Safely concluding your muffle furnace experiment is a critical process that extends beyond simply turning off the power. The correct procedure involves disengaging the heating element, allowing the furnace to cool down gradually to prevent damage, and then safely removing your sample once temperatures are manageable. Abruptly opening the furnace door can cause catastrophic failure of the refractory materials due to thermal shock.
The most critical principle of muffle furnace shutdown is gradual, controlled cooling. Abrupt temperature changes risk irreparable damage to the furnace lining and create significant safety hazards. Your post-experiment procedure must prioritize both equipment longevity and personal safety.
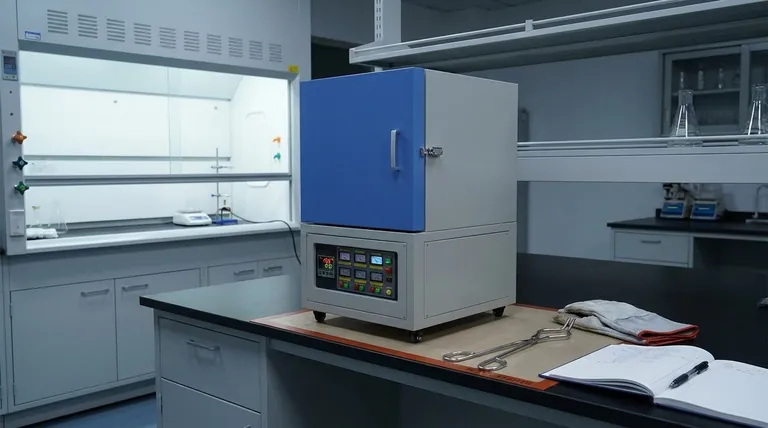

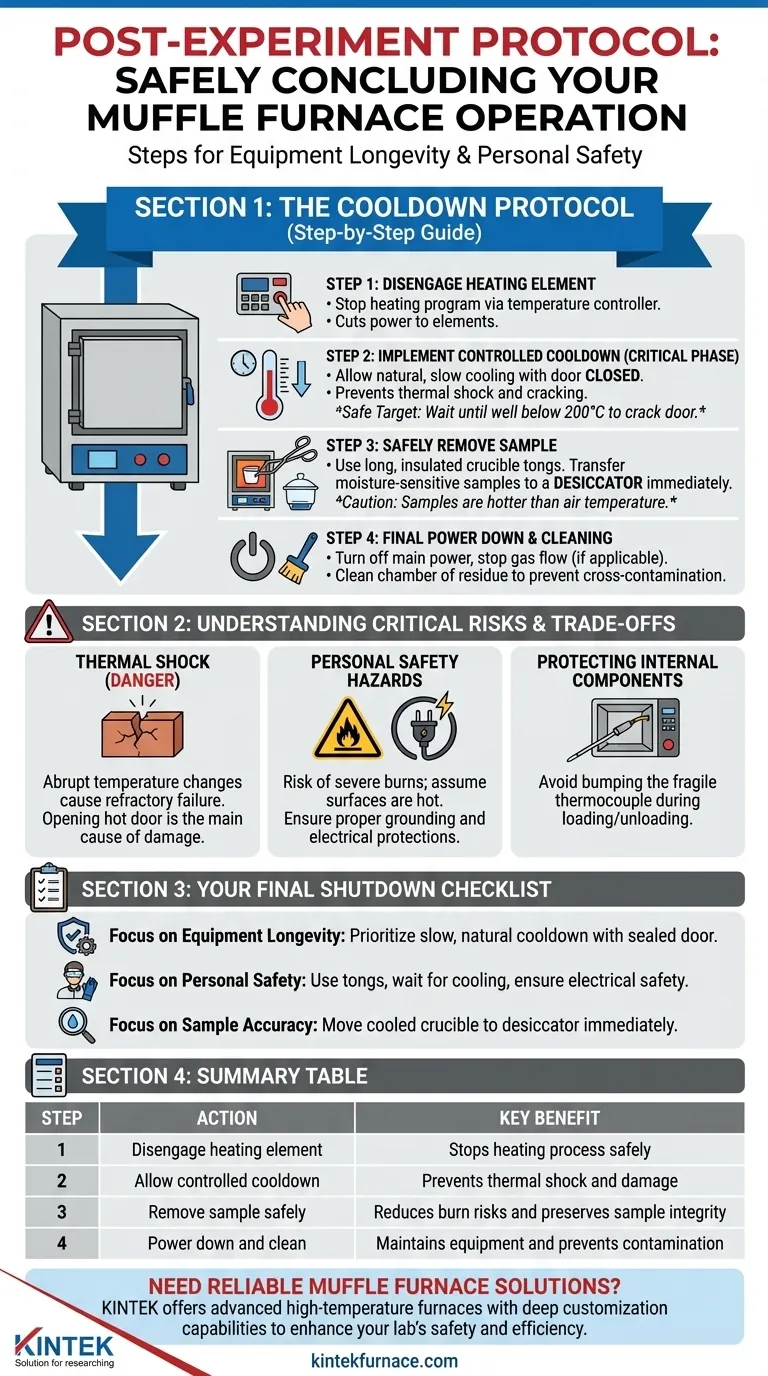
The Cooldown Protocol: A Step-by-Step Guide
Following a structured shutdown sequence is not just about safety; it is essential for maintaining the integrity of your equipment and the accuracy of your results.
Step 1: Disengage the Heating Element
The first step is to stop the heating process. On most modern furnaces, this is done through the temperature controller.
Press the "stop" or "off" button for the heating program. This cuts power to the heating elements but often leaves the main power on to run cooling fans or the control display.
Step 2: Implement a Controlled Cooldown
This is the most crucial phase. The goal is to allow the internal chamber to cool naturally and slowly.
Do not open the furnace door immediately after the heating cycle is complete. The extreme temperature difference between the hot interior and the ambient air will cause the ceramic insulation and furnace chamber to crack.
Allow the furnace temperature to drop naturally with the door fully closed. For faster cooling after the initial, most intense heat has dissipated, you can crack the door open a very small amount. A safe target is to wait until the internal temperature is well below 200°C before doing this.
Step 3: Safely Remove Your Sample
Only remove your sample when the temperature is low enough to do so safely.
Use long, insulated crucible tongs to handle any items inside the furnace. Even when the air temperature reads 100°C, the sample and crucible itself can be significantly hotter.
For materials sensitive to moisture, immediately transfer the hot crucible to a desiccator. This allows the sample to cool in a dry environment, preventing it from absorbing atmospheric water, which is critical for accurate gravimetric analysis.
Step 4: Final Power Down and Cleaning
Once the furnace is near room temperature and the sample has been removed, you can complete the shutdown.
Turn off the main power switch for the furnace. For experiments using a controlled atmosphere, you can now safely turn off the gas cylinder and stop the gas flow.
Finally, clean the furnace chamber of any residue or debris. This prevents cross-contamination between experiments and allows you to inspect the chamber for any signs of wear or damage.
Understanding the Critical Risks & Trade-offs
A muffle furnace is a powerful tool, and its operation involves inherent risks that must be managed through proper procedure.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
The primary risk to the equipment is thermal shock. The refractory ceramics that line a furnace are designed to withstand extreme heat, but they are brittle and cannot handle rapid temperature changes.
Opening a hot furnace door is the most common cause of damage, leading to cracks that compromise the furnace's efficiency and lifespan.
Personal Safety Hazards
The risk of severe burns is always present. The exterior of the furnace can remain hot for hours after the heating cycle ends. Assume all surfaces are hot until verified.
Electrical safety is also paramount. Ensure the furnace is properly grounded and connected to a dedicated circuit with an appropriate breaker or safety gate to prevent overloads. Keep a fire extinguisher rated for electrical fires nearby.
Protecting Internal Components
Care must be taken when loading and unloading the furnace to avoid damaging the thermocouple. This temperature-sensing probe extends into the chamber and is very fragile at high temperatures. Bumping it with a crucible can easily break it.
Your Final Shutdown Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure your procedure aligns with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Prioritize a slow, natural cooldown with the door sealed to prevent any risk of thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always use tongs, wait for the furnace to cool significantly before opening the door, and ensure all electrical safety measures are in place.
- If your primary focus is sample accuracy: Immediately move your cooled crucible to a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption and preserve your results.
A disciplined and consistent shutdown procedure is the hallmark of professional, safe, and repeatable scientific work.
Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Disengage heating element | Stops heating process safely |
| 2 | Allow controlled cooldown | Prevents thermal shock and damage |
| 3 | Remove sample safely | Reduces burn risks and preserves sample integrity |
| 4 | Power down and clean | Maintains equipment and prevents contamination |
Need reliable muffle furnace solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















