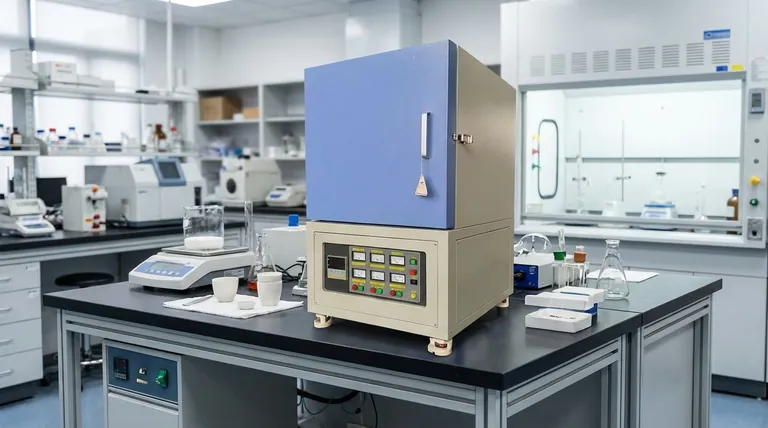
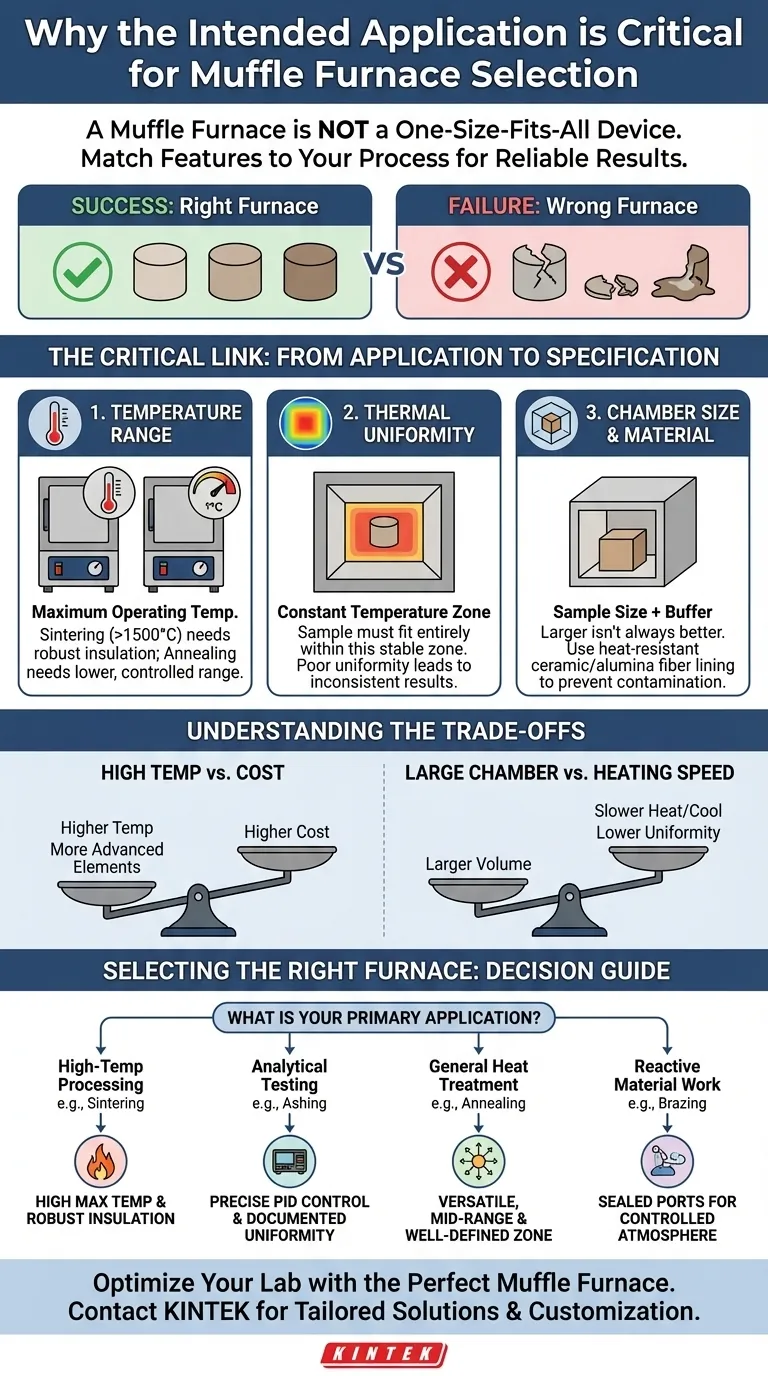
Selecting a muffle furnace based on its intended use is critical because the application dictates the required temperature range, thermal uniformity, and chamber design. A furnace optimized for a low-temperature annealing process will fail at high-temperature ceramic sintering, and one built for bulk material processing may lack the precision needed for sensitive analytical work. Choosing the right furnace prevents failed experiments, damaged samples, and unnecessary costs.
A muffle furnace is not a one-size-fits-all device. Viewing it as a precision instrument where specific features are matched to a specific scientific or industrial process is the only way to guarantee reliable and repeatable results.

The Critical Link: From Application to Specification
Understanding your application is the first step in translating your procedural needs into technical specifications. The most significant factors are temperature range, thermal uniformity, and chamber construction.
Temperature Range: The Primary Differentiator
The maximum operating temperature is the most fundamental specification of a muffle furnace. Different processes operate at vastly different thermal levels.
For example, sintering ceramics or creating metal alloys often requires extremely high temperatures, sometimes exceeding 1500°C. These furnaces must be built with robust, high-purity alumina fiber insulation to withstand the thermal stress.
In contrast, processes like annealing or other heat treatments may only require a lower, more controlled temperature range. Using a high-temperature furnace for these tasks is often an inefficient and unnecessarily expensive choice.
Thermal Uniformity: The Key to Repeatable Results
A furnace chamber is not uniformly heated. There is a specific volume within the chamber, known as the constant temperature zone, where the temperature is stable and consistent with the setpoint.
This zone is always smaller than the overall chamber dimensions. For any process requiring precision, from pharmaceutical development to materials research, the sample must fit entirely within this constant temperature zone.
Placing a sample in a part of the chamber with poor temperature uniformity will lead to inconsistent results, failed heat treatments, and unreliable data.
Chamber Size and Material
The required chamber size must be based on the size of your sample plus a buffer to ensure it fits within the constant temperature zone. A larger chamber is not always better.
The materials lining the chamber are also critical. For most high-temperature applications, heat-resistant ceramic or alumina fibers are used to ensure durability and prevent sample contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace excels at every task. The selection process always involves balancing competing factors and making an informed compromise.
High Temperature vs. Cost
Furnaces capable of reaching higher temperatures are exponentially more expensive. They require more advanced heating elements, superior insulation, and more sophisticated controllers, all of which increase cost and energy consumption.
Large Chamber vs. Heating Speed
A larger chamber volume naturally takes longer to heat up and cool down. It is also more challenging and energy-intensive to maintain tight temperature uniformity across a larger space.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Processes
Basic heat treatment can be done in a simple furnace. However, applications like ashing may require special ventilation to handle fumes, while brazing or reducing requires ports to introduce an inert or controlled atmosphere. These features add cost and are unnecessary for other tasks.
How to Select the Right Furnace for Your Application
Use your primary application to guide your decision-making process.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing (sintering, alloying): Prioritize a furnace with a very high maximum temperature and robust, high-purity insulation.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (ashing, gravimetric analysis): Focus on documented temperature uniformity and precise PID control, even if the max temperature is moderate.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment (annealing, tempering): A versatile, mid-range furnace with a well-defined constant temperature zone offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If you are working with reactive materials (brazing, reducing): Ensure the furnace has sealed ports for introducing a controlled atmosphere, as a standard air furnace will not work.
By defining your process first, you transform the furnace selection from a guess into a calculated, strategic decision.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Considerations | Recommended Furnace Features |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Material Processing (e.g., sintering, alloying) | Requires high max temperature (>1500°C) and robust insulation | High-purity alumina fiber insulation, advanced heating elements |
| Analytical Testing (e.g., ashing, gravimetric analysis) | Needs precise temperature control and uniformity | Documented constant temperature zone, PID control |
| General Heat Treatment (e.g., annealing, tempering) | Balances performance and cost | Mid-range temperature, well-defined constant temperature zone |
| Reactive Material Work (e.g., brazing, reducing) | Requires controlled atmosphere | Sealed ports for inert gases, atmosphere control systems |
Ready to optimize your lab with the perfect muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in materials research, pharmaceuticals, or industrial processing, we ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance to prevent failed experiments and reduce costs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory efficiency and achieve repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















