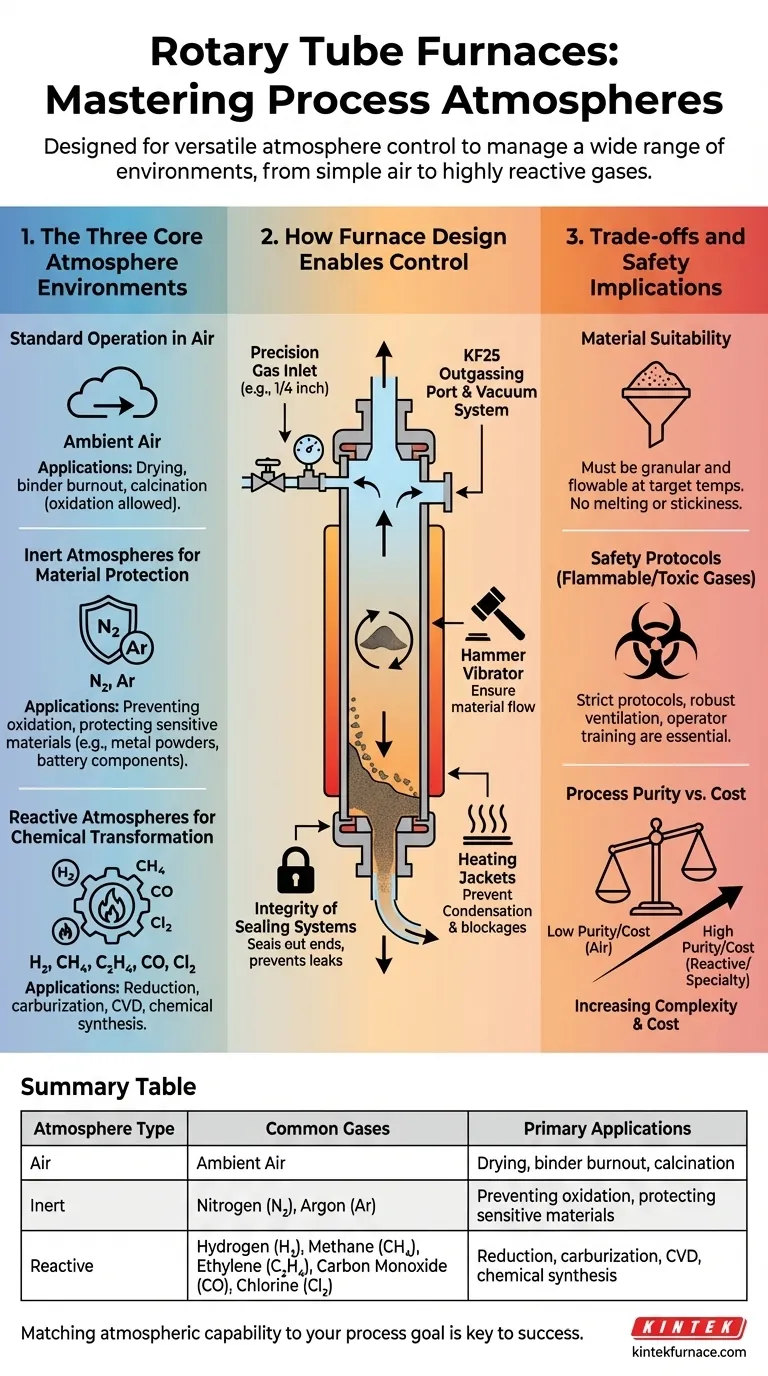
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are designed for atmosphere control, capable of handling a wide range of environments. They can operate with simple ambient air, inert gases like nitrogen and argon, and even highly reactive, flammable, or toxic gases such as hydrogen, methane, ethylene, carbon monoxide, and chlorine. The furnace's ability to safely and effectively manage these atmospheres is directly dependent on the quality of its sealing systems and gas control architecture.
The versatility of a rotary tube furnace isn't just about the heat; it's about its ability to create and maintain a specific chemical environment. Understanding your process goal—whether it's simple drying, preventing oxidation, or driving a chemical reaction—is the key to selecting the correct atmosphere.
The Three Core Atmosphere Environments
A rotary tube furnace's primary function is to provide a controlled environment for heat treatment. This environment is defined by the gas, or "atmosphere," inside the tube. These atmospheres fall into three main categories based on their purpose.
Standard Operation in Air
The most straightforward and common atmosphere is ambient air. This is suitable for processes like drying, binder burnout, or calcination where oxidation is either not a concern or is a desired part of the reaction. Operating in air is the simplest and most cost-effective method.
Inert Atmospheres for Material Protection
To prevent oxidation and other unwanted reactions, an inert atmosphere is used. Gases like nitrogen (N2) and argon (Ar) are pumped into the furnace to displace oxygen and other reactive atmospheric components. This is critical for processing sensitive materials like certain metal powders or advanced battery components where purity is paramount.
Reactive Atmospheres for Chemical Transformation
For processes that require a specific chemical change, a reactive atmosphere is necessary. These gases actively participate in the reaction with the material.
- Hydrogen (H2) is often used for reduction reactions.
- Methane (CH4) or ethylene (C2H4) can be used for carburization or certain chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes.
- Carbon monoxide (CO) or chlorine (Cl2) can be used for other highly specific chemical synthesis applications.
How Furnace Design Enables Atmosphere Control
The ability to handle these diverse and often hazardous gases is not inherent to all rotary furnaces. It depends entirely on specific engineering features designed for containment and precision.
The Critical Role of Sealing Systems
The effectiveness of any controlled atmosphere hinges on the integrity of the furnace seals. Superior seal designs are essential to prevent the process gas from leaking out and, just as importantly, to stop ambient air from leaking in. This is a non-negotiable safety requirement when using flammable or toxic gases and a process-critical feature for maintaining the purity of an inert atmosphere.
Precision Gas Handling and Control
Professional-grade furnaces include sophisticated gas handling systems. These often feature dedicated ports like a 1/4 inch inlet for inert gas and a KF25 outgassing port for efficient vacuum purging and gas exchange. These systems allow for precise control over flow rates, pressure, and the complete removal of atmospheric contaminants before the process begins.
Optional Features for Complex Processes
Specialized applications may require additional features. A hammer vibrator can be integrated to ensure high-viscosity or sticky materials continue to flow properly. For processes involving organic materials or tars, heating jackets around the exhaust lines prevent condensation and blockages, ensuring a smooth and safe gas exit path.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Implications
While incredibly versatile, selecting the right atmosphere involves balancing capability, safety, and material compatibility.
Material Suitability is Paramount
The most advanced atmosphere control system cannot fix a poor material choice. The material processed must remain granular and flowable at target temperatures. Materials that agglomerate, melt, or become sticky are not suitable for rotary tube furnaces, as they will disrupt the continuous flow and uniform heating.
Safety Protocols for Flammable and Toxic Gases
Using reactive atmospheres fundamentally changes the operational risk. Handling gases like hydrogen or chlorine requires strict, well-documented safety protocols, robust facility ventilation, and comprehensive operator training. The furnace itself must be rated for use with such materials.
Process Purity vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between the complexity of the atmosphere and the cost of operation. Running a process in air is inexpensive. Purging with high-purity nitrogen or argon adds cost and complexity. Utilizing highly pure, reactive specialty gases is the most demanding and expensive operational mode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of atmosphere must be driven by the intended outcome of your heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is drying or simple calcination: Operating in ambient air is often sufficient and the most cost-effective approach.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and ensuring material purity: Using an inert atmosphere like nitrogen or argon is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is inducing a specific chemical reaction: A reactive gas atmosphere is necessary, but this requires a furnace with advanced sealing, gas handling, and appropriate safety engineering.
Ultimately, you are choosing a tool to achieve a specific material transformation, and matching the furnace's atmospheric capability to that goal is the foundation of a successful process.

Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Common Gases | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Air | Ambient Air | Drying, binder burnout, calcination |
| Inert | Nitrogen (N2), Argon (Ar) | Preventing oxidation, protecting sensitive materials |
| Reactive | Hydrogen (H2), Methane (CH4), Ethylene (C2H4), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Chlorine (Cl2) | Reduction, carburization, CVD, chemical synthesis |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable rotary tube furnaces, muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need precise atmosphere control for inert or reactive gases. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















