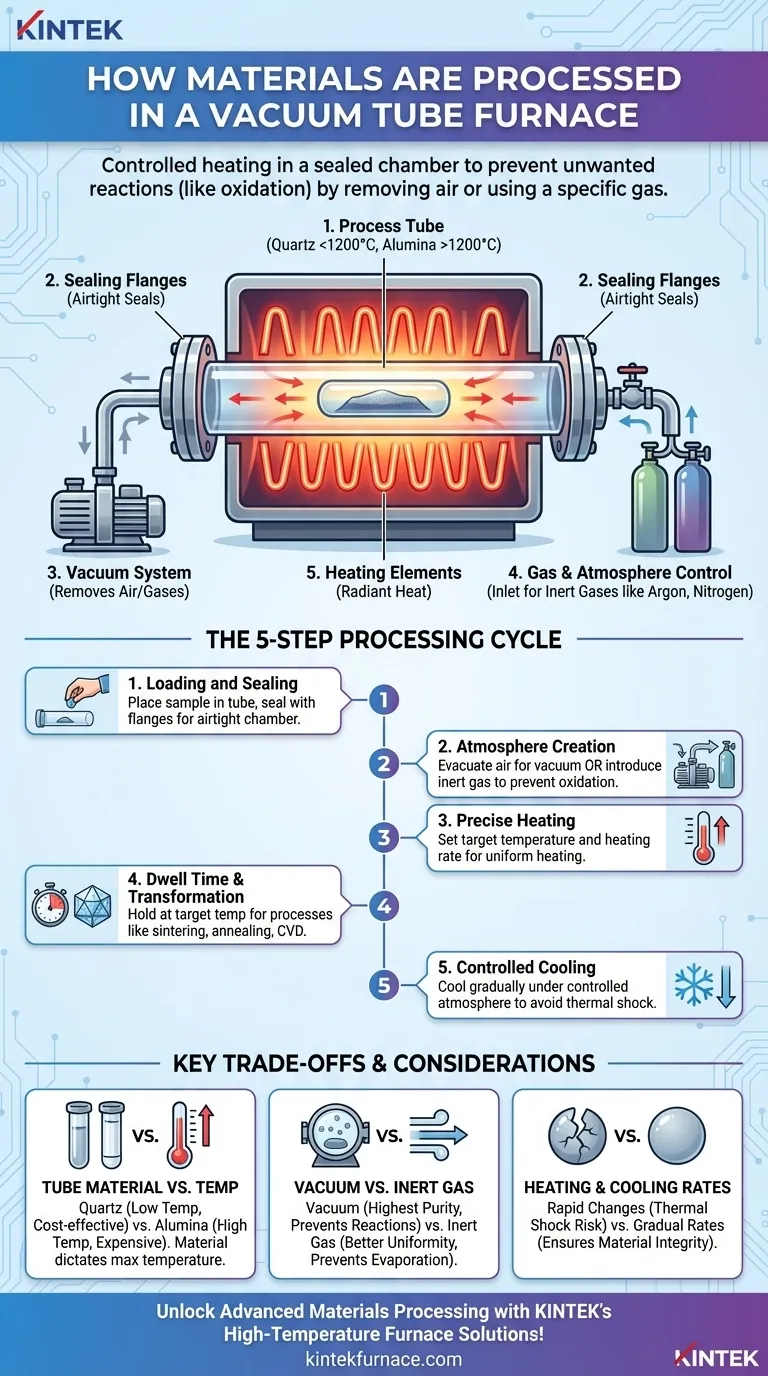
In short, processing materials in a vacuum tube furnace involves placing a sample into a sealed tube, removing the air to create a vacuum or filling it with a specific gas, and then heating it to a precise temperature. This controlled environment is the key to preventing unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, that would otherwise occur at high temperatures in open air.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum tube furnace is not just to heat materials, but to do so within a highly controlled atmosphere. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, it allows for high-temperature processes that would be impossible in a normal environment, ensuring material purity and enabling specific chemical transformations.

The Core Components and Their Roles
Understanding the process begins with knowing the key parts of the furnace and what each one does. The system is designed for containment, atmospheric control, and precise heating.
The Process Tube
The sample itself is placed inside a process tube, which is typically made of quartz for temperatures up to around 1200°C or a ceramic like corundum (alumina) for higher temperatures. This tube acts as the sealed chamber for the experiment.
The Sealing Flanges
To create an airtight environment, stainless steel sealing flanges are attached to the ends of the tube. These flanges contain ports for connecting the vacuum system and gas inlets, ensuring the internal atmosphere remains isolated.
The Vacuum System
A vacuum pump is connected to one of the flange ports. Its sole job is to evacuate the air from inside the tube, removing oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases.
Gas and Atmosphere Control
The flanges also feature a reserved air inlet. This is used not to let air in, but to introduce specific gases, such as inert gases like argon or nitrogen, to create a controlled, non-vacuum atmosphere when required.
The Heating Elements
The furnace itself contains electrical resistance heating elements that surround the process tube. They do not directly touch the tube but radiate heat, allowing for gradual, uniform, and precisely controlled temperature increases.
The Step-by-Step Processing Cycle
The operation follows a logical sequence, moving from sample preparation to the final cooled product. Each step is critical for achieving the desired outcome.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
First, materials are carefully placed inside the process tube. The tube is then inserted into the furnace, and the sealing flanges are securely clamped onto both ends to make the chamber airtight.
Step 2: Atmosphere Creation
This is the most critical step. The vacuum pump is activated to remove all the air from the sealed tube, creating a vacuum environment. Alternatively, the chamber can be purged with and then filled with a specific process gas.
Step 3: Precise Heating
Using the furnace controller, the user sets the target temperature and the heating rate. The furnace's heating elements then begin to gradually heat the exterior of the tube, which in turn heats the sample inside.
Step 4: Dwell Time and Transformation
The material is held at the target temperature for a specific duration, known as the "dwell time." During this phase, the intended process—such as sintering, annealing, or chemical vapor deposition—takes place.
Step 5: Controlled Cooling
After the dwell time is complete, the heating elements are turned off. The furnace cools down at a controlled rate, often while the vacuum or special atmosphere is maintained to prevent oxidation or thermal shock during the cooling phase. Samples are only removed once the furnace has returned to a safe temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While powerful, a vacuum tube furnace requires careful operation. The choices you make directly impact the success of your process.
Tube Material vs. Temperature
The material of your process tube dictates your maximum operating temperature. Quartz is common and cost-effective but is limited to about 1200°C. For higher temperatures, you must use more expensive ceramic tubes like alumina or mullite.
Vacuum vs. Inert Gas
A deep vacuum is ideal for preventing all atmospheric reactions and achieving the highest purity. However, processing under a flow of inert gas (like argon) can improve temperature uniformity and prevent certain elements in your sample from evaporating under vacuum.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Rapid temperature changes can cause thermal shock, cracking the process tube or the sample itself, especially with brittle materials like ceramics and glass. Always use gradual heating and cooling rates to ensure the integrity of your materials and equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific goal determines how you should approach the process.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity: Prioritize creating the deepest vacuum possible with your pump system to remove virtually all reactive contaminants.
- If your primary focus is a specific surface reaction (e.g., nitriding): Your goal is to use the gas inlet system to flow a specific reactive gas over your sample at a controlled temperature and pressure.
- If your primary focus is structural improvement (e.g., annealing metals): Concentrate on precise temperature control and, most importantly, a slow, controlled cooling rate to achieve the desired crystal structure.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace empowers you to control the fundamental relationship between heat and atmosphere, unlocking advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Loading and Sealing | Place sample in tube, seal with flanges | Create airtight chamber for controlled atmosphere |
| 2. Atmosphere Creation | Evacuate air or introduce inert gas | Prevent oxidation and enable specific reactions |
| 3. Precise Heating | Set temperature and rate via controller | Achieve uniform heating for material transformation |
| 4. Dwell Time | Hold at target temperature | Allow processes like sintering or annealing to occur |
| 5. Controlled Cooling | Cool gradually under vacuum or gas | Avoid thermal shock and maintain material integrity |
Unlock advanced materials processing with KINTEK's high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced vacuum tube furnaces, muffle furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, such as sintering, annealing, and chemical vapor deposition. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















