melting.
High-Temperature Material Studies
Researchers use these furnaces to study the structural properties and reaction mechanisms of materials at high temperatures. The ability to control the atmosphere (e.g., using an inert gas like argon or a reactive gas) allows for detailed investigation of how materials behave under specific chemical and thermal conditions.
Powder Roasting and Calcination
Calcination is a thermal treatment process that brings about a chemical change in a material, such as driving off volatile components or water. The continuous mixing inside a rotary tube furnace ensures this process happens completely and efficiently throughout the entire batch of powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its specific strengths and limitations is crucial for proper application.
Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity for Powders
For any process involving loose powders or granules that require exceptionally consistent thermal treatment, the rotary tube furnace is the superior choice. The dynamic mixing it provides cannot be replicated in a static system.
Advantage: Precise Atmosphere Control
Like other advanced tube furnaces, rotary models offer excellent control over the internal atmosphere. This allows researchers to perform reactions in inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments and even alter those conditions during a single processing cycle.
Limitation: Not for Solid Samples
The primary limitation is sample type. These furnaces are designed exclusively for free-flowing, loose materials. They are not suitable for processing solid objects, single crystals, or thin films on a substrate.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
The addition of a motor, seals, and a rotation mechanism makes these furnaces more mechanically complex and generally more expensive than their static counterparts. Maintenance of the rotating seals is also a key consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is uniform powder processing, sintering, or calcination: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal tool to ensure homogenous and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is annealing a solid wafer or growing a single crystal: A static tube furnace is the more appropriate and simpler choice.
- If your primary focus is studying reactions in a powder under a controlled atmosphere: A rotary tube furnace is superior because it guarantees the entire sample interacts with the gas, not just the surface layer.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace begins with understanding that its design is purpose-built to solve the specific challenge of uniform powder processing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Sintering | Uniform heating for particle fusion | Ceramics, nanomaterials |
| High-Temperature Material Studies | Controlled atmosphere for reactions | Investigating material behavior under specific conditions |
| Powder Roasting & Calcination | Complete, efficient thermal treatment | Driving off volatiles or water from powders |
Optimize your laboratory's powder processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for superior uniformity and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can elevate your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What materials are rotary tube furnaces typically constructed from? Choose the Right Tube for Your Process
- What optional features enhance the processing capabilities of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Customizations
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency
- What is the role of rotary tube furnaces in the energy sector? Boost Efficiency in Biomass and Battery Material Processing
- What level of process control do rotary tube furnaces provide? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Uniform Results



















