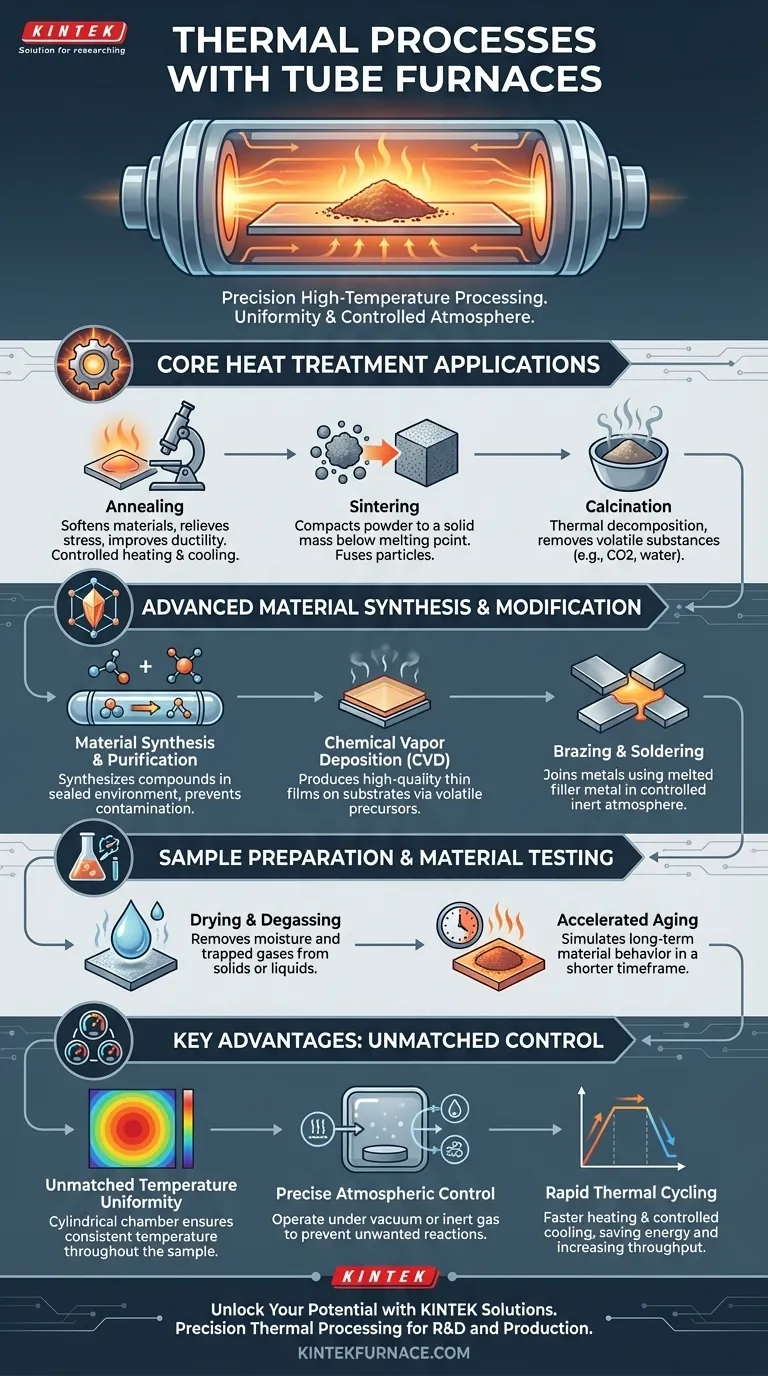
In essence, tube furnaces are designed to perform a wide array of high-temperature thermal processes where precision is paramount. They excel at tasks ranging from fundamental heat treatments like annealing and sintering to advanced applications such as material synthesis, purification, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
The core value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to create a highly uniform and tightly controlled thermal environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for processing sensitive materials where temperature consistency and atmospheric purity directly determine the final outcome.

Core Heat Treatment Applications
Heat treatment involves using controlled heating and cooling to alter the physical and chemical properties of a material. Tube furnaces provide the necessary precision for these sensitive operations.
Annealing
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and holding it there before a controlled cooling. This process softens materials, relieves internal stresses, and improves their ductility and toughness.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder through heat. The furnace heats the material below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together into a solid piece.
Calcination
This is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition. It is often used to remove volatile substances, such as carbon dioxide or water, from a compound.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Modification
Beyond altering existing materials, tube furnaces are crucial for creating new materials and applying functional layers. Their ability to manage the process atmosphere is key here.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are widely used in research and production to synthesize inorganic and organic compounds. The sealed tube environment prevents contamination and allows for precise control over the chemical reactions.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, a substrate is exposed to volatile precursors, which react or decompose on the substrate's surface to produce a high-quality thin film. The uniform temperature profile of a tube furnace is critical for creating consistent coatings.
Brazing and Soldering
These processes join two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint. A tube furnace can provide a controlled, inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation during the joining process.
Sample Preparation and Material Testing
Tube furnaces also serve as a vital tool for preparing samples for analysis or simulating environmental effects over time.
Drying and Degassing
Drying is the process of removing moisture from a material. Similarly, degassing removes trapped or dissolved gases from a liquid or solid, which is often a critical preparation step in vacuum and materials science applications.
Accelerated Aging
To understand how a material will behave over years of use, tube furnaces can perform accelerated aging. They subject materials to controlled high temperatures to simulate the effects of long-term aging in a much shorter timeframe.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The reason tube furnaces are chosen for these specific processes comes down to a few core technical advantages that differentiate them from other furnace types.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber naturally promotes an even distribution of thermal energy. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for consistent results in processes like annealing and CVD.
Precise Atmospheric Control
The tube can be easily sealed, allowing for processing under a vacuum or in a specific inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, which is vital for high-purity synthesis and metal treatments.
Rapid Thermal Cycling
Many modern tube furnaces offer rapid heating and cooling rates. Faster ramp-up times save energy and increase throughput, while controlled cooling can reduce thermal shock and stress in the material, improving final product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, align it with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is improving material properties: Use annealing to increase ductility and reduce hardness or stress relieving to remove internal stresses from manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or coatings: Use sintering to form solid parts from powders, or use Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to apply highly uniform thin films.
- If your primary focus is preparing or testing a sample: Use drying or degassing to remove contaminants and moisture, or use accelerated aging to simulate long-term performance.
Ultimately, a tube furnace empowers you to precisely manipulate materials at a fundamental level through controlled heat and atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Sintering, Calcination | Improves material properties, relieves stress |
| Material Synthesis | CVD, Purification, Brazing | Creates thin films, prevents contamination |
| Sample Preparation | Drying, Degassing, Accelerated Aging | Removes moisture, simulates aging effects |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our precise thermal processing equipment can enhance your material synthesis and heat treatment outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















