In short, a protective atmosphere box furnace is used in any high-temperature process where the material must be shielded from oxygen or other reactive gases in the air. Its primary application environments include the heat treatment of metals like steel and copper, advanced materials research, and specialized manufacturing of ceramics and glass.
The term "environment" for this furnace refers less to its physical location and more to the controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere it creates inside its chamber. This core function is what enables high-purity processing of materials that would otherwise be ruined by oxidation at high temperatures.
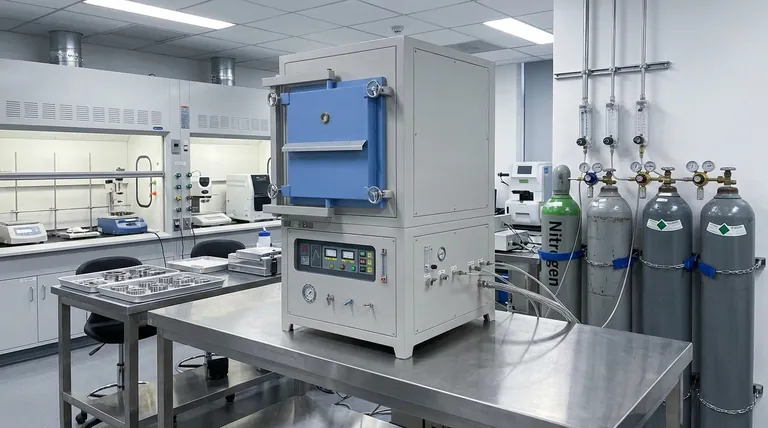

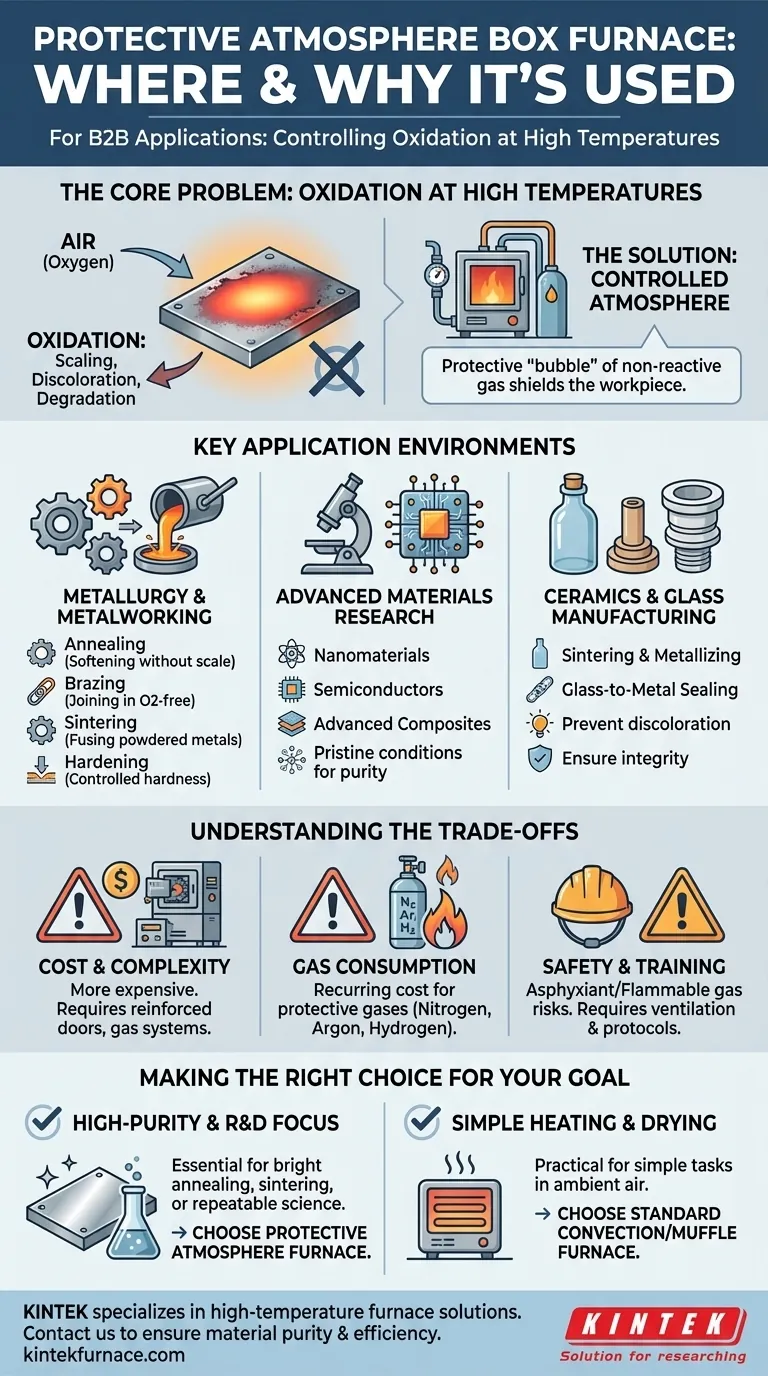
The Core Problem: Oxidation at High Temperatures
To understand where this furnace is used, you must first understand the problem it solves. Heat is a catalyst for chemical reactions, and the most common reaction is with the oxygen present in the air.
Why Air is the Enemy
When heating most materials, especially metals, the oxygen in the ambient air aggressively attacks the material's surface. This process, known as oxidation, can cause scaling, discoloration, and a degradation of the material's structural or electrical properties.
For many advanced applications, this damage is unacceptable.
The Solution: A Controlled Atmosphere
A protective atmosphere furnace solves this problem by creating a sealed environment. Before and during the heating cycle, the air inside the chamber is purged and replaced with a specific, non-reactive or beneficially reactive gas.
This protective "bubble" shields the workpiece from unwanted chemical changes.
Key Application Environments
The need to prevent oxidation dictates the environments where these furnaces are essential. They are tools for precision and purity, not general-purpose heating.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
This is the most common application. The furnace is used for processes where surface finish and material integrity are critical.
- Annealing: Softening metals like steel, copper, and aluminum alloys to improve ductility without creating surface scale.
- Brazing: Joining metals using a filler material in an oxygen-free environment to ensure a clean, strong bond.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered metals together at high temperatures to form a solid part, a process where oxygen would inhibit proper bonding.
- Hardening: Heat-treating steel parts under a controlled atmosphere to achieve desired hardness without decarburization (carbon loss at the surface).
Advanced Materials Research
In laboratories, purity is paramount. Researchers developing new materials rely on atmosphere furnaces to conduct experiments under pristine conditions.
This includes work on nanomaterials, semiconductors, and advanced composites, where even minor contamination from atmospheric gases can invalidate results or ruin the delicate material.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
Certain ceramic processes, such as sintering or metallizing, require specific atmospheric conditions. A protective atmosphere can prevent discoloration and ensure the final product meets its design specifications.
In glass-to-metal sealing, an inert atmosphere prevents the metal components from oxidizing, which would compromise the seal's integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these furnaces are not the default choice for all heating tasks. Their specialized nature comes with specific considerations.
Cost and Complexity
The systems required to create and maintain a sealed, controlled atmosphere—including reinforced doors, gas-tight seals, and gas delivery plumbing—make these furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than standard air furnaces.
Gas Consumption
Operating the furnace requires a continuous or intermittent supply of protective gas, such as nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen. The cost of these gases, particularly high-purity argon or flammable hydrogen, is a recurring operational expense.
Safety and Training
Using compressed gases introduces safety risks. Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are asphyxiants, while reducing gases like hydrogen are highly flammable. Proper facility ventilation, safety protocols, and operator training are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating equipment depends entirely on the required outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metal treatment: A protective atmosphere furnace is essential for processes like bright annealing, brazing, or sintering where an oxide-free surface is required.
- If your primary focus is R&D for sensitive materials: This furnace is a non-negotiable tool for creating the repeatable, contamination-free conditions needed for scientific discovery.
- If your primary focus is simple heating, drying, or tempering: A less expensive and simpler convection or muffle furnace that operates in ambient air is the more practical and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, choosing this furnace is a decision to control the chemistry of your process, not just its temperature.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy and Metalworking | Annealing, brazing, sintering, hardening |
| Advanced Materials Research | Nanomaterials, semiconductors, composites |
| Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing | Sintering, metallizing, glass-to-metal sealing |
Need precise, oxidation-free heating for your lab or manufacturing? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. Ensure material purity and efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios



















