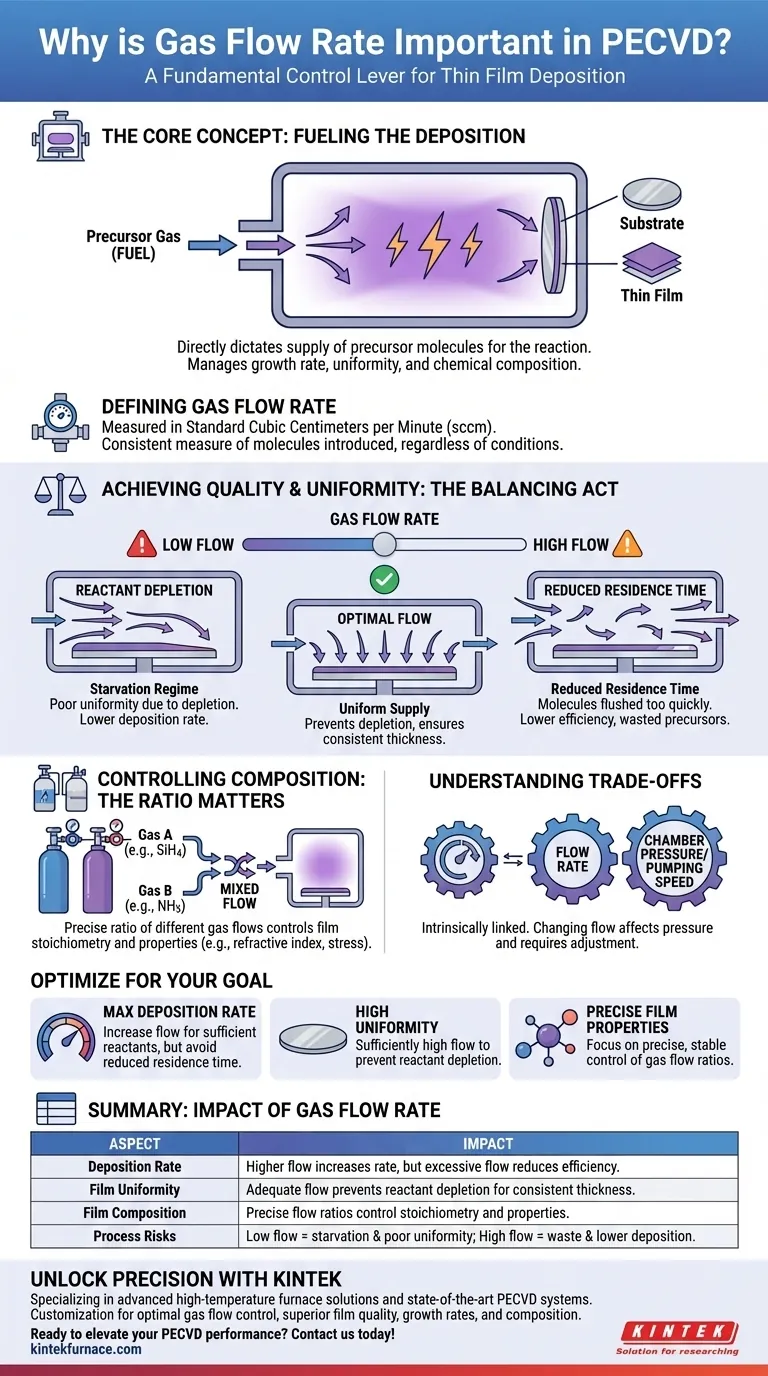
At its core, gas flow rate is a fundamental control lever in PECVD. It directly dictates the supply of precursor molecules available for the deposition reaction. This control over the reactant supply is what allows you to manage the final film's growth rate, its uniformity across the substrate, and its precise chemical composition.
The challenge of PECVD is not just supplying reactants, but supplying them correctly. Gas flow rate must be carefully balanced to provide enough material for uniform growth without flushing the molecules out of the reaction chamber before they have time to deposit.

The Role of Reactant Supply
The gases flowed into the chamber are the raw building blocks for the thin film. How you manage this supply chain directly impacts the final product.
Defining Gas Flow Rate
Gas flow rate is typically measured in Standard Cubic Centimeters per Minute (sccm). This unit represents a specific volume of gas per minute at a standard temperature and pressure, ensuring a consistent measure of the number of molecules being introduced, regardless of the process conditions.
The "Fuel" for Deposition
Think of the precursor gases as the fuel for the deposition process. The flow rate determines how much fuel is available to the plasma-enhanced reaction at any given moment. A higher flow rate means more atoms are available to build the film.
Impact on Deposition Rate
A sufficient gas flow is necessary to achieve a high deposition rate. If the reaction consumes reactants faster than they are supplied, the process becomes "starved," and the growth rate will be limited by the flow, not the plasma power or temperature.
Achieving Film Quality and Uniformity
Simply supplying gas isn't enough. The way it is supplied and distributed within the chamber is critical for creating a high-quality, uniform film.
The Problem of Reactant Depletion
As gases flow across the substrate, they are consumed by the deposition reaction. If the flow rate is too low, the gas near the outlet of the chamber will have a much lower concentration of reactants than the gas near the inlet. This reactant depletion causes the film to be thinner on one side of the substrate than the other.
How Flow Rate Combats Depletion
A higher gas flow rate helps to constantly replenish the reactants across the entire surface of the substrate. This maintains a more uniform concentration of precursor molecules, which is essential for achieving consistent film thickness from edge to edge.
Controlling Film Composition
For compound films like silicon nitride (SiN) or silicon dioxide (SiO2), the ratio of the different gas flows (e.g., silane and ammonia or silane and nitrous oxide) is critical. This ratio directly controls the stoichiometry of the film, which in turn determines its physical and optical properties, such as refractive index, stress, and etch rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing gas flow is a balancing act. Pushing the parameter in either direction has consequences that must be carefully managed.
The Risk of Low Flow: The Starvation Regime
Operating with an insufficient flow rate leads to a "mass-transport-limited" or "starvation" regime. The primary consequences are poor uniformity due to reactant depletion and a lower-than-expected deposition rate.
The Risk of High Flow: Reduced Residence Time
Conversely, an excessively high flow rate can also be detrimental. It reduces the residence time—the average amount of time a gas molecule spends inside the reaction chamber. If molecules are flushed out too quickly, they may not have enough time to be activated by the plasma and participate in the deposition reaction, which can paradoxically lower the deposition rate and waste expensive precursor gases.
The Link Between Flow and Pressure
Gas flow rate does not exist in isolation. It is intrinsically linked to the chamber pressure and the pumping speed of the vacuum system. Changing the flow rate will change the chamber pressure unless the pumping speed is adjusted, and vice-versa. This dynamic equilibrium must be managed as a single system.
Optimizing Gas Flow for Your Goal
The "correct" gas flow rate is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. Consider your primary objective to find the right balance for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition rate: You must increase flow to provide enough reactants, but monitor for the point where reduced residence time begins to hurt efficiency.
- If your primary focus is achieving high uniformity: A sufficiently high flow rate is non-negotiable to prevent reactant depletion across the substrate.
- If your primary focus is controlling film properties: Precise, stable control over the ratios of different gas flows is more important than the absolute total flow rate.
Ultimately, mastering gas flow rate is essential for moving from inconsistent results to reliable, repeatable control over your PECVD process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Gas Flow Rate |
|---|---|
| Deposition Rate | Higher flow increases rate, but excessive flow reduces efficiency due to low residence time. |
| Film Uniformity | Adequate flow prevents reactant depletion, ensuring consistent thickness across substrates. |
| Film Composition | Precise flow ratios control stoichiometry, influencing properties like refractive index and stress. |
| Process Risks | Low flow causes starvation and poor uniformity; high flow wastes precursors and lowers deposition. |
Unlock Precision in Your PECVD Processes with KINTEK
Struggling with inconsistent film deposition or poor uniformity in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our state-of-the-art PECVD systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal gas flow control for superior film quality, growth rates, and composition.
Our product line features Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all designed to enhance efficiency and reliability. Whether you're in semiconductor research, materials science, or any field requiring precise thin-film deposition, KINTEK delivers tailored solutions that drive results.
Ready to elevate your PECVD performance? Contact us today to discuss how our expertise and custom systems can solve your challenges and accelerate your innovations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication



















