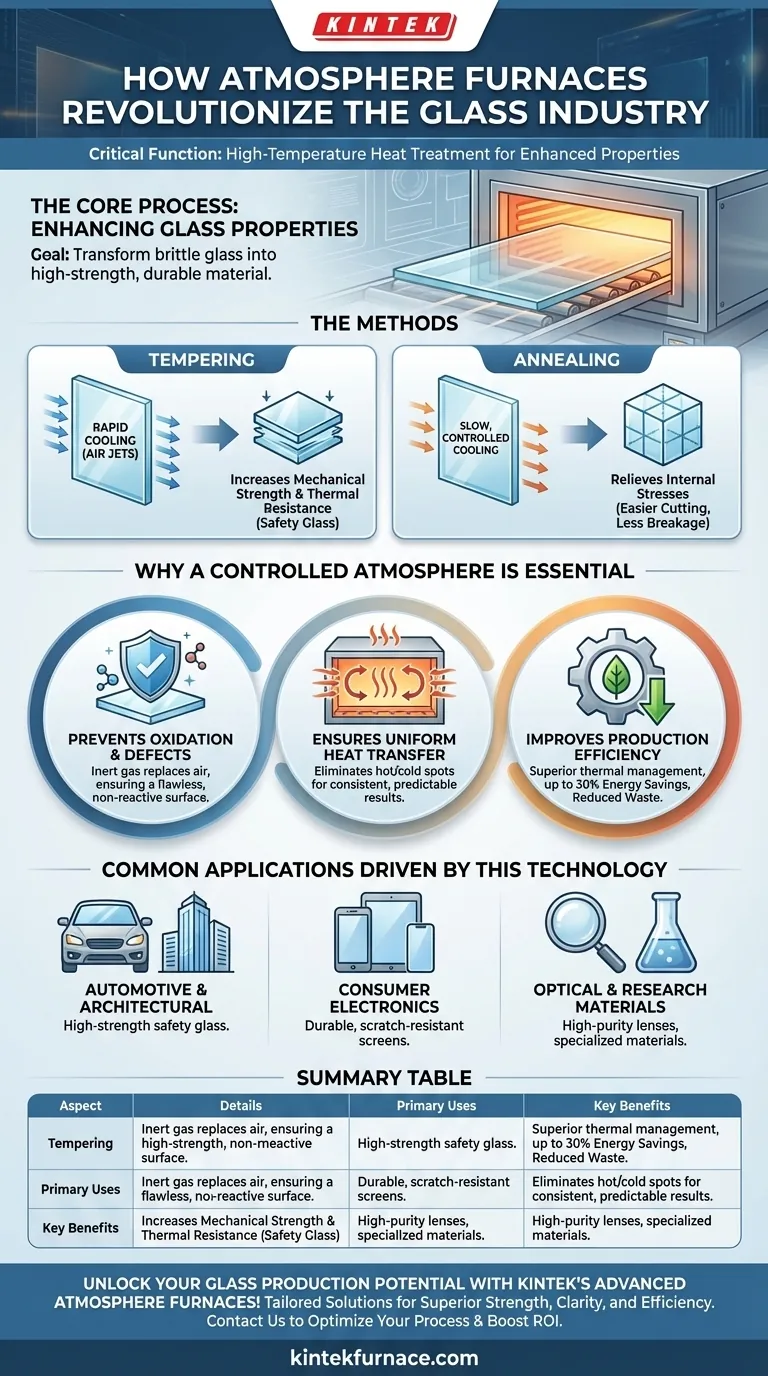
In the glass industry, atmosphere furnaces serve a critical function for high-temperature heat treatment. They are primarily used for processes like tempering and annealing, where glass is heated and then cooled under highly specific conditions to fundamentally change its physical properties. This controlled process is what creates the high-strength, durable glass required for modern applications.
The core challenge in treating glass is that high temperatures can introduce surface defects and internal stresses. Atmosphere furnaces solve this by replacing ambient air with a controlled gas environment, which prevents oxidation and ensures perfectly uniform heating for superior strength and clarity.

The Core Process: Enhancing Glass Properties
The goal of heat-treating glass isn't just to heat it, but to fundamentally restructure it for enhanced performance. Atmosphere furnaces provide the precise environment needed to achieve this transformation repeatably and reliably.
The Objective: Strength and Stability
Standard, untreated glass is brittle and highly susceptible to breaking from physical impact or sudden temperature changes (thermal shock).
The primary objective of heat treatment is to increase its mechanical strength and thermal resistance. This process rearranges the internal stresses within the glass to make it several times stronger than its untreated counterpart.
The Methods: Tempering and Annealing
Tempering involves heating glass to a uniform temperature, typically above 600°C, and then cooling its outer surfaces rapidly with jets of air. This "locks in" a state of high compression on the surface and tension in the core, giving the glass its strength.
Annealing, conversely, involves heating the glass and then cooling it very slowly. This process is designed to relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing, making the glass easier to cut and less likely to break spontaneously.
Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Essential
Using a standard furnace for these processes would lead to inconsistent quality and a high rate of failure. The "atmosphere" in an atmosphere furnace is the key to overcoming these challenges.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Defects
At high temperatures, oxygen in the air can react with the glass surface. This can cause discoloration, blemishes, and other microscopic defects that compromise both the appearance and the structural integrity of the final product.
An atmosphere furnace purges the oxygen and replaces it with an inert or specific gas mixture. This non-reactive environment ensures the glass surface remains pristine throughout the heating cycle.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Transfer
For tempering or annealing to be successful, every square millimeter of the glass must be at the exact same temperature. Any cold or hot spots will create uneven internal stresses, which can cause the glass to warp or even shatter.
The controlled, circulating atmosphere within the furnace guarantees uniform and efficient heat transfer, eliminating temperature variations and ensuring a consistent, predictable outcome.
Improving Production Efficiency
Modern atmosphere furnaces are engineered for superior heat retention and distribution. This focus on thermal management delivers several key business benefits.
Compared to older or conventional furnace designs, they can achieve energy savings of up to 30%. This directly reduces operational costs. Furthermore, by preventing defects, these furnaces dramatically reduce material waste and product rejection rates.
Common Applications Driven by This Technology
The ability to produce strong, reliable, and clear glass has made it an essential component in numerous high-value industries.
Automotive and Architectural Glazing
The safety glass used for car windshields, side windows, and architectural panels is tempered glass. Its high strength resists impact, and if it does break, it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than dangerous shards.
Consumer Electronics
The durable screens on smartphones, tablets, and other devices rely on chemically strengthened or tempered glass. The precision of atmosphere furnaces is essential for producing thin, lightweight glass that is also highly resistant to scratches and impacts.
Optical and Research Materials
For specialized applications like high-purity optical lenses or materials science research, atmosphere furnaces provide the ultimate level of environmental control. This allows for the creation of materials with specific properties, free from any atmospheric contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific heat treatment process you use is determined entirely by the desired end-state of the glass.
- If your primary focus is producing high-strength safety glass: Tempering in an atmosphere furnace is the definitive method for creating the necessary surface compression and internal tension.
- If your primary focus is removing internal stresses for easier cutting or processing: Annealing in a controlled atmosphere provides the slow, uniform cooling required to create a stable, stress-free product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production efficiency: The significant energy savings and dramatic reduction in defects offered by modern atmosphere furnaces provide a clear return on investment.
Ultimately, mastering the atmospheric conditions during heat treatment is the key to producing modern, high-performance glass.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Uses | Tempering and annealing glass for enhanced strength and stability |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, ensures uniform heating, reduces defects, saves energy (up to 30%) |
| Common Applications | Automotive glazing, consumer electronics screens, optical materials |
| Processes | Heating above 600°C with controlled gas environments for consistent results |
Unlock the full potential of your glass production with KINTEK's advanced atmosphere furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior strength, clarity, and efficiency. Don't let inconsistent results hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes and boost your ROI!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















