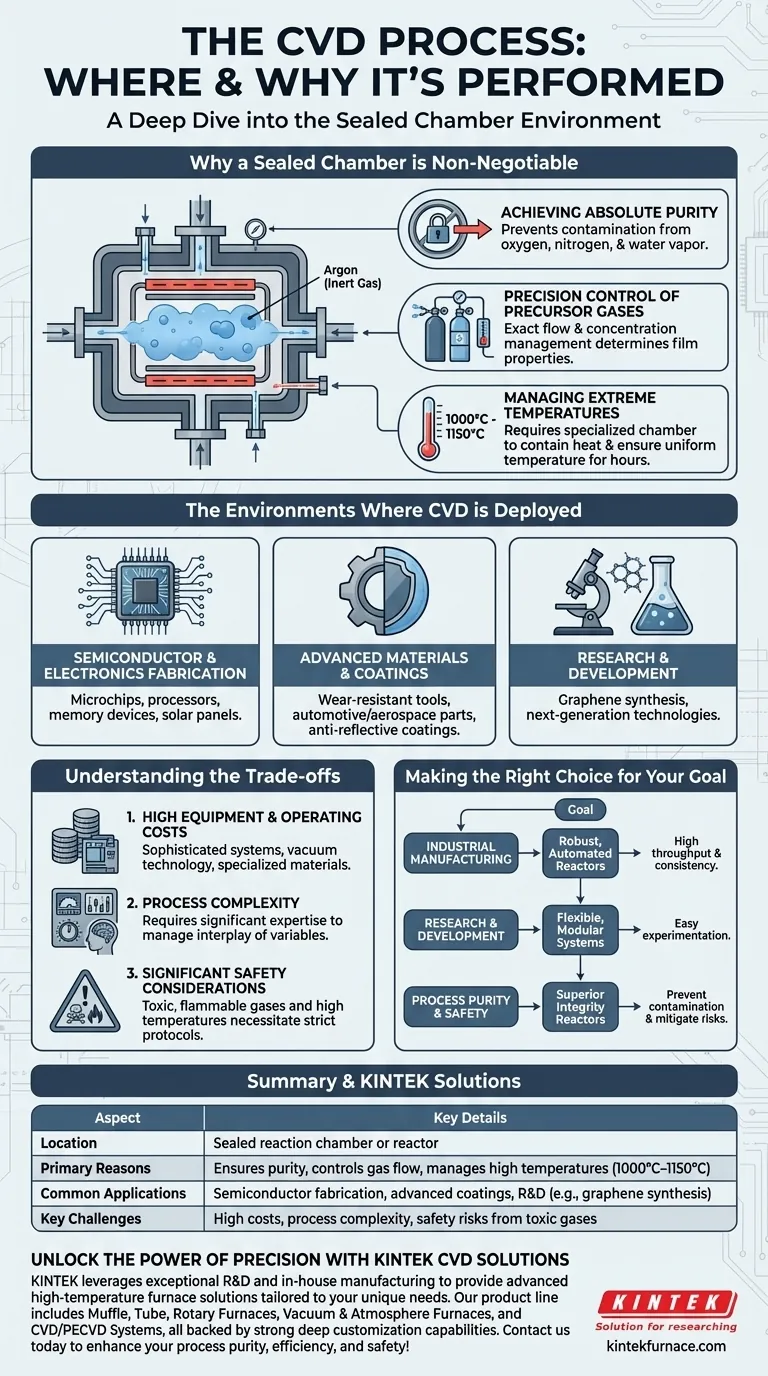
In short, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is performed within a highly controlled reaction chamber or reactor. This sealed environment is not merely a container; it is a precisely engineered system designed to manage extreme conditions and prevent any external contamination. The success of depositing a pure, high-quality thin film is entirely dependent on the integrity of this specialized chamber.
The use of a sealed chamber for CVD is fundamental to the process. It is the only way to achieve the absolute purity, extreme temperatures, and precise gas compositions required to build functional materials one atomic layer at a time.

Why a Sealed Chamber is Non-Negotiable
The core function of a CVD reactor is to create an ideal, artificial environment where specific chemical reactions can occur predictably. The atmosphere we live in is hostile to these delicate processes.
Achieving Absolute Purity
The CVD process is exceptionally sensitive. Exposure to atmospheric air, which contains oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, would introduce contaminants that cause unwanted chemical reactions.
This contamination compromises the structural and electronic properties of the final film. To prevent this, the chamber is first purged of air and then filled with a neutral or inert gas, such as Argon, which serves as a carrier for the reactants but does not interfere with the deposition chemistry.
Precision Control of Precursor Gases
The film itself is built from specific chemical precursors, which are introduced into the chamber as gases. These gases contain the essential elements of the desired material.
The chamber allows for the exact control of the flow rates and concentrations of these reactant gases. This control is what determines the film's final composition, thickness, and material properties.
Managing Extreme Temperatures
Many CVD processes operate at incredibly high temperatures, often between 1000°C and 1150°C.
A specialized reaction chamber is required to safely contain this heat, provide uniform temperature across the substrate, and maintain thermal stability throughout the deposition, which can last for hours.
The Environments Where CVD is Deployed
Because of its ability to create high-performance materials, CVD is a cornerstone technology across numerous high-tech fields. You will find these specialized chambers in three primary settings.
Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
This is the most widespread use of CVD. It is essential for creating the thin insulating and conductive layers that make up microchips, processors, and memory devices. The process is also critical for manufacturing solar panels.
Advanced Materials and Coatings
CVD is used to apply ultra-hard, corrosion-resistant, or functional coatings. This includes creating wear-resistant surfaces on cutting tools, protective layers on high-performance automotive and aerospace parts, and even the anti-reflective coatings on sunglasses and architectural glass.
Research and Development
Universities, national labs, and corporate R&D centers rely on CVD systems for materials science innovation. These systems are used to synthesize novel materials, such as graphene sheets, and to develop next-generation processes for future technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the reliance on a complex chamber-based process brings inherent challenges that are important to understand.
High Equipment and Operating Costs
CVD reactors are sophisticated and expensive pieces of equipment. They must be capable of holding a vacuum, handling corrosive gases, and sustaining extreme temperatures, all of which requires specialized engineering and materials.
Process Complexity
Successfully running a CVD process requires significant expertise. An operator must precisely manage a complex interplay of variables, including temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and chemistry, where small deviations can lead to failed depositions.
Significant Safety Considerations
The precursor gases used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Combined with the high operating temperatures, this necessitates strict safety protocols, gas detection systems, and proper ventilation to ensure operator safety and prevent environmental contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific type of CVD chamber and process is always dictated by the end goal. Whether you are in production, research, or process engineering, the focus changes.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: The priority is investing in robust, automated single-wafer or batch reactors that deliver high throughput and exceptional consistency.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The best choice is often a flexible, modular chamber system that allows for easy experimentation with different precursors, temperatures, and substrates.
- If your primary focus is process purity and safety: The critical factor is a reactor with superior vacuum integrity, high-purity gas lines, and comprehensive safety interlocks to prevent contamination and mitigate risks.
Ultimately, understanding the "why" behind the CVD chamber transforms it from a simple box into the very heart of modern material science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Sealed reaction chamber or reactor |
| Primary Reasons | Ensures purity, controls gas flow, manages high temperatures (1000°C–1150°C) |
| Common Applications | Semiconductor fabrication, advanced coatings, R&D (e.g., graphene synthesis) |
| Key Challenges | High costs, process complexity, safety risks from toxic gases |
Unlock the Power of Precision with KINTEK CVD Solutions
Are you in semiconductor manufacturing, advanced materials development, or research and need reliable, high-performance CVD systems? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our CVD technologies can enhance your process purity, efficiency, and safety—let's build the future of materials together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication



















