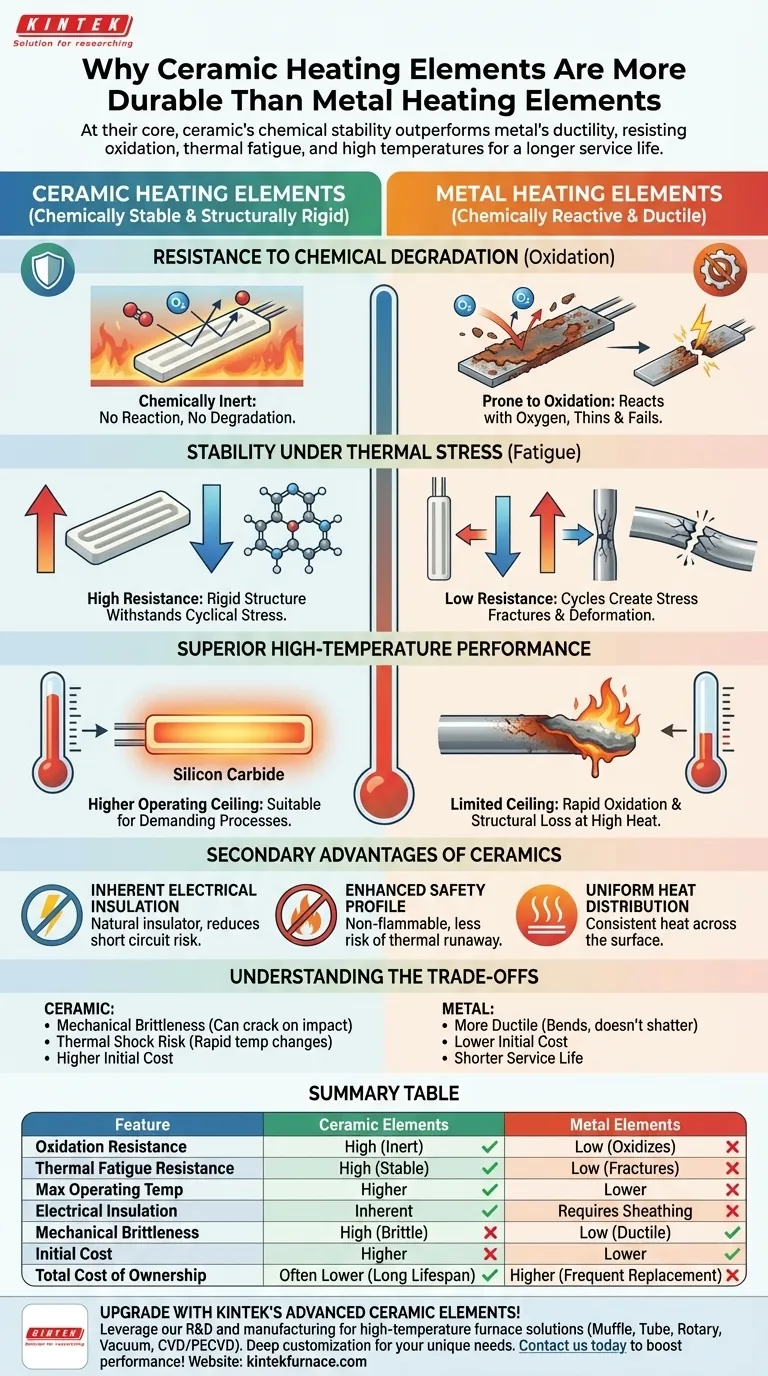
At their core, ceramic heating elements are more durable than metal ones because of their fundamental material properties. Unlike metals, which chemically degrade through oxidation and physically weaken from repeated expansion and contraction, advanced ceramic materials are inherently resistant to high temperatures, corrosion, and thermal fatigue. This chemical inertness and structural stability directly translate to a longer and more reliable service life.
The choice between ceramic and metal is a choice between chemical stability and mechanical ductility. Metal heaters fail primarily due to oxidation (a chemical reaction) and thermal fatigue, while ceramic heaters are engineered to be chemically inert and structurally stable in harsh, high-temperature environments.

The Fundamental Differences in Material Science
To understand the durability gap, we must look at how each material behaves under the stress of heat and oxygen. The failure points for metal are often the default strengths of ceramic.
Resistance to Chemical Degradation (Oxidation)
Metal heating elements, especially when hot, react with oxygen in the air. This process, known as oxidation, is similar to rusting.
Over time, this chemical reaction degrades the metal, thinning it and increasing its electrical resistance until it eventually burns out and fails.
Ceramic materials, by contrast, are often already oxides or are synthetically produced to be chemically inert. They do not react with the air, even at extreme temperatures, and therefore do not suffer from this primary mode of failure.
Stability Under Thermal Stress
Heating elements undergo constant cycles of expansion and contraction as they heat up and cool down. This is known as thermal fatigue.
In metal elements, these repeated cycles create microscopic stress fractures that grow over time, leading to physical deformation, warping, and eventual breakage.
Ceramics possess a more rigid and stable molecular structure that better withstands this cyclical stress. Materials like silicon carbide show very little deformation over their lifespan, ensuring consistent performance.
Superior High-Temperature Performance
Most standard metal heating elements have a clear operational ceiling. Beyond a certain temperature, they will oxidize rapidly, lose their structural integrity, or even melt.
Specialized ceramic elements, such as those made from silicon carbide, can operate at significantly higher temperatures than their metal counterparts, making them suitable for demanding industrial processes.
Beyond Durability: The Secondary Advantages of Ceramics
The material properties that make ceramics durable also provide critical benefits in safety and efficiency.
Inherent Electrical Insulation
Ceramic materials are natural electrical insulators. The element itself does not conduct electricity to its surface, which significantly reduces the risk of short circuits or electrical shock.
Metal elements are conductive and must be carefully sheathed in a separate insulating material, which can itself become a point of failure over time.
Enhanced Safety Profile
The combination of electrical insulation and a non-flammable nature makes ceramic heaters inherently safer. They are far less likely to cause electrical hazards or fires from incidents like thermal runaway.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Ceramic heaters are known for providing very even and consistent heat across their entire surface. This is a direct result of their solid, uniform composition and efficient thermal conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ceramic offers superior durability in many contexts, no technology is without its trade-offs. Objectivity requires acknowledging where metal elements can have an advantage.
Mechanical Brittleness
Ceramics are extremely hard, but they can also be brittle. A sharp physical impact or shock can cause a ceramic element to crack or shatter, while a metal element would be more likely to bend or dent.
Thermal Shock
Some ceramic formulations can be susceptible to thermal shock—cracking if subjected to an extremely rapid change in temperature. Modern advanced ceramics have largely mitigated this, but it can be a factor in certain designs.
Initial Cost
High-performance ceramic heating elements can have a higher upfront cost than simple metal wire elements. However, their longer service life and reduced need for replacement often result in a lower total cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use ceramic or metal should be driven by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity and high-temperature operation: The chemical stability and heat resistance of ceramic is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is operational safety in sensitive equipment: The inherent electrical insulation of ceramic heaters offers a clear advantage over sheathed metal.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost for a less demanding application: A traditional metal element may be sufficient, accepting the trade-off of a shorter service life.
Ultimately, understanding the material science of your heating element allows you to match its properties directly to your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ceramic Heating Elements | Metal Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Resistance | High (chemically inert) | Low (prone to oxidation) |
| Thermal Fatigue Resistance | High (stable structure) | Low (micro-fractures form) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Higher (e.g., silicon carbide) | Lower |
| Electrical Insulation | Inherent | Requires sheathing |
| Mechanical Brittleness | High (can crack on impact) | Low (more ductile) |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Often lower (longer lifespan) | Higher (frequent replacements) |
Upgrade your lab's heating solutions with KINTEK's advanced ceramic elements! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and boost your performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















