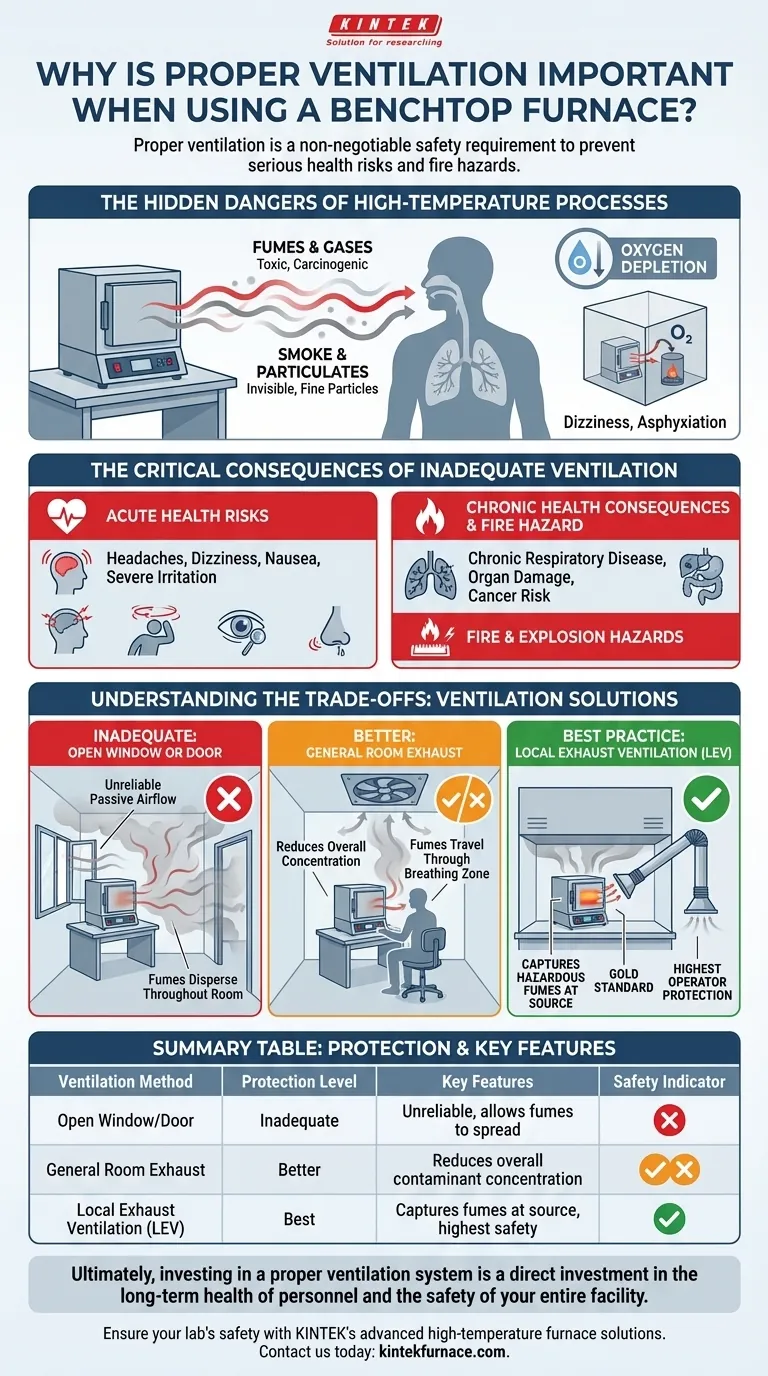
Proper ventilation is a non-negotiable safety requirement when operating a benchtop furnace because the heating process releases harmful fumes, invisible gases, and smoke. These byproducts, generated from the materials being heated or from contaminants on their surface, can pose serious health risks and create a fire hazard if allowed to accumulate in the workspace.
A benchtop furnace concentrates intense heat in a small area, and the materials you heat will almost certainly off-gas hazardous substances. Effective ventilation is not just about comfort; it is the primary engineering control that protects you from immediate respiratory harm and long-term health consequences.

The Hidden Dangers of High-Temperature Processes
Operating a furnace involves more than just heat. The chemical and physical reactions that occur release substances directly into your breathing space unless they are actively removed.
Generation of Fumes and Gases
When materials like metals, plastics, chemicals, or items with binders and coatings are heated, they break down. This process releases a cocktail of fumes and gases, many of which can be toxic or carcinogenic even in small quantities.
Creation of Smoke and Particulates
Visible smoke is an obvious indicator of incomplete combustion or vaporization, but the greater danger often lies in the invisible, microscopic particulates. These fine particles can be inhaled deep into the lungs, causing respiratory damage over time.
The Risk of Oxygen Depletion
In a poorly ventilated or small, sealed room, a high-temperature furnace can consume a significant amount of oxygen. While less common, this can lead to an oxygen-deficient atmosphere, causing dizziness, confusion, and ultimately, asphyxiation.
The Critical Consequences of Inadequate Ventilation
Failing to properly ventilate your workspace exposes operators and the facility to significant, preventable risks.
Acute Health Risks
Immediate exposure to concentrated fumes can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and severe irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. For sensitive individuals, this can trigger significant respiratory distress.
Chronic Health Consequences
Long-term, repeated exposure to low levels of certain fumes is even more dangerous. It is linked to chronic respiratory diseases, organ damage, and an increased risk of cancer. These effects build up over years and are often irreversible.
Fire and Explosion Hazards
Many substances release flammable vapors when heated. Without ventilation to disperse them, these vapors can accumulate, reach an explosive concentration, and be ignited by the furnace's own heating elements or an external spark.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ventilation Solutions
Not all ventilation methods are created equal. Choosing the right one depends on the materials you are working with and the frequency of use.
Inadequate: An Open Window or Door
Relying on passive airflow from a window is unreliable and often insufficient. It does not create the consistent, directed airflow needed to capture contaminants at the source, allowing fumes to disperse throughout the room before exiting.
Better: General Room Exhaust
A room equipped with a powerful exhaust fan is a step up. This method, known as dilution ventilation, reduces the overall concentration of contaminants in the air. However, it still allows fumes to travel through the operator's breathing zone before being removed.
Best Practice: Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV)
This is the gold standard. An LEV system, such as a fume hood or a snorkel extractor arm, is designed to capture hazardous fumes directly at the source, before they can escape into the workspace. It provides the highest level of operator protection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When setting up your furnace, your choice of ventilation strategy should be guided by a principle of maximum safety.
- If your primary focus is processing materials with binders, oils, or unknown contaminants: Your non-negotiable standard must be a dedicated fume hood or LEV system.
- If your primary focus is simple heat-treating of clean, known metals: A dedicated room with a high-capacity mechanical exhaust system may suffice, but LEV is always the safer choice.
- If your primary focus is ensuring operator safety and regulatory compliance: Always default to local exhaust ventilation (LEV) to capture and remove hazardous byproducts at their source.
Ultimately, investing in a proper ventilation system is a direct investment in the long-term health of personnel and the safety of your entire facility.
Summary Table:
| Ventilation Method | Protection Level | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Open Window/Door | Inadequate | Unreliable, allows fumes to spread |
| General Room Exhaust | Better | Reduces overall contaminant concentration |
| Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) | Best | Captures fumes at source, highest safety |
Ensure your lab's safety with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique ventilation and experimental needs. Contact us today to protect your operators and facility!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















