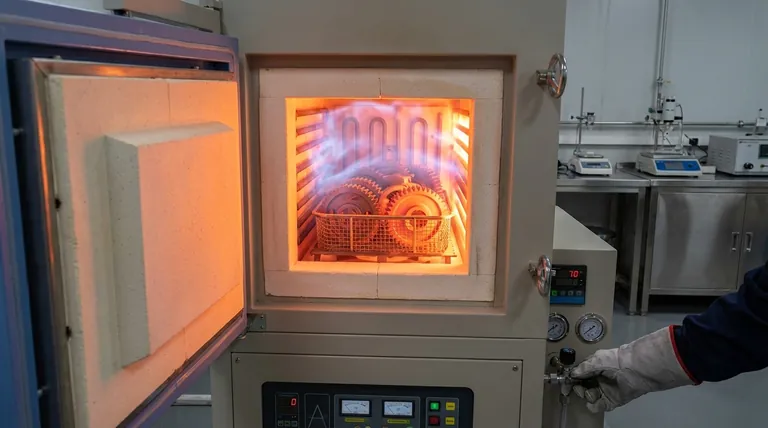
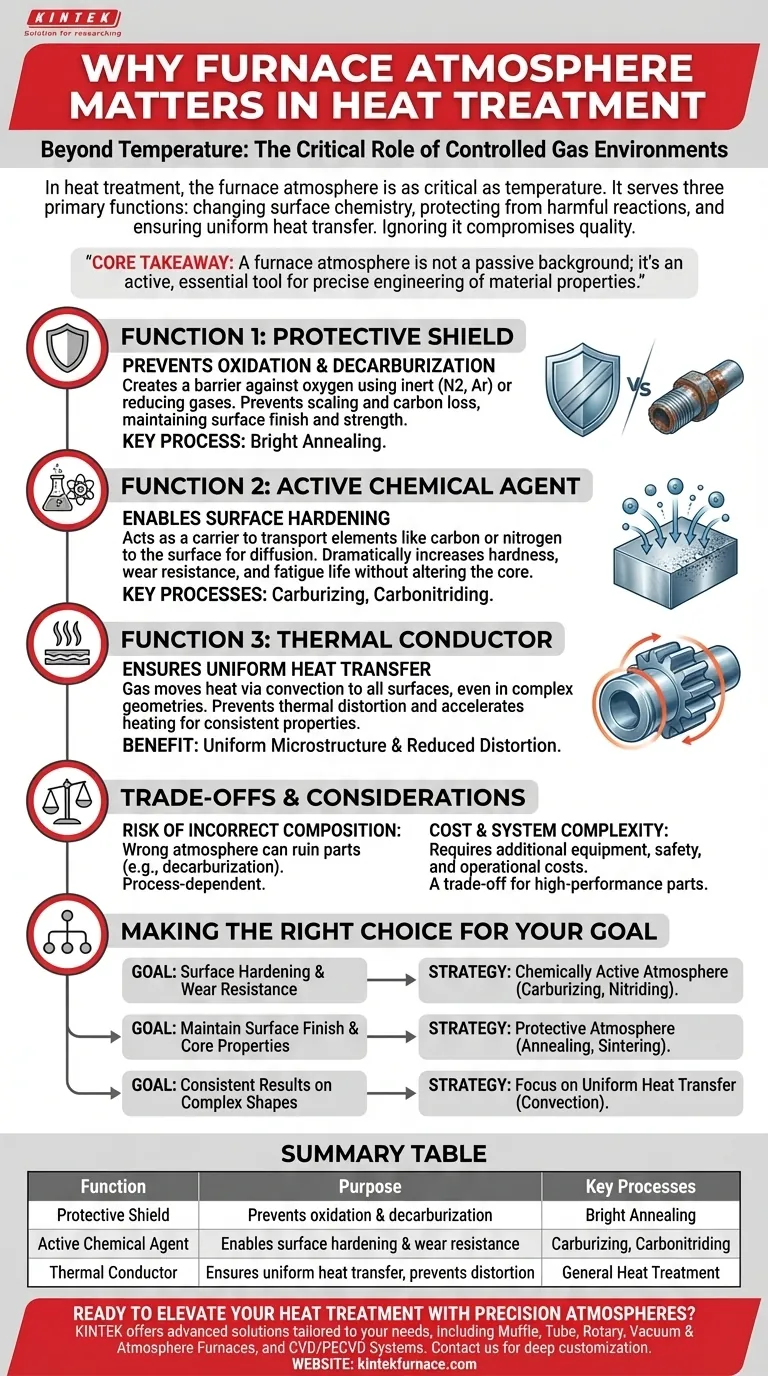
In heat treatment, the furnace atmosphere is as critical as the temperature itself. This controlled gas environment serves three primary functions: to actively change the chemistry of a part's surface for enhanced properties, to protect the part from harmful reactions with air at high temperatures, and to ensure uniform, efficient heat transfer. Ignoring the atmosphere means ignoring a fundamental variable that dictates the final quality, performance, and integrity of the component.
The core takeaway is that a furnace atmosphere is not a passive background element; it is an active and essential tool. It can be precisely engineered to either shield a material from change or to intentionally cause specific, desirable chemical reactions on its surface, directly controlling the outcome of the heat treatment process.

The Three Core Functions of a Furnace Atmosphere
To understand its importance, we must view the atmosphere as having three distinct roles. Depending on the process, one or more of these functions will be paramount.
Function 1: As a Protective Shield
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, most metals become highly reactive with the oxygen present in ambient air.
A protective atmosphere creates a barrier, preventing these unwanted reactions. This is often achieved using inert gases like nitrogen or argon, or reducing gases that actively consume oxygen.
The primary goal is to prevent oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), both of which compromise the material's strength, surface finish, and performance. Processes like bright annealing rely entirely on a protective atmosphere to maintain a clean, unaltered surface.
Function 2: As an Active Chemical Agent
In many cases, the goal is not to prevent reactions but to cause a specific, controlled chemical reaction at the surface of the part. Here, the atmosphere acts as a carrier.
It transports specific elements, such as carbon or nitrogen, to the component's surface, where they diffuse into the material. This is the fundamental principle behind surface hardening processes like carburizing and carbonitriding.
By changing the surface chemistry, these processes dramatically increase a component's hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life without altering the tougher, more ductile core.
Function 3: As a Thermal Conductor
The gas inside a furnace also plays a crucial role in heat transfer. It moves heat from the furnace walls and heating elements to the workpiece through convection.
A properly circulating atmosphere ensures all surfaces of the part, even those in complex geometries, are heated at a uniform rate.
This uniformity is critical for preventing thermal distortion and ensuring that the entire component achieves the desired microstructure and properties consistently. It accelerates the heating process and promotes an even temperature throughout the load.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While essential, creating and managing a furnace atmosphere introduces complexities that must be carefully managed. The choice of atmosphere is a critical decision with direct consequences.
The Risk of Incorrect Composition
There is no universal atmosphere; the ideal composition is entirely process-dependent. An atmosphere designed for carburizing will ruin a part that is meant to be bright annealed.
Imprecise control is a significant risk. For example, an atmosphere that is not sufficiently reducing can lead to decarburization in steel, weakening the surface instead of hardening it.
Cost and System Complexity
Heating a part in open air is simple and cheap. Generating and maintaining a specific gas mixture—whether endothermic gas, nitrogen, hydrogen, or argon—requires additional equipment, safety protocols, and operational costs.
The decision to use a controlled atmosphere is therefore a trade-off between the higher process cost and the required final properties of the component. For high-performance parts in industries like aerospace and automotive, it is a non-negotiable requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your heat treatment goal directly dictates your atmospheric strategy. Consider the primary objective for your component.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening and wear resistance: You must use a chemically active (carrier) atmosphere, as in carburizing or nitriding, to introduce new elements to the surface.
- If your primary focus is maintaining surface finish and core properties: You need a protective (inert or reducing) atmosphere to prevent oxidation and decarburization during processes like annealing or sintering.
- If your primary focus is consistent results on complex shapes: Pay close attention to the atmosphere's role in uniform heat transfer, as its convection properties directly impact distortion and final microstructure.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise engineering discipline.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Shield | Prevents oxidation and decarburization | Bright Annealing |
| Active Chemical Agent | Enables surface hardening and wear resistance | Carburizing, Carbonitriding |
| Thermal Conductor | Ensures uniform heat transfer and prevents distortion | General Heat Treatment |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment process with precision furnace atmospheres? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed for industries like aerospace and automotive, where quality and performance are critical. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material outcomes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















