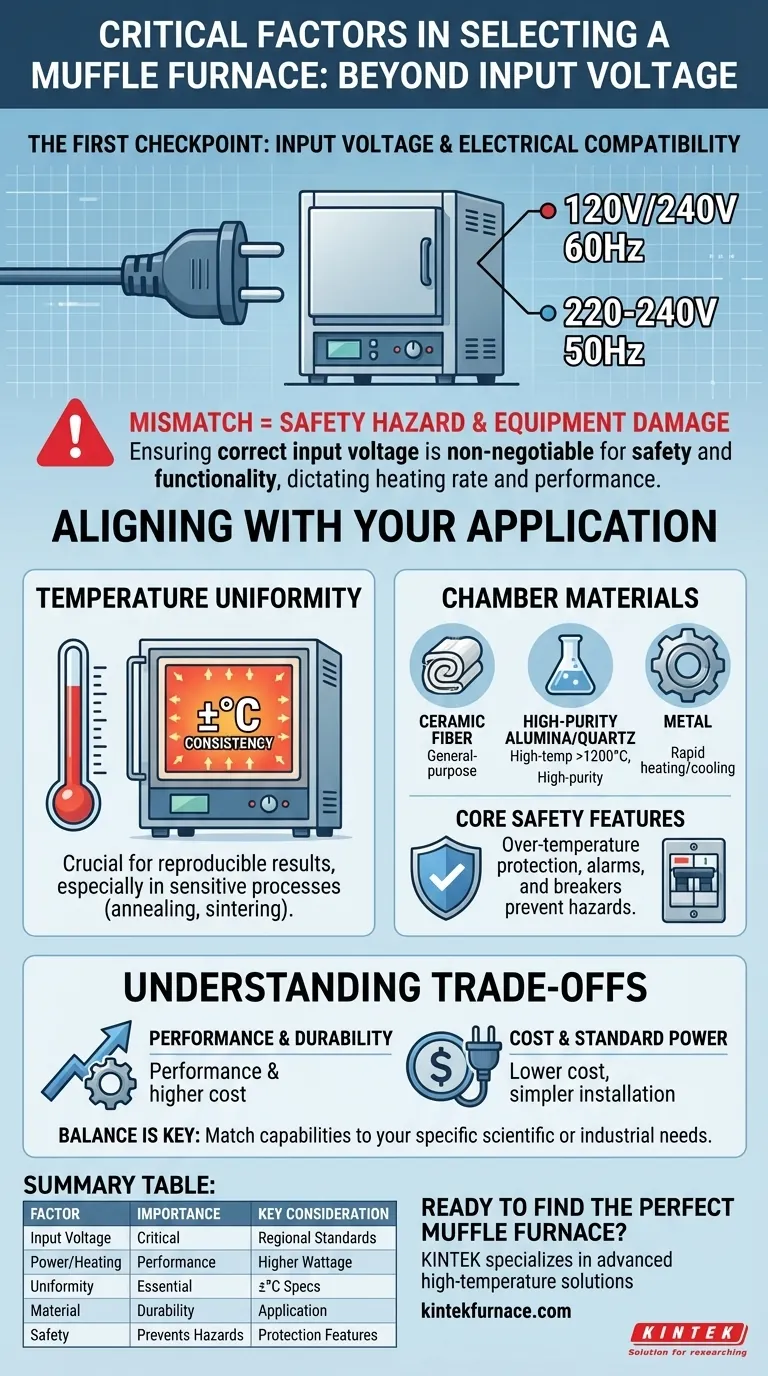
Ensuring the correct input voltage for a muffle furnace is the first and most critical checkpoint for both safety and functionality. A mismatch between the furnace's required voltage and your facility's power supply will, at best, prevent the unit from operating, and at worst, cause catastrophic damage to the equipment or create a significant electrical hazard.
While matching the voltage is a non-negotiable prerequisite, the truly important decision lies deeper. The correct voltage simply ensures the furnace will turn on; the correct furnace is one whose temperature range, chamber material, and uniformity are precisely aligned with your specific scientific or industrial application.

The Critical Role of Electrical Compatibility
A muffle furnace is a powerful piece of heating equipment. Its electrical requirements are not just a suggestion but a fundamental design constraint that dictates its performance and safety.
Matching Voltage and Frequency
The most basic check is for compatibility with your regional power grid. North America typically uses 120V or 240V at 60Hz, while other regions use 220-240V at 50Hz. A furnace designed for one system will not function properly on another.
Many high-performance or large-capacity furnaces require power sources beyond a standard wall outlet, often needing dedicated 240V or even three-phase power circuits. Always verify the furnace's nameplate specifications against your lab's available power infrastructure before purchase.
Power, Performance, and Heating Rate
Input voltage is directly tied to the furnace's power (wattage), which dictates how quickly it can reach its target temperature. A higher-power furnace will generally have a faster heating rate but will demand a more robust electrical circuit.
Attempting to run a high-power furnace on an inadequate circuit can lead to tripped breakers and an inability to reach or maintain the desired temperature, rendering your process useless.
Beyond Voltage: Aligning the Furnace with Your Application
Once electrical compatibility is confirmed, the focus must shift to the technical capabilities that will ensure your work is successful and reproducible. The "why" behind your work dictates the "what" of your furnace.
Temperature Range and Uniformity
The primary function of a furnace is to provide a stable thermal environment. Temperature uniformity—the consistency of temperature throughout the entire heating chamber—is arguably the most critical performance metric.
Poor uniformity means samples in different locations are processed at different temperatures, invalidating results for sensitive processes like annealing, sintering, or materials analysis. Always look for specifications on temperature uniformity, often expressed as ±°C.
Chamber Materials and Chemical Compatibility
The furnace chamber's material dictates its temperature limits and chemical resistance. This choice is determined entirely by your planned application.
- Ceramic Fiber: Excellent for general-purpose heat treating and ashing. Offers great insulation but can be susceptible to chemical attack from certain vapors.
- High-Purity Alumina/Quartz: Necessary for high-temperature work (>1200°C) or when working with high-purity materials where contamination from the furnace elements or insulation must be avoided.
- Metal: Suited for applications requiring very rapid heating and cooling cycles, but often with lower maximum temperatures.
Core Safety Features
Modern furnaces should be equipped with essential safety systems. Over-temperature protection is a vital, independent circuit that shuts the furnace down if it exceeds a user-set temperature, protecting both your samples and the furnace itself. Standard electrical breakers and alarms are also non-negotiable features.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and operational requirements. There is no single "best" furnace, only the one best suited to your needs.
Performance vs. Cost
A furnace with a higher maximum temperature, tighter temperature uniformity, and a specialized chamber material like quartz will be significantly more expensive. Over-specifying a furnace for a simple application leads to unnecessary capital expense.
Standard vs. Specialized Power
Opting for a furnace that runs on a standard 120V or 240V single-phase circuit simplifies installation. A furnace requiring specialized three-phase power may offer faster heating, but it adds significant installation complexity and cost if your facility is not already equipped for it.
Durability vs. Application
The furnace chamber must be chemically compatible with the materials you plan to heat. Using a furnace for a process that releases corrosive vapors (e.g., acids) can rapidly degrade a standard ceramic fiber chamber, leading to premature failure and cross-contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct muffle furnace, start by confirming electrical compatibility and then rigorously match the unit's technical specifications to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or simple heat treatment: A standard ceramic fiber furnace with a reliable temperature controller and over-temperature protection is a cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is materials research or alloying: Prioritize excellent temperature uniformity (±5°C or better) and a chamber material that ensures purity at your target temperatures.
- If your primary focus is processing with chemical vapors: You must select a furnace with a chamber designed for corrosion resistance, such as one made of quartz or a specialized alloy.
Ultimately, a successful purchase is one where the furnace's capabilities are a perfect match for the demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Importance | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | Critical for safety and operation | Match regional standards (e.g., 120V/240V, 50Hz/60Hz) |
| Power and Heating Rate | Determines performance | Higher wattage for faster heating; requires robust circuits |
| Temperature Uniformity | Essential for accuracy | Look for ±°C specs to ensure consistent results |
| Chamber Material | Affects durability and purity | Choose based on application (e.g., ceramic fiber, alumina, quartz) |
| Safety Features | Prevents hazards | Includes over-temperature protection and alarms |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing safety, efficiency, and results. Don't compromise on performance—contact us today to discuss how we can support your scientific or industrial applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















