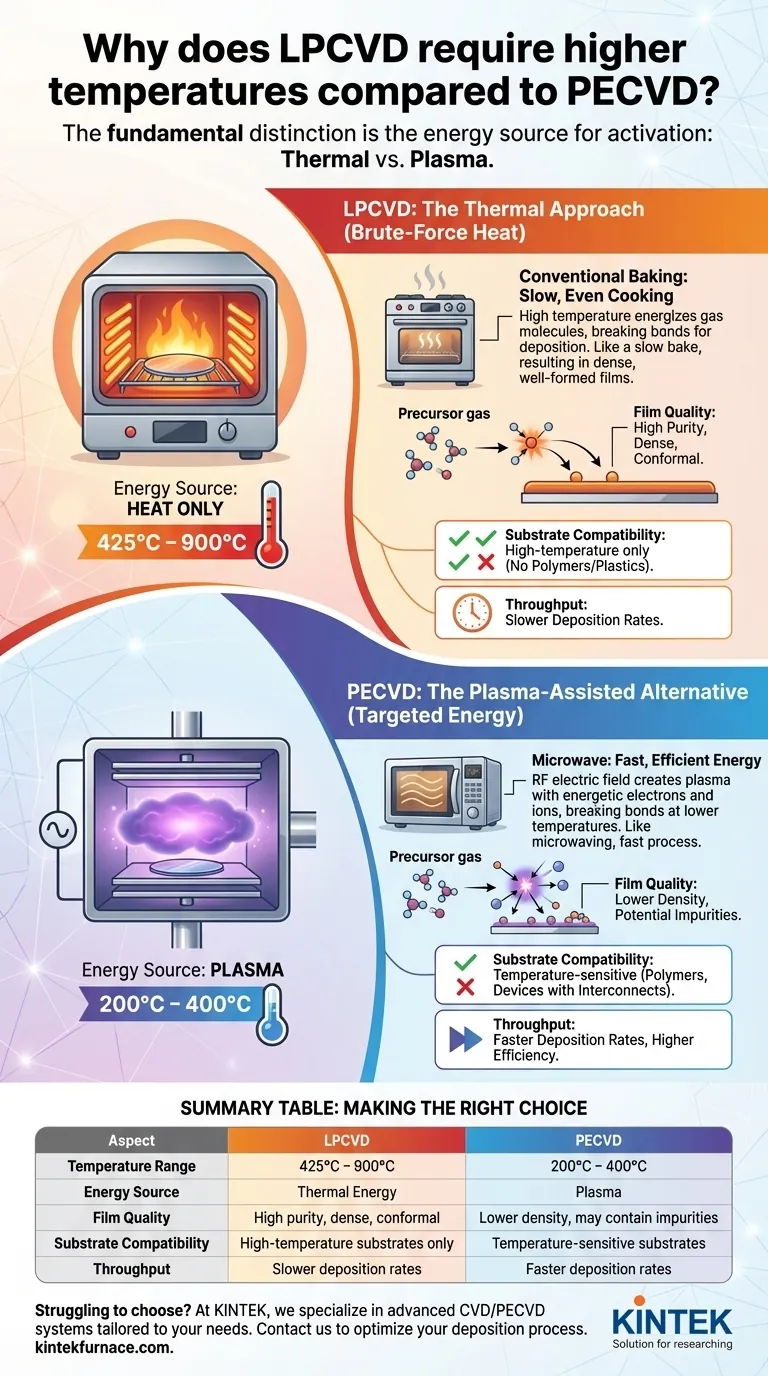
At its core, the difference comes down to the energy source. Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) relies exclusively on high thermal energy to initiate the chemical reactions needed for film deposition. In contrast, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) uses an electric field to generate plasma, which provides the necessary energy, allowing the process to run at much lower temperatures.
The fundamental distinction is how each process supplies the activation energy required to break down precursor gases. LPCVD uses brute-force heat, while PECVD uses the targeted energy of a plasma, fundamentally changing the temperature requirements and the resulting trade-offs.

The Role of Energy in Deposition
All Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes share a common goal: to decompose gaseous chemical precursors so they react and form a solid thin film on a substrate. This decomposition requires a significant amount of energy, known as activation energy. The method used to supply this energy is what separates LPCVD from PECVD.
LPCVD: The Thermal Approach
LPCVD operates in a high-temperature furnace, typically between 425°C and 900°C. In this method, heat is the only energy source.
The high temperature uniformly energizes the gas molecules within the low-pressure chamber. When the molecules gain enough thermal energy to overcome the activation energy barrier, they break apart and deposit a highly uniform and conformal film on the substrate.
Think of it like conventional baking. The oven's heat slowly and evenly cooks the ingredients, resulting in a dense, well-formed final product.
PECVD: The Plasma-Assisted Alternative
PECVD operates at much lower temperatures, usually between 200°C and 400°C. It achieves this by introducing a secondary energy source: plasma.
An RF (radio frequency) electric field is applied to the gas, ionizing it and creating a plasma—a highly energetic state of matter containing ions and free electrons. These energetic particles collide with the precursor gas molecules.
These collisions, not the background heat, provide the energy to break the chemical bonds. This allows the deposition reaction to proceed without requiring high temperatures. This is like using a microwave, which uses a different form of energy to cook food quickly at a lower ambient temperature than a conventional oven.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The difference in energy source creates a critical set of trade-offs between film quality, substrate compatibility, and processing speed. Choosing the wrong method can lead to damaged components or poor device performance.
Film Quality and Purity
LPCVD generally produces higher-quality films. The slow, thermally-driven process allows atoms to settle into a more ordered, dense, and stable structure. This results in films with excellent purity, low stress, and superior step coverage over complex topographies.
PECVD films can have lower density and contain impurities, such as hydrogen, which becomes incorporated from the precursor gases. The faster, plasma-driven deposition can also result in higher internal film stress.
Substrate Compatibility
This is the most significant advantage of PECVD. Its low operating temperature makes it the only viable option for depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates.
This includes polymers, plastics, or fully fabricated devices that already contain low-melting-point metals (like aluminum interconnects). The high heat of an LPCVD process would destroy these components.
Throughput and Cost
PECVD typically offers higher deposition rates than LPCVD. The plasma-assisted reaction is more efficient, allowing for faster processing and greater manufacturing throughput.
The lower temperature and faster cycle time can also lead to reduced energy consumption and overall lower cost per wafer, which is a major factor in high-volume manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on the balance between the required film quality and the thermal limitations of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality, purity, and conformality: Use LPCVD, but only if your substrate can withstand temperatures exceeding 425°C.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is your only viable option and the industry standard for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is high manufacturing throughput and lower cost: PECVD is generally the more efficient process, provided its film quality meets your device requirements.
Understanding this trade-off between thermal energy and plasma energy empowers you to select the precise tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | LPCVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 425°C - 900°C | 200°C - 400°C |
| Energy Source | Thermal Energy | Plasma |
| Film Quality | High purity, dense, conformal | Lower density, may contain impurities |
| Substrate Compatibility | High-temperature substrates only | Temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., polymers) |
| Throughput | Slower deposition rates | Faster deposition rates |
Struggling to choose the right CVD process for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your experimental requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to ensure precise performance. Whether you need LPCVD for superior film quality or PECVD for temperature-sensitive applications, our experts are here to help. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your deposition processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















