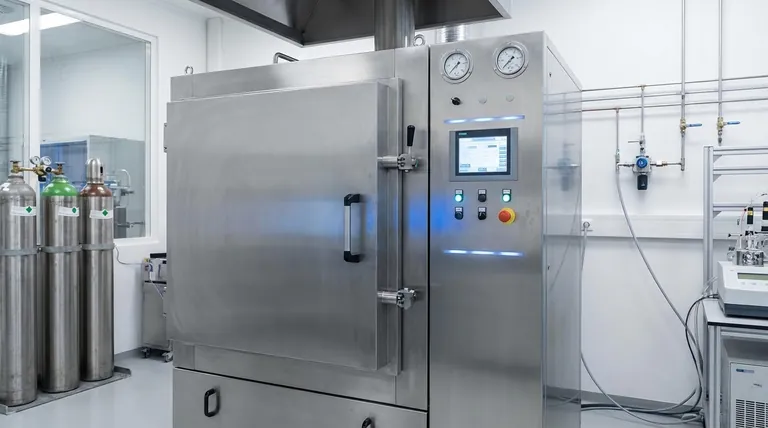
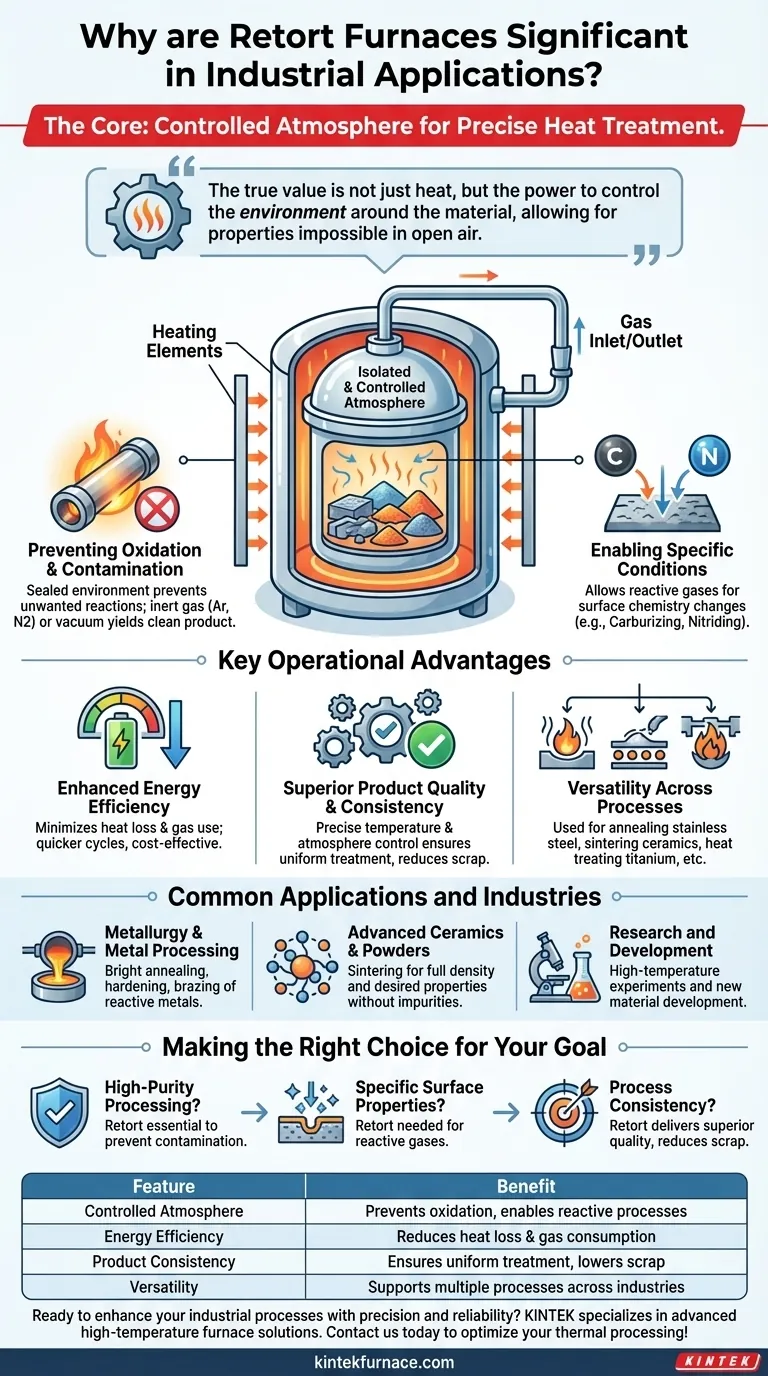
At its core, the significance of a retort furnace lies in its ability to perform precise heat treatment within a completely isolated and controlled atmosphere. Unlike conventional furnaces open to the air, a retort furnace uses a sealed container—the retort—to house the material, protecting it from oxidation and contamination while enabling highly specific chemical environments for superior results.
The true value of a retort furnace is not simply the heat it provides, but its power to control the environment around the material being heated. This control is what allows for the production of advanced materials with properties that are impossible to achieve in an open-air process.

The Defining Principle: The Controlled Atmosphere
The defining feature that sets a retort furnace apart is the retort itself—a sealed, gas-tight chamber that isolates the workload from the heating elements and the outside atmosphere. This fundamental design unlocks several critical capabilities.
### Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many advanced metals, alloys, and ceramics are highly reactive with oxygen, especially at high temperatures. Heating them in a normal furnace leads to oxidation, scaling, and compromised material integrity.
The retort creates a sealed environment where the ambient air can be pumped out and replaced with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, or even a vacuum. This completely prevents unwanted reactions, resulting in a clean, bright, and uncompromised final product.
### Enabling Specific Atmospheric Conditions
Beyond just preventing contamination, the retort allows for the introduction of specific reactive gases to achieve desired chemical changes in the material.
Processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen) rely on this capability to precisely alter the surface chemistry and hardness of a part. This level of process control is fundamental to modern metallurgy.
Key Operational Advantages
The design of a retort furnace directly translates into tangible benefits in efficiency, consistency, and cost-effectiveness.
### Enhanced Energy Efficiency
By containing the heat and atmosphere within a sealed chamber, retort furnaces minimize heat loss and reduce the volume of gas needed for processing.
This leads to quicker heating cycles and a significant decrease in fuel or electricity consumption, making the overall process more cost-effective.
### Superior Product Quality and Consistency
The combination of precise temperature control and a managed atmosphere ensures that every part in a batch receives the exact same treatment.
This eliminates process variability, resulting in highly consistent material properties, reduced scrap rates, and improved reliability for critical components used in industries like electronics and metallurgy.
### Versatility Across Processes
Retort furnaces are not single-task machines. Their environmental control makes them incredibly versatile for a wide range of thermal processes.
They are used for everything from annealing stainless steel and heat treating titanium to sintering advanced ceramics and roasting specialized powders for chemical applications.
Common Applications and Industries
The unique capabilities of retort furnaces make them indispensable across several high-tech fields.
### Metallurgy and Metal Processing
In metallurgy, retort furnaces are essential for processes that require a clean finish or specific surface properties. Key applications include bright annealing of stainless steel, hardening, brazing, and the heat treatment of reactive metals like titanium.
### Advanced Ceramics and Powders
The production of high-performance ceramics and metal powders relies on a process called sintering, where particles are fused together at high temperatures.
A retort furnace provides the clean, controlled environment necessary to achieve full density and the desired material properties without introducing impurities.
### Research and Development
Universities, national labs, and corporate R&D departments widely use retort furnaces for high-temperature experiments and new material development. The ability to precisely control every variable makes them an ideal tool for scientific investigation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a retort furnace is necessary, you must evaluate the atmospheric requirements of your specific thermal process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing: A retort furnace is non-negotiable for preventing oxidation and contamination of sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific surface properties: The ability to introduce reactive gases makes a retort furnace essential for processes like nitriding or carburizing.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for critical components: The unmatched temperature and atmospheric control of a retort furnace will deliver superior quality and reduce scrap.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize absolute process control and final product integrity over all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and contamination, enables reactive gas processes |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces heat loss and gas consumption for cost savings |
| Product Consistency | Ensures uniform treatment, lowers scrap rates |
| Versatility | Supports annealing, sintering, and more across industries |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with precision and reliability? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including retort furnaces tailored for metallurgy, ceramics, and R&D. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique needs with products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















