At their core, both tube and box furnaces most commonly rely on two primary types of heating elements for high-temperature applications: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). For lower-temperature operations, typically below 1200°C, furnaces often use more conventional metallic wire-wound elements. The specific choice is dictated by the required operating temperature and the atmospheric conditions inside the furnace.
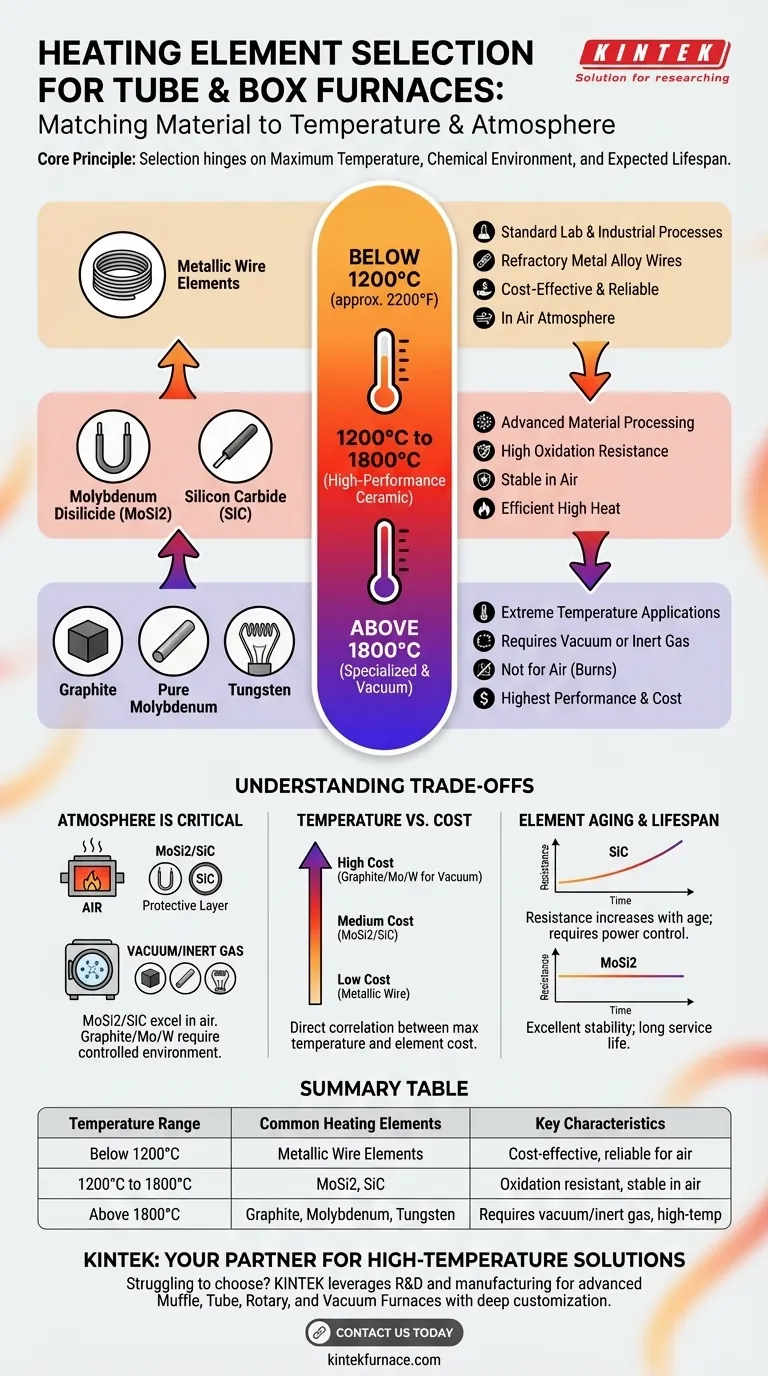
The selection of a furnace heating element is not a matter of preference but a direct consequence of physics. The decision hinges on three factors: the maximum required temperature, the chemical environment (air, inert gas, or vacuum), and the expected lifespan of the element.

The Core Principle: Matching Material to Temperature
The fundamental challenge in furnace design is finding a material that can both generate immense heat and survive the extreme environment it creates. Different materials excel at different temperature ranges.
Below 1200°C: Metallic Wire Elements
For many standard laboratory and industrial processes, operating temperatures do not exceed 1200°C (approx. 2200°F).
In these furnaces, refractory metal alloy wires are the most common and cost-effective choice. These elements are typically wound and embedded directly into the furnace's insulation, which maximizes thermal uniformity and usable chamber space.
1200°C to 1800°C: High-Performance Ceramic Elements
This is the range where most advanced material processing, sintering, and annealing takes place. Metallic elements cannot reliably survive these temperatures in an air atmosphere.
The dominant materials here are Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). These are robust ceramic elements that are highly resistant to oxidation and can produce very high temperatures efficiently.
Above 1800°C: Specialized and Vacuum Elements
For extreme-temperature applications or those requiring a controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere, a different class of elements is necessary.
Materials like Graphite, pure Molybdenum, and Tungsten can reach temperatures of 2200°C and beyond. However, they will rapidly burn up in the presence of oxygen and must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing performance, cost, and operational constraints. No single element is perfect for every application.
Atmosphere is Critical
This is the most important trade-off. MoSi2 and SiC are prized for their ability to operate in air because they form a protective glassy layer of silicon oxide on their surface.
In contrast, elements like Graphite and Tungsten offer higher temperature limits but are completely intolerant of oxygen at high heat. Their use mandates a more complex and expensive vacuum or inert gas system.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between the maximum operating temperature of an element and its cost.
Metallic wire elements are the most economical. SiC and MoSi2 represent a significant step up in both performance and price. Graphite, Molybdenum, and Tungsten systems for vacuum or inert atmospheres are typically the most expensive.
Element Aging and Lifespan
Heating elements degrade over time. SiC elements, for example, experience an increase in electrical resistance as they age, which may require a more sophisticated power controller to maintain consistent output.
MoSi2 elements are known for their excellent stability and long service life, showing very little change in resistance over time. This reliability is a key reason for their widespread adoption in demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of furnace, and thus its heating elements, should be guided entirely by your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general lab work in air up to 1200°C: A furnace with metallic wire-wound elements provides the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in air (1200°C - 1800°C): Look for furnaces with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements for their high performance and durability.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature work or requires a controlled atmosphere: You must use a furnace specifically designed with Graphite, Molybdenum, or Tungsten elements within a vacuum or inert gas chamber.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between your target temperature and operating atmosphere will guide you to the correct heating element technology.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Heating Elements | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Below 1200°C | Metallic Wire Elements | Cost-effective, reliable for air atmospheres |
| 1200°C to 1800°C | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Resistant to oxidation, stable performance in air |
| Above 1800°C | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten | Requires vacuum or inert gas, high-temperature capable |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your lab furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















