In a laboratory, a retort furnace is far more than a simple heat source; it is a precisely controlled atmospheric environment. These furnaces are primarily used for high-temperature processes like material synthesis, metal treatment, and chemical distillation where the composition of the surrounding gas is critical. Their defining feature is a sealed inner chamber—the retort—that allows operators to create a specific atmosphere (such as inert, reducing, or reactive) and even alter it during a single thermal cycle.
The essential value of a retort furnace lies not in its ability to generate heat, but in its power to completely isolate a process from air. This absolute atmospheric control prevents unwanted oxidation and enables specific chemical reactions, making it an indispensable tool for advanced material science and chemical research.
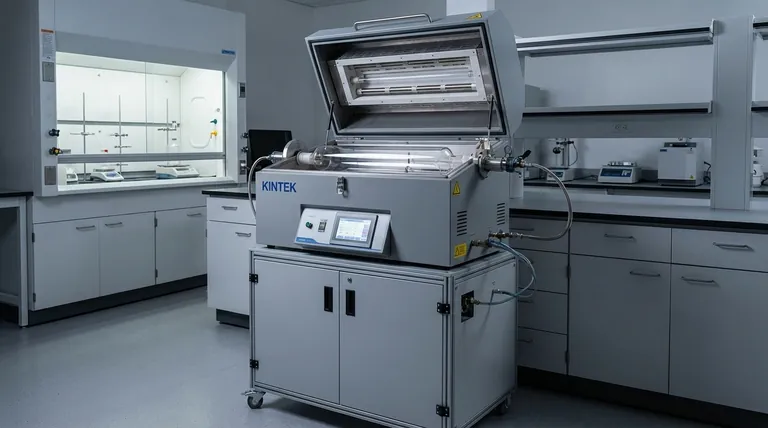

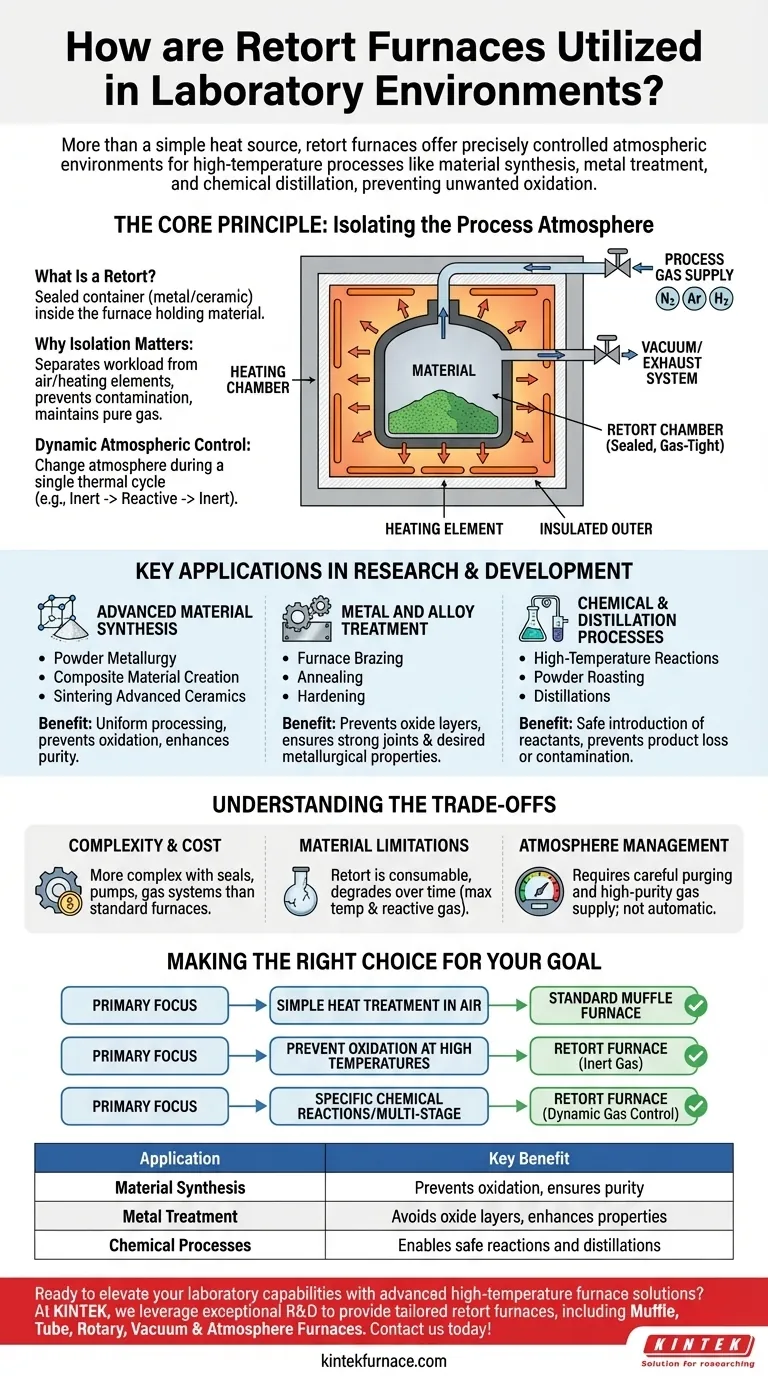
The Core Principle: Isolating the Process Atmosphere
The unique capabilities of a retort furnace stem from its fundamental design, which separates the heating function from the process environment.
What Is a Retort?
A retort is a sealed, gas-tight container, typically made of high-temperature metal alloys or ceramics. This container holds the material being processed and is placed inside the main insulated furnace chamber where the heating elements are located.
Why Isolation Matters
This "furnace within a furnace" design is critical. It separates the workload from the heating elements and the outside air. This prevents contamination and allows a very specific, pure gas environment to be introduced and maintained with minimal gas consumption.
Dynamic Atmospheric Control
The most significant advantage is the ability to change the atmosphere during a single firing. A process can begin in an inert gas like argon, switch to a reactive gas like hydrogen for a specific reaction, and finish with another purge of inert gas, all without opening the furnace.
Key Applications in Research and Development
This precise control unlocks a range of processes that are impossible in a standard furnace open to the air.
Advanced Material Synthesis
Retort furnaces are essential for creating new materials with enhanced properties. This includes powder metallurgy, composite material creation, and the sintering of advanced ceramics. The controlled atmosphere ensures uniform processing, prevents oxidation that would compromise material purity, and promotes better densification.
Metal and Alloy Treatment
In metallurgy, surface properties are paramount. Processes like furnace brazing, annealing, and hardening require a controlled atmosphere to prevent the formation of oxide layers on the metal's surface. A clean, oxygen-free environment ensures strong braze joints and the desired metallurgical properties in the finished part.
Chemical and Distillation Processes
Researchers use retort furnaces to study high-temperature chemical reactions and perform distillations. The sealed retort allows for the safe introduction of specific reactants and ensures that products are not lost or contaminated. Applications like powder roasting rely on this control to achieve a specific chemical conversion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a retort furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations.
Complexity and Cost
The retort itself, along with the required seals, vacuum pumps, and gas delivery systems, makes these furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than a standard muffle furnace.
Material Limitations of the Retort
The retort is a consumable component. It has a maximum service temperature and can degrade over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures and reactive gases. Its lifespan is a key operational and maintenance consideration.
Atmosphere Management
Achieving and maintaining a high-purity atmosphere is not automatic. It requires careful operational procedures, including purging cycles to remove air, and a reliable source of high-purity process gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on the level of atmospheric control your process requires.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment in air: A standard muffle furnace is more cost-effective and simpler to operate.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation at high temperatures: A retort furnace charged with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is essential.
- If your primary focus is driving specific chemical reactions or multi-stage processes: A retort furnace with dynamic gas control is the only tool that provides the necessary atmospheric flexibility.
Ultimately, selecting a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize atmospheric control, unlocking a new tier of material and chemical experimentation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Prevents oxidation, ensures purity |
| Metal Treatment | Avoids oxide layers, enhances properties |
| Chemical Processes | Enables safe reactions and distillations |
Ready to elevate your laboratory capabilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse labs with tailored retort furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise atmospheric control for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















