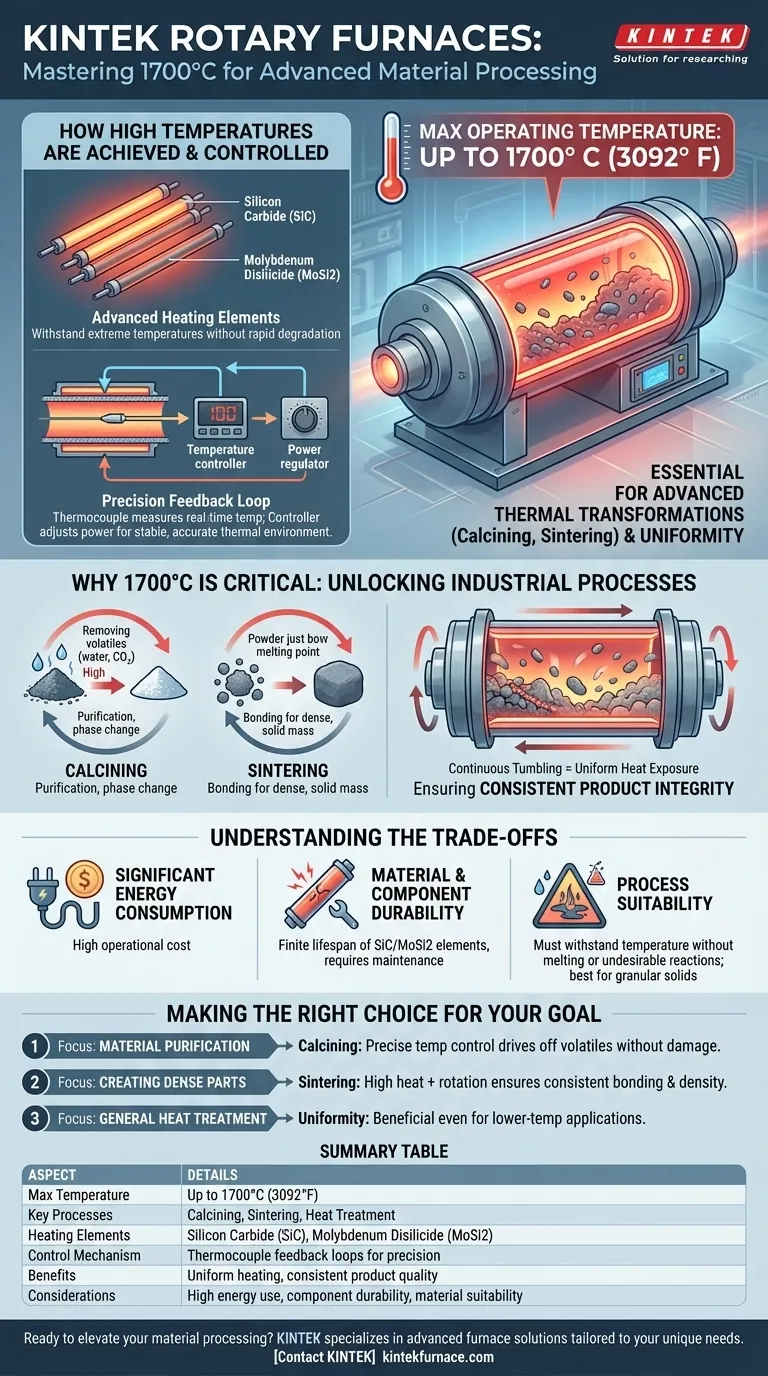
At their peak, resistance-heated rotary furnaces can maintain operating temperatures up to 1700° Celsius (3092° F). This high-temperature capability is essential for advanced material processing, as it provides the intense and uniform thermal energy required for specific chemical and physical transformations, such as calcining and sintering.
The value of a rotary furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to apply that heat with exceptional uniformity and precision. This combination enables the creation of high-quality, consistent materials that are impossible to achieve with less sophisticated methods.

How High Temperatures Are Achieved and Controlled
Sustaining extreme temperatures requires a system of specialized components working in concert. The furnace's design is focused on generating, maintaining, and precisely controlling heat.
The Role of Advanced Heating Elements
The ability to reach 1700°C is primarily due to the use of advanced electric heating elements. Materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are chosen because they can withstand and operate effectively at these extreme temperatures without rapid degradation.
Precision Through Feedback Loops
Heat generation alone is not enough; precision is critical. A thermocouple inside the furnace measures the real-time temperature and converts it into an electrical signal. This signal is sent to a temperature controller, which compares it to the desired setpoint and automatically adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain a stable and accurate thermal environment.
Why 1700°C Is a Critical Threshold for Materials
The ability to operate at such high temperatures unlocks specific industrial processes that are fundamental to manufacturing advanced materials. This capability directly impacts the final product's quality and properties.
Enabling Thermal Transformation Processes
Many advanced materials require intense heat to achieve their desired state.
- Calcining: This process uses high heat to remove volatile substances, such as water or carbon dioxide, from materials to purify them or induce a phase change.
- Sintering: This involves heating powdered materials to just below their melting point, causing the particles to bond and form a solid, dense mass.
Ensuring Uniform Product Quality
The rotary motion of the furnace is just as important as the temperature. As the furnace tube rotates, it continuously tumbles the material inside. This ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source, preventing hot spots and guaranteeing consistent processing throughout the entire batch for superior product integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, high-temperature rotary furnaces come with inherent operational considerations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for effective implementation.
Significant Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures up to 1700°C is an energy-intensive process. The power required to run the heating elements constitutes a major operational cost that must be factored into any process plan.
Material and Component Durability
Operating at extreme heat places immense stress on all furnace components, from the furnace tube itself to the heating elements. Elements like SiC and MoSi2 have a finite lifespan and will require periodic replacement, representing a key maintenance consideration.
Process Suitability
Not all materials are suitable for high-temperature rotary processing. The material must be able to withstand the target temperature without melting or undergoing undesirable chemical reactions. The process is best suited for granular or powdered solids that can tumble freely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on your desired outcome. Use the furnace's capabilities to match your specific material objective.
- If your primary focus is material purification (calcining): The furnace's precise temperature control is critical for driving off specific volatiles without damaging the base material.
- If your primary focus is creating dense parts from powder (sintering): The combination of high heat and uniform exposure from rotation ensures consistent bonding and density throughout the final product.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment: The furnace provides an exceptionally uniform environment, which is beneficial even for lower-temperature applications where consistency is paramount.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between temperature, uniformity, and your material's properties empowers you to leverage this technology for superior results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) |
| Key Processes | Calcining, sintering, heat treatment |
| Heating Elements | Silicon carbide (SiC), molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) |
| Control Mechanism | Thermocouple feedback loops for precision |
| Benefits | Uniform heating, consistent product quality, precise temperature control |
| Considerations | High energy use, component durability, material suitability |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on calcining, sintering, or other thermal processes, our furnaces deliver uniform heat and consistent results for superior product integrity. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and achieve your material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















