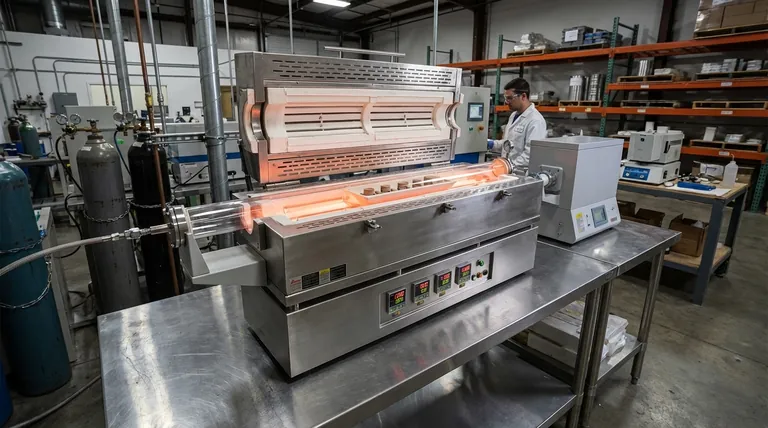
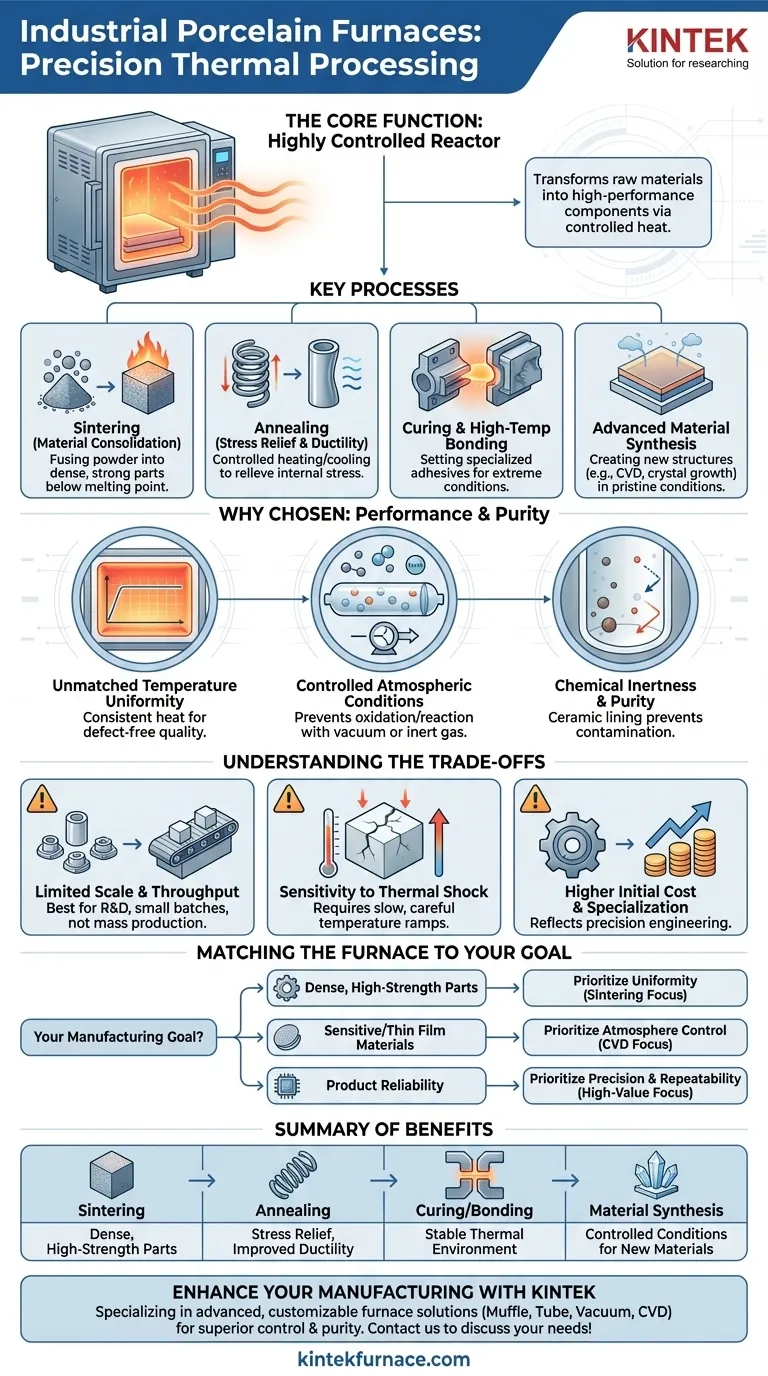
In industrial settings, porcelain furnaces are primarily used for high-precision thermal processes like sintering and ceramic glue discharge. These specialized furnaces excel at creating and maintaining extremely stable and uniform high-temperature environments, which is critical for manufacturing advanced components where material integrity and consistency are paramount.
The true value of a porcelain furnace in manufacturing is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to act as a highly controlled reactor. It enables the precise manipulation of material properties at a microscopic level, transforming raw powders or sensitive components into finished products with specific, engineered characteristics.

The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
The fundamental purpose of an industrial porcelain furnace is to apply controlled heat to a material to deliberately change its physical or chemical properties. This is a cornerstone of modern materials science and advanced manufacturing.
Sintering for Material Consolidation
Sintering is a process where heat is applied to a powdered material, causing the particles to fuse together and form a solid, dense mass. This happens at temperatures below the material's melting point.
This technique is essential for producing high-strength ceramic parts, metallic filters, and other components from materials that are difficult to melt and cast. The furnace's uniform heat ensures the part densifies evenly without warping or cracking.
Annealing for Stress Relief and Ductility
Annealing involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly. This process relieves internal stresses created during manufacturing, softens the material, and improves its ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing).
In industries like electronics and metallurgy, components are often annealed to ensure they can withstand mechanical stress and thermal cycling during operation without failing.
Curing and High-Temperature Bonding
Some applications, described as "ceramic glue discharge," involve curing specialized adhesives that are designed to operate at extreme temperatures.
These furnaces provide the stable thermal environment needed to properly set these bonds, which are often used in assembling complex devices for the aerospace or semiconductor industries.
Advanced Material Synthesis
These furnaces are also used as reactors for creating entirely new materials or structures. Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), pyrolysis, and crystal growth rely on a pristine, controlled thermal environment.
For example, a furnace can be used to grow a thin film of a specific material onto a substrate, which is a foundational process for producing semiconductors and advanced coatings.
Why Porcelain Furnaces Are Chosen
While many types of furnaces exist, porcelain and similar ceramic-lined furnaces are chosen for specific reasons related to performance and purity.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The primary advantage is the ability to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the entire heating chamber. This uniformity is non-negotiable for processes like sintering, where even small temperature variations can lead to defects and inconsistent product quality.
Controlled Atmospheric Conditions
Many of these furnaces, especially tubular designs, can be sealed and operated under a vacuum or filled with an inert gas like argon. This prevents the material being processed from oxidizing or reacting with air, which is critical for sensitive metals and advanced alloys.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
Porcelain, alumina, and other high-purity ceramics are chemically inert. This means the furnace chamber itself will not react with or contaminate the materials being processed, even at extreme temperatures. This purity is vital for medical implants, electronics, and research applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Limited Scale and Throughput
Many high-precision ceramic furnaces, particularly tube furnaces, are best suited for laboratory, R&D, and small-batch production. Their design prioritizes control over volume, making them less practical for mass-producing very large parts.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Ceramics can crack if heated or cooled too rapidly. This means processing cycles often require slow, carefully programmed temperature ramps, which can increase overall production time compared to more robust metal-lined furnaces.
Higher Initial Cost and Specialization
These are specialized, high-performance instruments, not general-purpose ovens. Their cost reflects the engineering required to achieve high levels of temperature uniformity and atmospheric control.
Matching the Furnace to Your Manufacturing Goal
To apply this technology effectively, align the furnace's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-strength ceramic or metal parts: Prioritize a furnace with documented, exceptional temperature uniformity to ensure consistent results from the sintering process.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials or creating pure thin films: A tube furnace with superior vacuum and atmospheric control is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and unwanted reactions.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product reliability in high-value components: The precision and repeatability of a dedicated porcelain furnace are a necessary investment to achieve the required quality standards.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about controlling the physics of your material to achieve predictable, high-performance results.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sintering | Uniform heating for dense, high-strength parts |
| Annealing | Stress relief and improved ductility |
| Curing/Bonding | Stable thermal environment for high-temperature adhesives |
| Material Synthesis | Controlled conditions for CVD, pyrolysis, and crystal growth |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing with precise thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can deliver superior temperature control, purity, and reliability for your industrial applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















