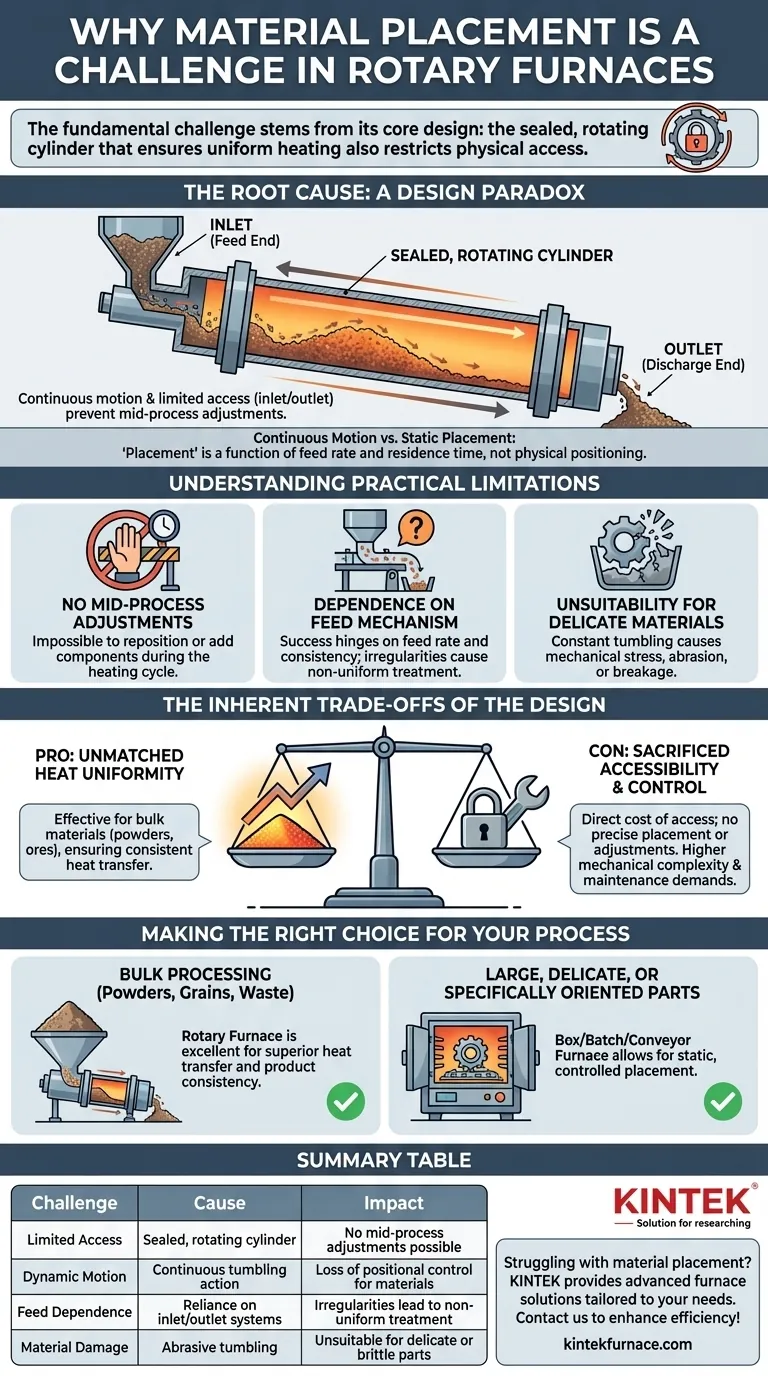
The fundamental challenge with material placement in a rotary furnace stems directly from its core design. The enclosed, rotating cylinder that makes it exceptionally effective at uniform heating also inherently restricts physical access, complicating how materials are introduced and managed during a process.
The very feature that defines a rotary furnace—its constant rotation for uniform heat treatment—is also its greatest limitation for material placement. You gain temperature consistency at the direct expense of accessibility and positional control.
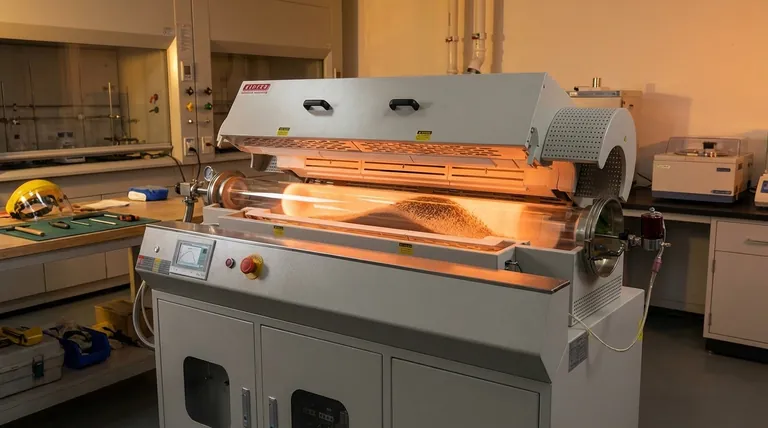

The Root Cause: A Design Paradox
A rotary furnace operates on a simple but powerful principle. Understanding this principle reveals why material placement is not a simple task.
The Sealed, Rotating Cylinder
At its heart, a rotary furnace is a slightly inclined tube that rotates continuously. Material is fed into the higher end and slowly tumbles its way to the lower end as it's heated.
This design is purpose-built for mixing and ensuring every surface of the material is exposed to the heat source.
Limited Access Points
Because the central chamber is a sealed, rotating tube, you cannot simply open a door to adjust the contents. Access is restricted to the inlet (feed end) and the outlet (discharge end).
This makes any mid-process intervention or adjustment nearly impossible without interrupting the entire operation.
Continuous Motion vs. Static Placement
Unlike a box or batch furnace where items can be carefully placed on shelves or fixtures, a rotary furnace is designed for dynamic material flow.
The tumbling action means you have no control over the specific orientation or position of any individual piece once it is inside the furnace. "Placement" becomes a function of feed rate and residence time, not physical positioning.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
This design paradigm has direct consequences for the types of processes a rotary furnace can handle effectively.
No Mid-Process Adjustments
The most significant limitation is the inability to reposition materials or add new components during the heating cycle.
Processes that require frequent human intervention or precise, multi-stage arrangements are fundamentally incompatible with this furnace type.
Dependence on Feed Mechanism
Success hinges on the design and calibration of the material feed system. "Careful placement" in this context refers to controlling the rate and consistency of the material entering the furnace.
Any irregularity in the feed will directly translate to non-uniform treatment, as you cannot correct for it once the material is inside the tube.
Unsuitability for Delicate Materials
The constant tumbling can cause mechanical stress, abrasion, or breakage.
This makes rotary furnaces a poor choice for delicate, brittle, or large, complex parts that could be damaged by the cascading motion.
The Inherent Trade-offs of the Design
Choosing a rotary furnace means accepting a critical trade-off between thermal efficiency and operational flexibility.
Pro: Unmatched Heat Uniformity
For bulk materials like powders, ores, granules, or pellets, the tumbling action is the most effective way to achieve exceptional temperature uniformity and efficient heat transfer.
Con: Sacrificed Accessibility and Control
This uniformity comes at the direct cost of access. You cannot place items with precision, protect specific surfaces, or adjust their position once the process has begun.
Con: Higher Maintenance Demands
The rotating mechanism itself, particularly the seals that must function at high temperatures, introduces mechanical complexity. These components require specialized expertise and more frequent maintenance compared to a static furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application's specific requirements will determine if a rotary furnace is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is bulk processing of fungible materials (powders, grains, waste): A rotary furnace is an excellent choice, as its continuous tumbling provides superior heat transfer and product consistency.
- If your primary focus is treating large, delicate, or specifically oriented parts: A box, batch, or conveyor belt furnace that allows for static, controlled placement is the more appropriate solution.
Ultimately, understanding this core trade-off between uniform heating and material access is the key to selecting the right thermal processing equipment.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Access | Sealed, rotating cylinder | No mid-process adjustments possible |
| Dynamic Motion | Continuous tumbling action | Loss of positional control for materials |
| Feed Dependence | Reliance on inlet/outlet systems | Irregularities lead to non-uniform treatment |
| Material Damage | Abrasive tumbling | Unsuitable for delicate or brittle parts |
Struggling with material placement in your thermal processes? KINTEK is here to help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Don't let design limitations hold you back—contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















