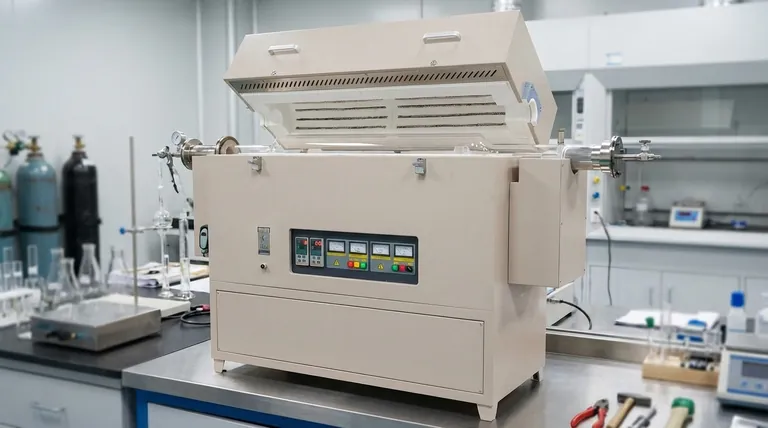
In multi-gradient experimental tube furnaces, the most common high-temperature heating elements are Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2). These materials are chosen for their ability to generate intense, stable heat when an electric current is applied, which is essential for creating precise and varied temperature zones along the length of the furnace tube.
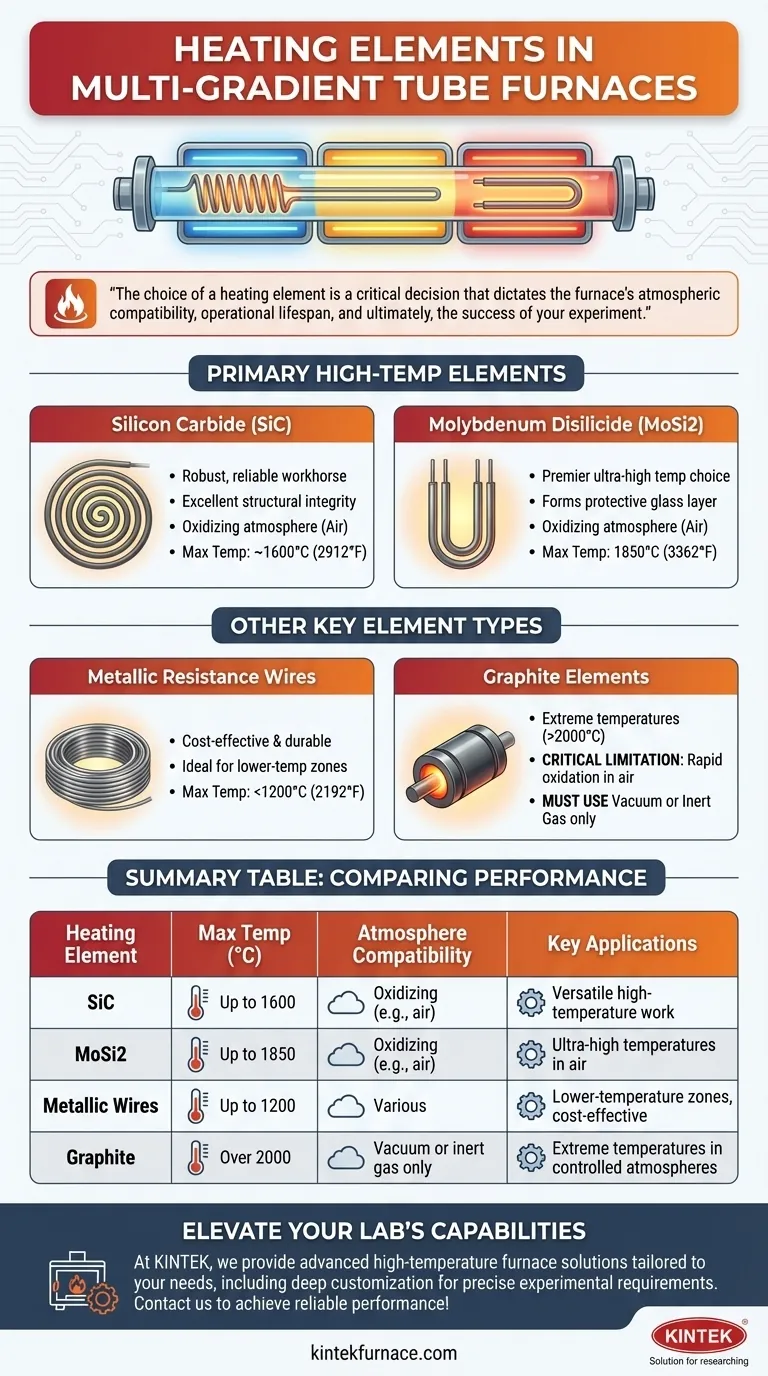
The choice of a heating element is not merely about reaching a target temperature; it is a critical decision that dictates the furnace's atmospheric compatibility, operational lifespan, and ultimately, the success of your experiment.

A Closer Look at the Primary Heating Elements
To understand why specific elements are used, we must look at their individual properties. The two most prevalent materials, SiC and MoSi2, serve the majority of high-temperature applications.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are robust, reliable workhorses for a wide range of thermal processes. They are often formed into rods or spiral grooves.
These elements are known for their excellent structural integrity at high temperatures. They are less prone to deformation and can be used in oxidizing atmospheres (i.e., in air) up to approximately 1600°C (2912°F).
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the premier choice for reaching very high to ultra-high temperatures. They are typically U-shaped and made from a cermet material.
When heated, MoSi2 elements form a protective layer of quartz-glass on their surface, which prevents further oxidation. This allows them to operate reliably in air at temperatures up to 1850°C (3362°F), significantly higher than most other elements.
Expanding the Options: Other Key Element Types
While SiC and MoSi2 dominate high-temperature work, other elements are used for specific temperature ranges and atmospheric conditions.
Metallic Resistance Wires
For lower temperature applications, typically below 1200°C (2192°F), metallic resistance wires (such as Kanthal, an FeCrAl alloy) are extremely common.
These wires are cost-effective and durable, making them ideal for the lower-temperature zones of a multi-gradient furnace or for experiments that do not require extreme heat.
Graphite Elements
Graphite can reach extremely high temperatures, well over 2000°C (3632°F). However, it has a critical limitation.
It will rapidly oxidize and burn away in the presence of oxygen. Therefore, graphite heating elements can only be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere, which adds complexity and cost to the furnace system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing performance, operating conditions, and cost. Each choice comes with clear advantages and disadvantages.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the most straightforward factor. MoSi2 offers the highest temperature ceiling, followed by SiC, and then metallic resistance wires. Graphite can go the highest but comes with major atmospheric restrictions.
Atmospheric Compatibility
This is a critical, non-negotiable parameter. If your process must run in air, graphite is not an option. SiC and MoSi2 are excellent for use in oxidizing atmospheres due to their material properties.
Element Lifespan and Brittleness
All heating elements degrade over time, a process known as "aging." This can slightly alter their resistance and heat output. MoSi2 elements, while high-performing, are also quite brittle at room temperature and must be handled with care during installation and maintenance.
Cost and Replacement
Generally, higher-temperature capability correlates with higher cost. MoSi2 elements are typically more expensive than SiC elements, which are in turn more expensive than metallic resistance wires. This cost must be factored into the furnace's total operational budget.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your experimental goal directly informs the ideal heating element configuration for your multi-gradient furnace.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures (above 1600°C) in an air atmosphere: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the definitive choice for its unmatched performance and stability.
- If your primary focus is versatile high-temperature work (up to 1600°C) in air: Silicon Carbide (SiC) provides a robust, reliable, and slightly more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is lower temperature processes or zones (below 1200°C): Metallic resistance wires offer excellent performance and are the most economical option.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (above 2000°C) in a controlled atmosphere: Graphite elements are a high-performance option, provided the experiment is conducted in a vacuum or inert gas.
Understanding these core components empowers you to select not just a furnace, but the precise instrument your research demands.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Temp (°C) | Atmosphere Compatibility | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600 | Oxidizing (e.g., air) | Versatile high-temperature work |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1850 | Oxidizing (e.g., air) | Ultra-high temperatures in air |
| Metallic Resistance Wires | Up to 1200 | Various | Lower-temperature zones, cost-effective |
| Graphite | Over 2000 | Vacuum or inert gas only | Extreme temperatures in controlled atmospheres |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with the perfect heating element? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve precise temperature control and reliable performance in your multi-gradient experiments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing



















