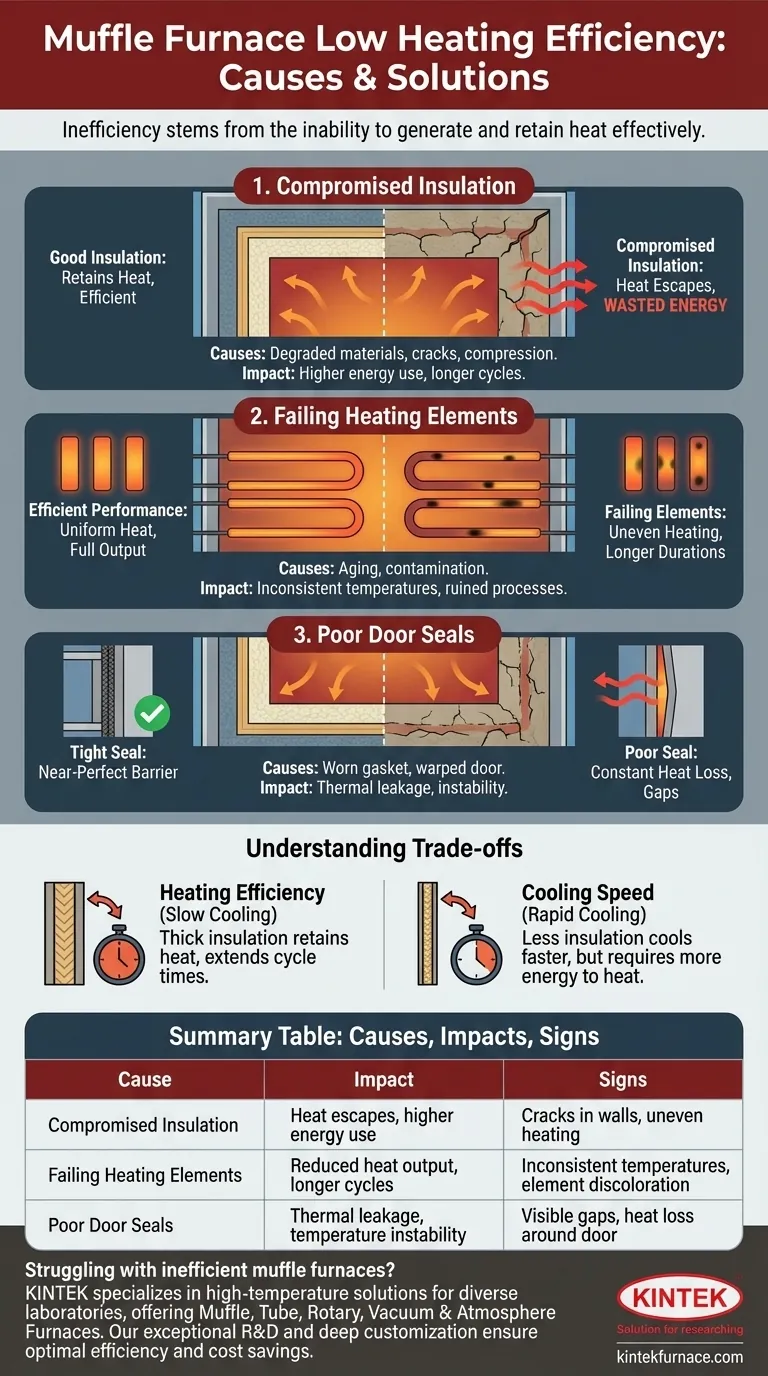
At its core, low heating efficiency in a muffle furnace stems from its inability to generate and retain heat effectively. This is almost always caused by compromised insulation, failing heating elements, or poor seals that allow thermal energy to escape the chamber, forcing the system to consume more power for longer periods to reach and maintain the target temperature.
The efficiency of a muffle furnace is not just a feature—it is the direct outcome of its design integrity. Any flaw that allows heat to escape or prevents it from being generated uniformly will directly translate into wasted energy, longer processing times, and higher operational costs.

The Core Components of Thermal Efficiency
To understand inefficiency, you must first understand the system's critical components. A muffle furnace is a closed thermal system, and its performance hinges on three key areas.
The Critical Role of Insulation
The primary defense against heat loss is the furnace's insulation. Its job is to keep the thermal energy concentrated within the main chamber.
Degraded or damaged insulation is the most common culprit for low efficiency. Over time, the fireproof ceramic or fiber materials can crack or compress, creating direct paths for heat to escape.
A well-designed furnace uses thick, multi-layered walls of high-quality insulation to minimize this thermal leakage, ensuring that the energy consumed is used to heat the sample, not the surrounding room.
Heating Element Performance
The heating elements are the heart of the furnace, converting electrical energy into thermal energy. Their condition and placement are paramount.
Aging or contaminated elements may fail to heat evenly or reach their maximum output. This forces them to draw power for longer durations and can lead to non-uniform heating, which ruins process consistency and wastes energy on failed runs.
Efficient heat transfer also depends on the insulation immediately surrounding the elements. This material protects the elements from vapors but also directs their heat effectively into the chamber.
Integrity of the Furnace Chamber and Door
The single largest potential point of failure in a sealed chamber is the door. A poor seal is like leaving a window open in winter.
The gasket or fiber seal around the door can wear out, compress, or become damaged, allowing a constant stream of heat to escape. Even a slight warp in the door or a weak latch can create a significant gap.
Modern furnaces use robust, insulated doors with tight-fitting seals to create a near-perfect thermal barrier, which is essential for both efficiency and temperature stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pursuing maximum efficiency introduces inherent compromises that you must factor into your operational planning.
Heating Efficiency vs. Cooling Speed
The very same high-quality, thick insulation that makes a furnace heat-efficient also makes it cool down very slowly.
Because the insulation is designed to prevent heat from escaping, it naturally retains that heat long after the power is turned off. This can significantly extend cycle times if your process requires rapid cooling.
Initial Cost vs. Operational Cost
A furnace with superior insulation, advanced heating elements, and a robust door design will have a higher initial purchase price.
However, a cheaper model with inferior components will almost certainly lead to higher long-term operational costs through wasted energy and more frequent maintenance. The initial savings are often lost to higher utility bills and lower productivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your definition of "efficiency" depends entirely on your application. Use these principles to guide your decision-making, whether diagnosing an old unit or purchasing a new one.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy costs: Prioritize furnaces with specifications detailing multi-layered ceramic fiber insulation and a tightly sealing door design.
- If your primary focus is process speed and high throughput: Acknowledge the slow-cooling trade-off and look for models that may offer assisted cooling features, even if it adds to the initial cost.
- If you suspect poor performance in an existing furnace: Begin with a visual inspection of the chamber insulation for cracks and verify the integrity of the door seal before investigating the heating elements.
By understanding that efficiency is a function of the entire thermal system, you can more effectively diagnose problems and select equipment that aligns with your operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Low Efficiency | Impact | Common Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Compromised Insulation | Heat escapes, higher energy use | Cracks in walls, uneven heating |
| Failing Heating Elements | Reduced heat output, longer cycles | Inconsistent temperatures, element discoloration |
| Poor Door Seals | Thermal leakage, temperature instability | Visible gaps, heat loss around door |
Struggling with inefficient muffle furnaces? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature solutions for diverse laboratories, offering Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring optimal efficiency and cost savings. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















