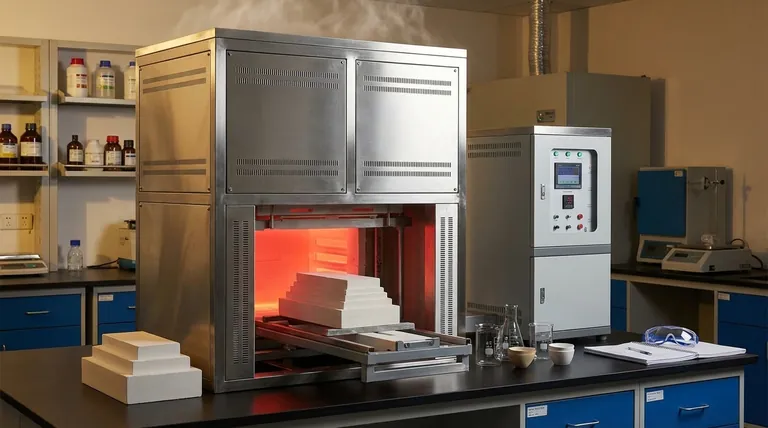
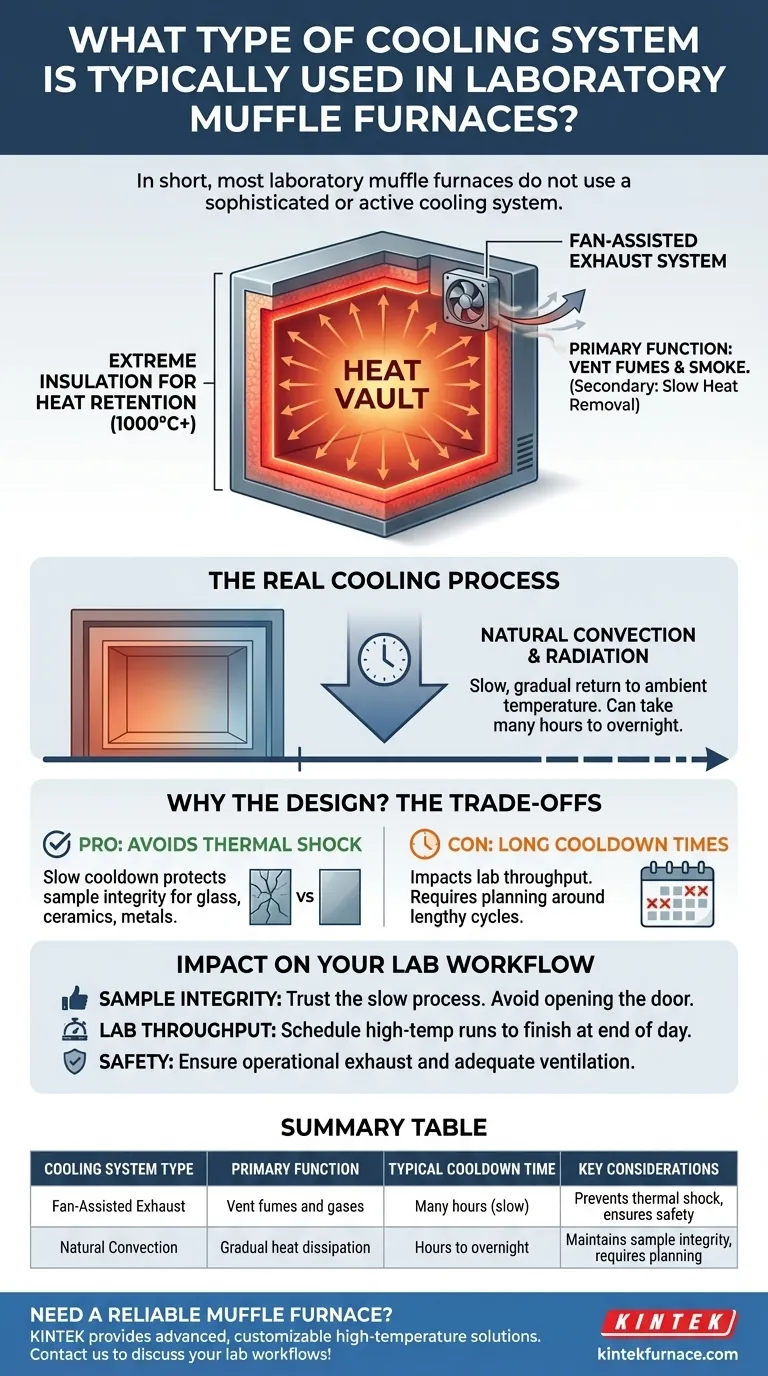
In short, most laboratory muffle furnaces do not use a sophisticated or active cooling system. The vast majority rely on simple fan-assisted exhaust to vent fumes and allow the heavily insulated chamber to cool down naturally over a long period.
The core design principle of a muffle furnace is to achieve and maintain extreme, stable temperatures. Its "cooling" system is therefore not for rapid temperature reduction but is primarily an exhaust system for fumes, facilitating a slow, gradual return to ambient temperature.

Why Muffle Furnaces Are Designed for Heat Retention, Not Cooling
The function of a muffle furnace is to heat materials to very high temperatures (often over 1000°C) and hold them there with high stability. This goal directly influences every aspect of its design, especially cooling.
The Priority is Insulation
A muffle furnace is built like a vault for heat. It uses thick refractory ceramic insulation to prevent heat from escaping.
This design is essential for reaching extreme temperatures efficiently and keeping them stable for processes like annealing, ashing, or creating ceramic coatings. Actively cooling the chamber would work directly against this primary purpose.
The "Cooling" System is an Exhaust System
The fan you see on a muffle furnace is not there to cool the chamber quickly. Its primary job is to vent fumes, smoke, and other gaseous byproducts generated during the heating process.
This exhaust function is critical for safety and for preventing contamination of the sample or the furnace interior. While it does help move hot air out of the chamber once the heating elements are turned off, this effect is secondary to venting.
Natural Convection Does Most of the Work
Once a heating cycle is complete, the furnace cools down almost entirely through natural convection and radiation.
Heat slowly dissipates from the furnace body into the surrounding air. Because of the extreme insulation, this is a very slow process that can take many hours.
Understanding the Trade-offs of This Design
The simple, passive approach to cooling has significant implications for how these furnaces are used in a laboratory setting.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
For many applications like creating glass, ceramics, or treating metals, rapid cooling is highly undesirable.
Cooling a material too quickly from an extreme temperature can cause thermal shock, leading to cracks and structural failure. The furnace's naturally slow cooldown rate is often a procedural benefit, protecting the integrity of the sample.
The Downside: Long Cooldown Times
The most significant operational drawback is the time it takes for the furnace to cool. You cannot simply finish one run and immediately start another that requires a low starting temperature.
Workflows must be planned around these lengthy cooldown cycles, which can impact laboratory throughput.
Special Cases: Chimneys and Vents
In some specific cases, a muffle furnace may be connected to a dedicated chimney or flue.
This is not for enhanced cooling but for safely managing large volumes of hazardous or corrosive fumes that cannot be simply vented into the room by a small fan.
How This Impacts Your Laboratory Workflow
Choosing and using a muffle furnace requires understanding that its design favors heat retention above all else.
- If your primary focus is sample integrity: Trust the furnace's slow, natural cooldown process. Avoid opening the door to try and speed it up, as this can introduce thermal shock and ruin your materials.
- If your primary focus is laboratory throughput: You must schedule your work to account for long cooldown periods. High-temperature runs should be planned to finish at the end of the day to cool overnight.
- If your primary focus is safety: Always ensure the exhaust fan is operational and that the furnace has adequate ventilation to remove all process fumes from the laboratory environment.
Understanding that a muffle furnace is engineered for stable heat, not rapid cooling, is the key to operating it safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Cooling System Type | Primary Function | Typical Cooldown Time | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fan-Assisted Exhaust | Vent fumes and gases | Many hours (slow) | Prevents thermal shock, ensures safety |
| Natural Convection | Gradual heat dissipation | Hours to overnight | Maintains sample integrity, requires planning |
Need a reliable muffle furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















