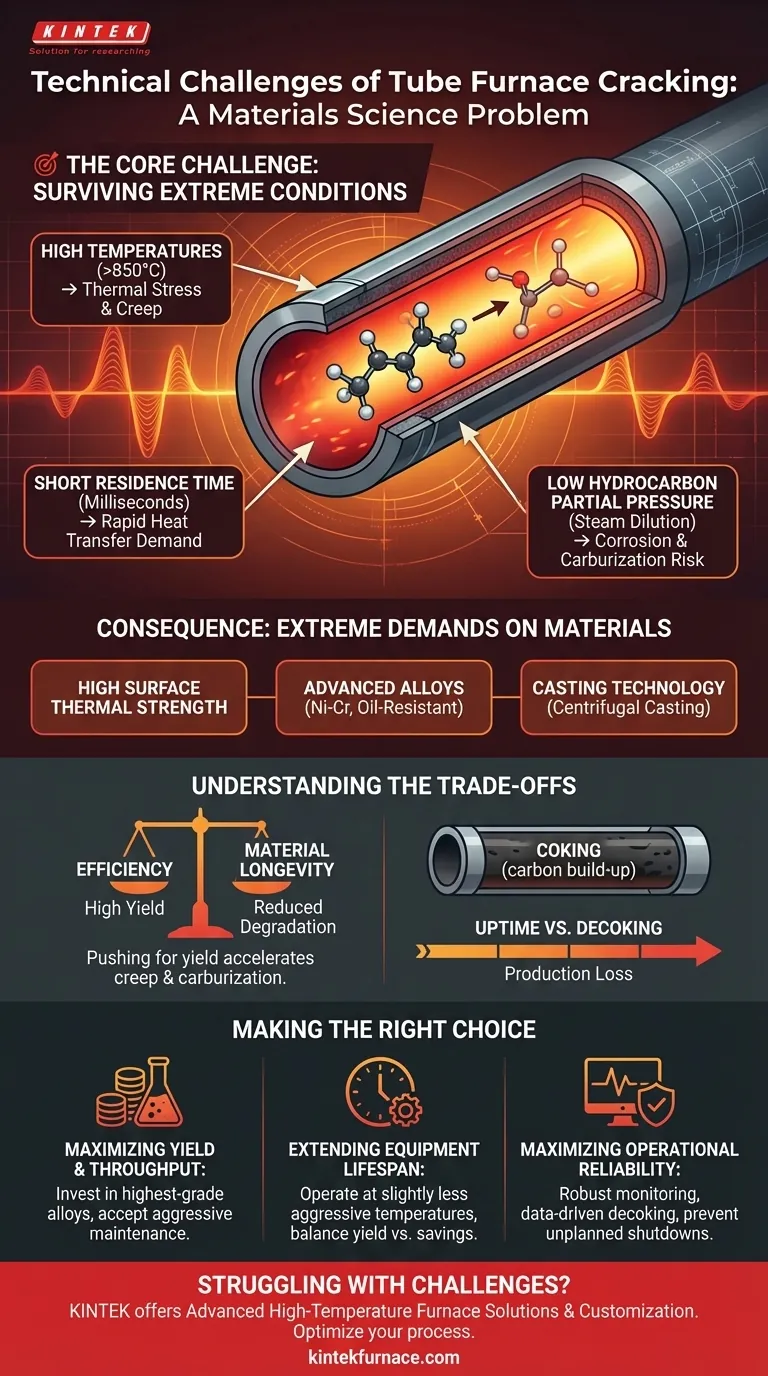
At its core, the primary technical challenge of tube furnace cracking is a materials science problem. The process demands operating conditions so extreme—specifically high temperatures, short residence times, and low hydrocarbon partial pressure—that they push the physical limits of the furnace tubes, requiring specialized, high-performance materials and manufacturing techniques to prevent catastrophic failure.
The relentless pursuit of higher yields and efficiency in cracking forces engineers to operate furnaces at their absolute material and thermal limits. The central challenge, therefore, is not just running the process, but managing the inevitable degradation of the very equipment that makes it possible.

The Core Challenge: Surviving Extreme Process Conditions
To understand the technical difficulties, we must first appreciate the harsh environment inside a cracking furnace. The entire design is a balancing act, pushing conditions to maximize the production of valuable products like ethylene and propylene while trying to mitigate the destructive side effects.
The Demand for High Temperatures
Cracking hydrocarbons into smaller, more valuable molecules is an endothermic reaction that requires immense energy input. Process temperatures inside the tubes can exceed 850°C (1560°F), placing enormous thermal stress on the tube material.
The Need for Short Residence Time
To maximize the yield of desired products and prevent them from degrading into less valuable ones (like methane and coke), the feedstock must pass through the furnace's hottest zone very quickly, often in milliseconds. This necessitates an incredibly high rate of heat transfer from the tube wall to the process fluid.
The Role of Low Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure
Yield is further improved by diluting the hydrocarbon feedstock with steam. This lowers the partial pressure of the hydrocarbons, favoring the chemical reactions that produce ethylene. However, this environment, particularly at high temperatures, can also accelerate certain forms of material corrosion.
Consequence 1: Extreme Demands on Furnace Tube Materials
These process conditions converge to create a single, critical requirement: the furnace tubes must exhibit exceptional strength and stability in a hostile environment.
High Surface Thermal Strength
The combination of high temperatures and the need for rapid heat transfer creates a demand for what is known as high surface thermal strength. The material must not only withstand the heat but also efficiently conduct it without losing its structural integrity, warping, or creeping over time.
The Requirement for Advanced Alloys
Standard steels fail instantly under these conditions. The solution lies in using high-temperature alloy pipes, typically nickel-chromium alloys. These materials are specifically designed to be "oil-resistant," meaning they can resist carburization (the absorption of carbon, which makes them brittle) and oxidation in the process environment.
The Importance of Casting Technology
The material itself is only half the solution. Advanced cast pipe technology, most notably centrifugal casting, is required to manufacture the tubes. This method produces a dense, uniform grain structure, which is critical for providing consistent strength and resistance to creep damage at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While cracking technology is mature and highly efficient, its operation is governed by a series of difficult engineering trade-offs.
Efficiency vs. Material Longevity
The core conflict is between process optimization and equipment life. Pushing for higher yields by increasing furnace temperature directly accelerates material degradation mechanisms like creep and carburization, shortening the expensive tube's lifespan.
The Inevitability of Coking
Even under optimal conditions, a persistent challenge is coking—the formation of hard carbon deposits on the inner tube wall. This coke layer acts as an insulator, reducing heat transfer and forcing operators to increase the external furnace temperature to compensate, which in turn damages the tubes faster.
Uptime vs. Decoking
The build-up of coke eventually chokes the tube and necessitates a shutdown for a "decoking" cycle, where the carbon is burned off with steam and air. This represents a significant loss of production, pitting the advantage of continuous operation against the reality of required maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating these challenges requires a clear understanding of your primary operational objective. Your strategy for materials selection, operating parameters, and maintenance will shift based on your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield and throughput: You must invest in the highest-grade alloys and potentially advanced anti-coking coatings, accepting higher capital costs and a more aggressive maintenance schedule.
- If your primary focus is extending equipment lifespan and managing cost: You will need to operate at slightly less aggressive temperatures, balancing a potential minor reduction in yield against significant long-term savings in tube replacement and maintenance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational reliability: Your priority should be robust monitoring systems for tube skin temperature and process pressure, combined with a predictable and data-driven decoking schedule to prevent unplanned shutdowns.
Ultimately, successfully operating a cracking furnace is a masterclass in managing the delicate balance between process chemistry and materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Details |
|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Exceed 850°C, causing thermal stress and material creep |
| Short Residence Time | Milliseconds in hot zone, demanding rapid heat transfer |
| Low Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure | Dilution with steam accelerates corrosion and carburization |
| Coking | Carbon deposits insulate tubes, reduce efficiency, require decoking |
| Material Degradation | Requires nickel-chromium alloys and centrifugal casting for durability |
Struggling with tube furnace cracking challenges? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet the unique experimental requirements of diverse laboratories, ensuring enhanced efficiency, reliability, and longevity. Contact us today to optimize your process and overcome extreme operational demands!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















