In a laboratory setting, retort furnaces are utilized for thermal processes that demand a highly controlled atmosphere, completely isolated from the furnace's heating elements and the ambient air. This unique design makes them essential for tasks like the distillation of substances, sintering oxygen-sensitive materials, and furnace brazing of metals. Their core function is to create a specific, stable, and pure environment—such as a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere—that is impossible to achieve in a standard furnace.
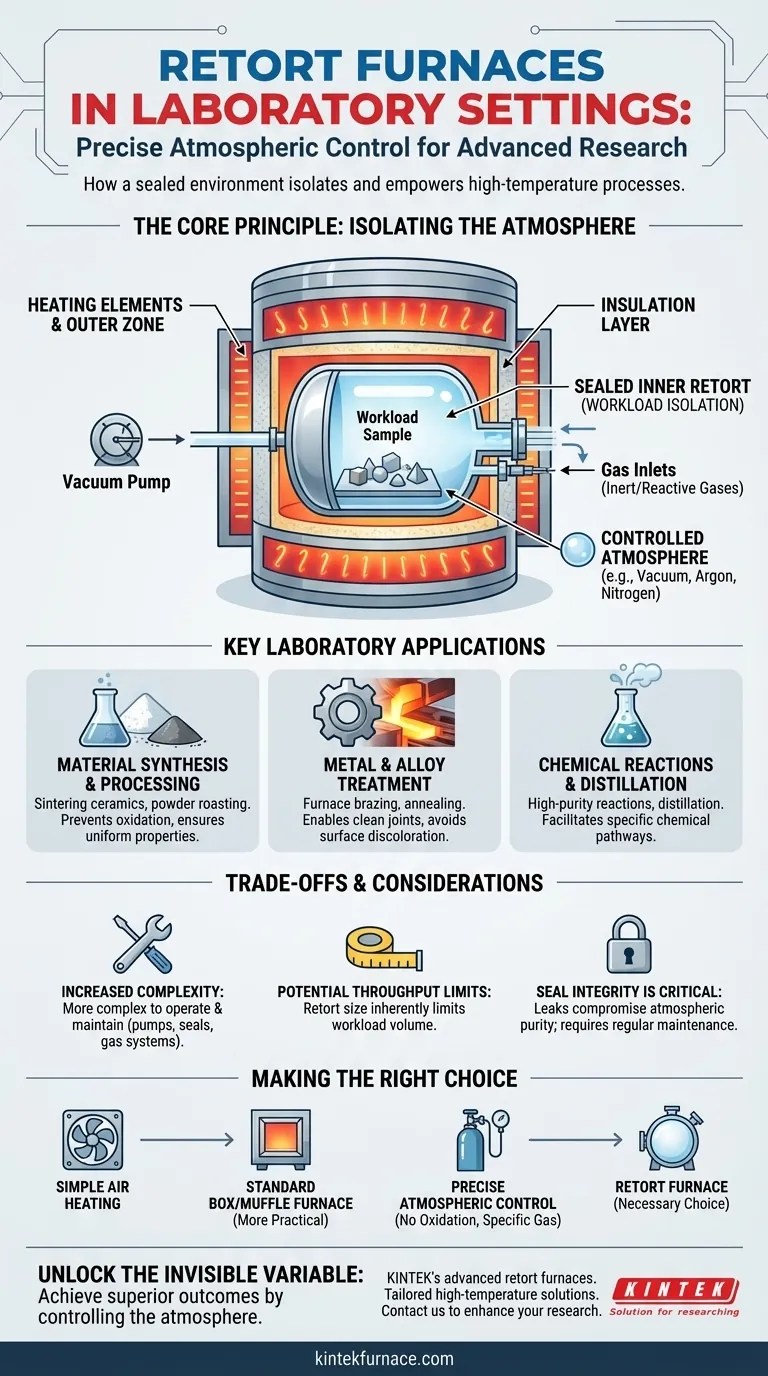
The defining feature of a retort furnace is its sealed inner chamber (the retort), which separates the workload from the heating elements. This separation is the key to enabling precise atmospheric control, which is critical for preventing oxidation, removing contaminants, and facilitating specific chemical reactions.
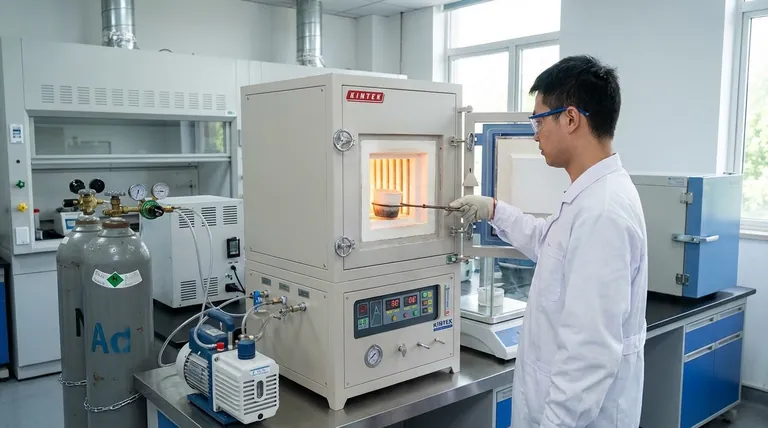

The Core Principle: Isolating the Atmosphere
A retort furnace's value comes from its fundamental design, which centers on creating a pure, controlled environment for your sample or components.
What is a Retort?
A retort is a sealed, gas-tight vessel, typically made of metal alloy or ceramic, that is placed inside the main heated chamber of the furnace. Your materials are placed inside this retort, not in the main furnace cavity.
This design creates two distinct zones: an outer zone where the heating elements operate and an inner zone within the retort where the atmospheric conditions can be precisely managed.
The Benefit of Separation
By separating the workload from the heating elements, the retort prevents any contamination from the elements themselves or from the furnace insulation.
More importantly, it allows for the complete evacuation of air (oxygen and nitrogen) and the backfilling of the chamber with a specific gas or gas mixture.
Enabling Precise Control
The sealed retort is equipped with ports for a vacuum pump and gas inlets. This allows a user to create a high-purity environment, such as:
- Inert Atmosphere: Using gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions.
- Reactive Atmosphere: Introducing gases like hydrogen for reduction processes or other specific chemical reactions.
- Vacuum: Removing all atmospheric gases to perform processes in a clean, evacuated space.
This control is dynamic, meaning the atmosphere can be altered during a single heating cycle to suit a multi-stage process.
Key Laboratory Applications
The ability to manipulate the atmosphere makes retort furnaces indispensable for a range of advanced research and development tasks.
Material Synthesis and Processing
Many advanced materials are highly sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures. A retort furnace is essential for powder roasting and the sintering of ceramics and powdered metals that would otherwise oxidize. It ensures uniform processing and high densification, leading to materials with enhanced properties.
Metal and Alloy Treatment
In metallurgy, retort furnaces are used for processes that require a pristine surface finish. This includes furnace brazing, where a controlled atmosphere prevents the oxidation of both the filler and base metals, ensuring a strong, clean joint. It is also used for annealing or hardening metals and alloys without surface discoloration or degradation.
Chemical Reactions and Distillation
As a primary use case, retort furnaces provide the ideal environment for studying high-temperature chemical reactions under specific atmospheric conditions. They are also used for the distillation of substances where purity and the prevention of side-reactions are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a retort furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations.
Increased Complexity
The addition of a retort, vacuum pumps, seals, and gas delivery systems makes these furnaces more complex to operate and maintain than a simple air-atmosphere muffle furnace.
Potential Throughput Limits
The size of the retort vessel inherently limits the volume or dimensions of the workload. For simple heat treatment of non-sensitive parts, a larger, non-retort furnace may be more efficient.
Seal Integrity is Critical
The effectiveness of the furnace depends entirely on the integrity of the seals on the retort. Regular inspection and maintenance are required to prevent leaks that would compromise the atmospheric purity and ruin the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Choosing a furnace depends entirely on the atmospheric requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or contamination: A retort furnace is the necessary choice for processing sensitive metals, advanced ceramics, or high-purity materials.
- If your primary focus is studying reactions in a specific gas environment: The precise atmospheric control of a retort furnace is non-negotiable for this type of research.
- If your primary focus is simple heating in ambient air: A standard, less complex box or muffle furnace is likely a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, a retort furnace empowers you to control the invisible variable—the atmosphere—that is often the deciding factor in a successful experiment.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Prevents oxidation, ensures uniform processing |
| Metal Treatment | Enables clean brazing and annealing |
| Chemical Reactions | Facilitates high-purity distillation and reactions |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows inert, reactive, or vacuum environments |
Unlock precise atmospheric control for your lab with KINTEK's advanced retort furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met for optimal results. Contact us today to enhance your research efficiency and achieve superior outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















