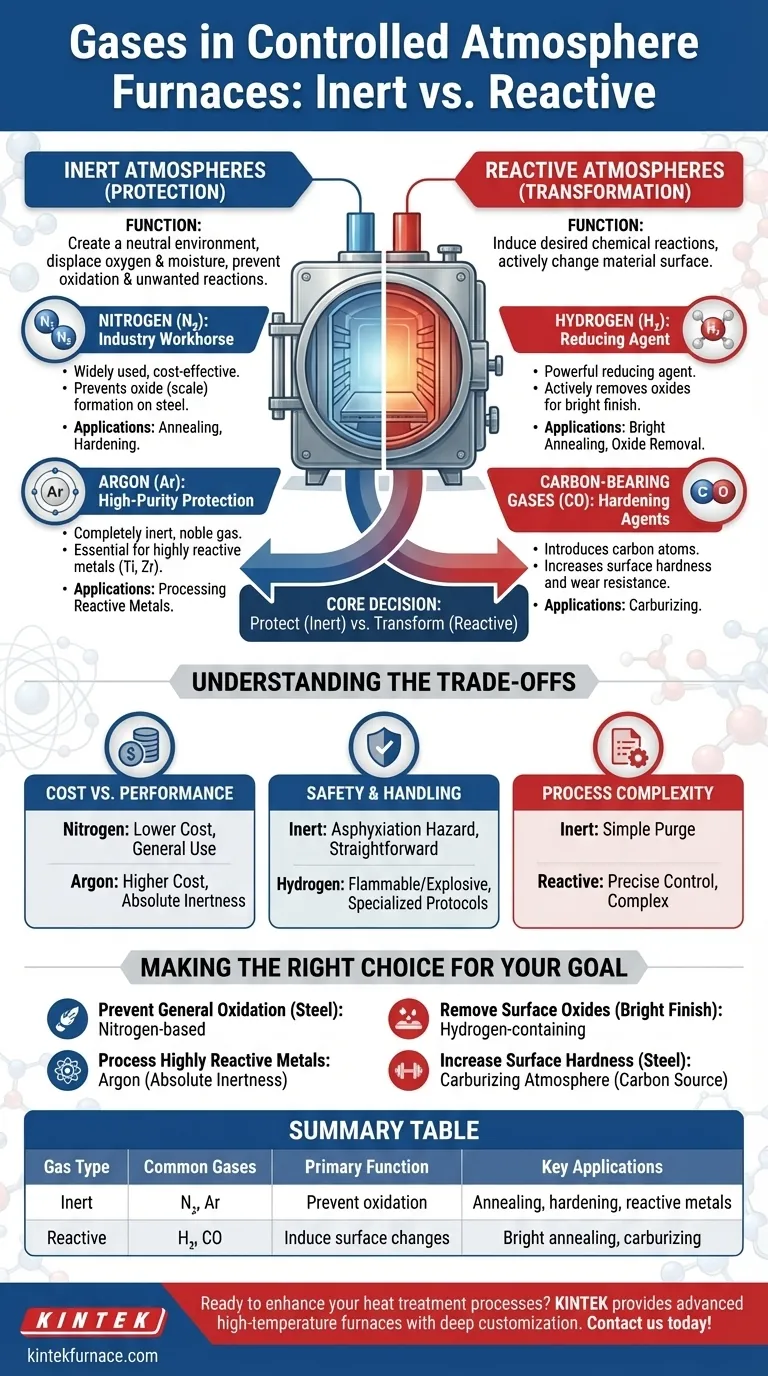
In a controlled atmosphere furnace, the specific gas used is a critical process variable, chosen to either protect the material or actively change it. The most common gases fall into two distinct categories: inert gases like nitrogen and argon which prevent unwanted reactions, and reactive gases such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide which are used to intentionally cause chemical changes on the material's surface.
The core decision in selecting a furnace gas is not about the gas itself, but its purpose. You must first determine if your goal is simply to protect the material from the environment (an inert atmosphere) or to transform its surface chemistry (a reactive atmosphere).

The Role of Inert Atmospheres (Protection)
Inert atmospheres create a neutral, non-reactive environment. Their primary job is to displace oxygen and moisture, preventing oxidation, discoloration, and other unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Nitrogen (N2): The Industry Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most widely used atmosphere gas due to its excellent balance of cost and performance. It is technically inert for most common heat treatment applications, especially for ferrous metals.
By purging the furnace chamber of air, a nitrogen atmosphere effectively prevents the formation of oxides (scale) on the surface of steel parts during processes like annealing or hardening.
Argon (Ar): High-Purity Protection
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is completely inert and will not react with any material at any temperature. This makes it essential for processing highly reactive metals.
Metals like titanium, zirconium, and certain stainless steels would react even with nitrogen at high temperatures. For these sensitive applications, the superior (though more expensive) inertness of argon is non-negotiable.
The Role of Reactive Atmospheres (Transformation)
Reactive atmospheres are chosen specifically to induce a desired chemical reaction with the surface of the material being treated. This goes beyond mere protection and becomes a part of the metallurgical process itself.
Hydrogen (H2): The Reducing Agent
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent. Its primary function is not just to prevent oxidation, but to actively remove existing oxides from a material's surface by reacting with them to form water vapor (H₂O).
This process, known as bright annealing or bright hardening, results in a clean, bright, and oxide-free surface finish. It is often used in mixtures with nitrogen to control cost and reactivity.
Carbon-Bearing Gases: The Hardening Agents
Gases like carbon monoxide (CO), often produced from an endothermic gas generator, are used for surface hardening processes like carburizing.
In this process, the gas introduces carbon atoms into the surface of a low-carbon steel part. This creates a hard, wear-resistant outer case while leaving the core of the part tough and ductile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere involves balancing performance, cost, and safety. There is no single "best" gas, only the most appropriate one for a specific goal.
Cost vs. Performance
Nitrogen is significantly less expensive than argon. For general-purpose protection of common metals, nitrogen is the default economic choice. Argon is reserved for applications where its absolute inertness is a strict technical requirement.
Safety and Handling
Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are safe and straightforward to handle, though they are asphyxiation hazards in confined spaces. Hydrogen, however, is highly flammable and can be explosive, requiring specialized safety protocols, leak detection systems, and furnace designs.
Process Complexity
Creating a simple inert atmosphere is relatively easy, often requiring just a purge to displace oxygen. Reactive processes like carburizing are far more complex, demanding precise control over gas composition, temperature, and time to achieve the desired surface carbon concentration and case depth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material and desired outcome are the only factors that should guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is preventing general oxidation on steels: A nitrogen-based atmosphere is the most cost-effective and practical solution.
- If you are processing highly reactive metals like titanium or require absolute inertness: Argon is the only appropriate choice to guarantee no reaction occurs.
- If your goal is to remove existing surface oxides for a bright, clean finish: A reducing atmosphere containing a percentage of hydrogen is required.
- If you need to increase the surface hardness of steel parts: A carburizing atmosphere containing a source of carbon is the correct metallurgical approach.
Understanding the function of each gas transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Gases | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen, Argon | Prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions | Annealing, hardening of steels, processing reactive metals |
| Reactive | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide | Induce surface changes like oxide removal or carburizing | Bright annealing, carburizing for surface hardening |
Ready to enhance your heat treatment processes with tailored furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for inert protection or reactive transformations. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















