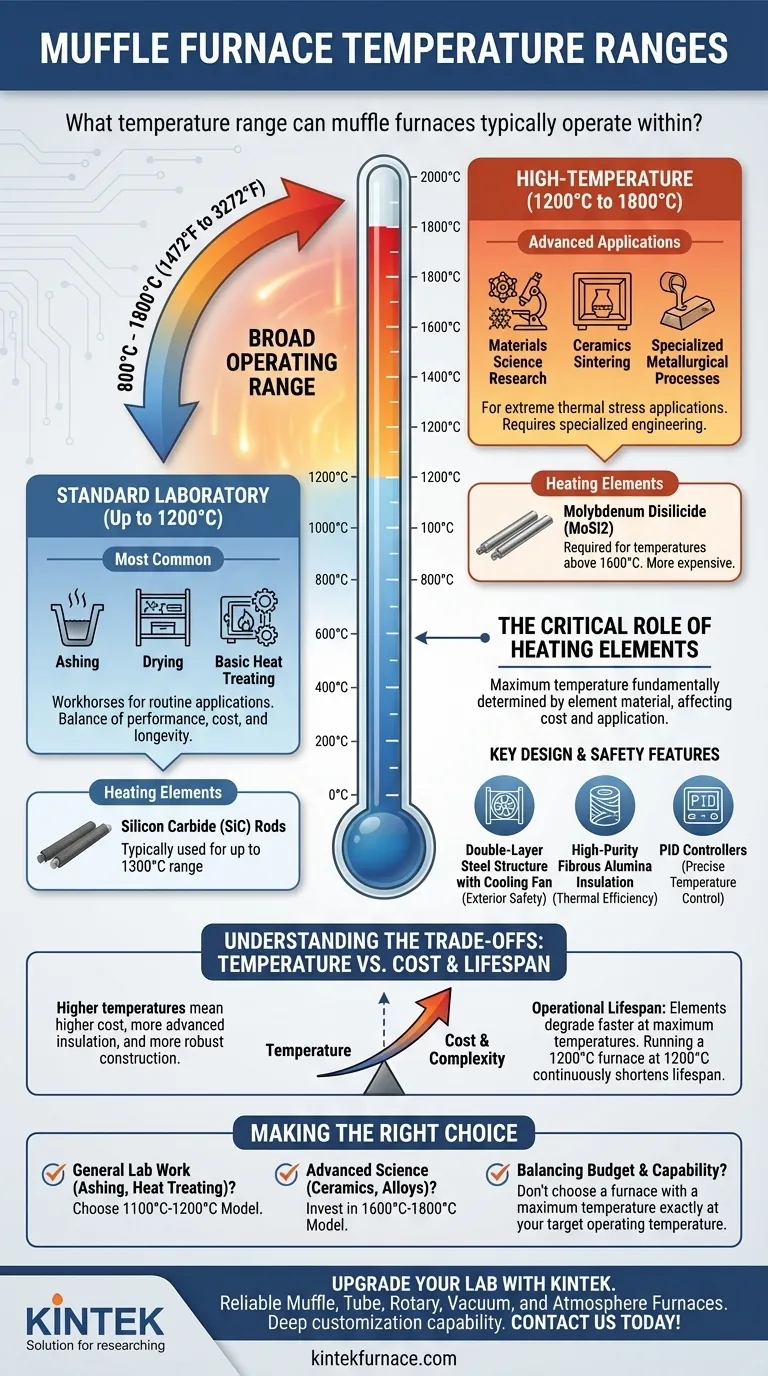
At a glance, muffle furnaces typically operate within a broad temperature range of 800°C to 1800°C (1472°F to 3272°F). However, this wide spectrum is segmented, with the most common laboratory models operating up to 1200°C, while specialized high-temperature units are required for applications demanding up to 1800°C.
The term "muffle furnace" describes a category of high-temperature ovens, not a single device with one temperature range. The maximum achievable temperature is fundamentally determined by the furnace's construction—specifically, the material used for its heating elements—which dictates its cost and intended application.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range
The vast temperature range of muffle furnaces exists because different scientific and industrial processes require vastly different thermal conditions. The furnace's design, from its heating elements to its insulation, is tailored to meet a specific temperature target.
Standard Laboratory Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
The most common muffle furnaces found in general-purpose labs are designed for a maximum temperature between 1000°C and 1200°C.
These "box-type" furnaces are workhorses for routine applications like ashing, drying, heat-treating metals, and materials testing that do not require extreme heat. They offer a balance of performance, cost, and longevity.
High-Temperature Furnaces (1200°C to 1800°C)
For more advanced applications, high-temperature models are necessary. These units are capable of reaching temperatures between 1500°C and 1800°C.
You will find these furnaces in materials science research, ceramics sintering, and specialized metallurgical processes where materials must be tested or created under extreme thermal stress.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The single most important factor determining a furnace's maximum temperature is the material of its heating elements.
- Standard Elements (Up to 1300°C): Furnaces operating up to the 1100°C to 1300°C range typically use robust elements like silicon carbide (SiC) rods.
- High-Temperature Elements (Above 1600°C): To achieve temperatures of 1600°C or higher, furnaces must use more exotic and expensive elements, most commonly molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
Key Design and Safety Features
Achieving and maintaining these temperatures safely requires specific engineering. Modern furnaces include a double-layer steel structure with a cooling fan to keep the exterior safe to touch.
They also rely on high-purity fibrous alumina insulation for thermal efficiency and PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers for precise, programmable temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature vs. Cost
Choosing a muffle furnace involves more than just finding one that gets hot enough. Higher temperatures introduce significant trade-offs in cost, complexity, and operational demands.
The High Cost of Extreme Heat
There is a direct and steep correlation between maximum temperature and price. A furnace rated for 1700°C is substantially more expensive than a 1200°C model.
This price increase is driven by the need for costly MoSi2 heating elements, more advanced insulation, and a more robust overall construction to handle the thermal stress.
Operational Lifespan and Maintenance
Heating elements are consumable components; they degrade over time and eventually fail. This process is accelerated dramatically when operating a furnace at or near its maximum rated temperature.
Running a 1200°C furnace at 1200°C continuously will shorten its element lifespan far more than running it at 1000°C. High-temperature models require careful management to preserve the life of their expensive components.
Specialization Adds Complexity
Some processes require not only high heat but also a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an inert gas. These specialized furnaces (e.g., tube or vacuum furnaces) add another layer of complexity and cost to the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, you must first define your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or basic heat treating: An 1100°C to 1200°C furnace is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials science, sintering technical ceramics, or high-temperature alloy testing: You must invest in a high-temperature model capable of reaching at least 1600°C to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is balancing budget and capability: Never purchase a furnace with a maximum temperature that is exactly your target operating temperature; this will lead to premature failure.
Matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific process ensures you acquire the right tool for the job without overspending on unnecessary capacity.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Ashing, drying, basic heat treating | Silicon carbide (SiC) |
| 1200°C to 1800°C | Materials science, ceramics sintering | Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres



















