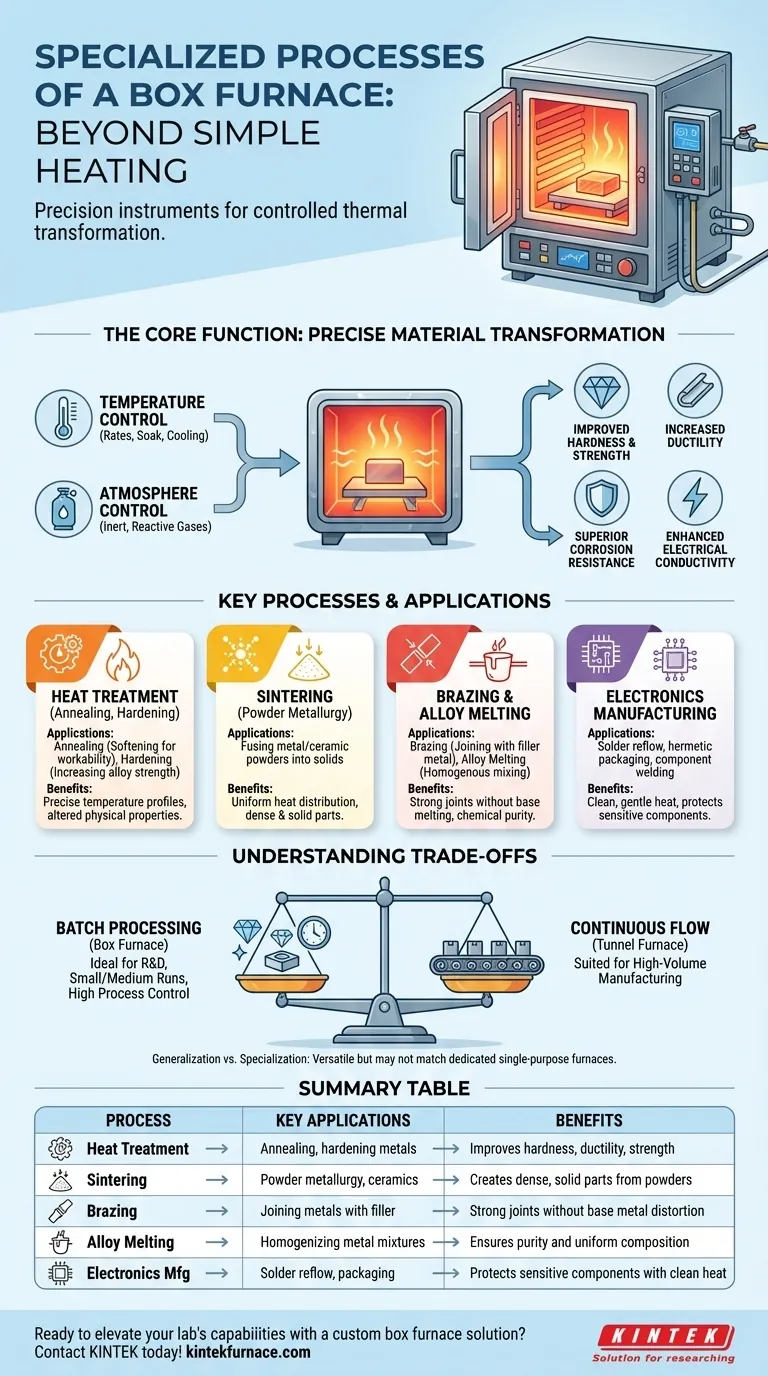
Beyond simple heating, a box furnace is a precision instrument for fundamentally altering material properties through a variety of specialized thermal processes. It excels at tasks like heat treatment, sintering, brazing, and alloy melting, where precise control over temperature and atmosphere is critical to achieving a desired outcome.
The core value of a box furnace lies not just in its ability to get hot, but in its capacity for controlled thermal transformation. By providing a highly uniform and stable environment, it enables manufacturers and researchers to predictably modify a material's internal structure to enhance its strength, conductivity, or other key characteristics.

The Core Function: Precise Material Transformation
A box furnace is chosen when the process of heating and cooling is as important as the final temperature reached. Its primary advantage is its ability to execute a programmed thermal cycle with high fidelity.
Controlling Temperature and Atmosphere
The two most critical variables in thermal processing are temperature and atmosphere. A box furnace allows for precise, programmable control over heating rates, soak times (holding at a specific temperature), and cooling rates.
Many models, known as atmosphere box furnaces, also allow for the introduction of specific gases (like nitrogen or argon) to create an inert or reactive environment, preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions.
Achieving Specific Material Properties
By manipulating these variables, engineers can produce specific, desirable changes in a material. These outcomes include improved hardness, increased ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing), enhanced strength, and superior corrosion resistance or electrical conductivity.
Key Processes and Their Applications
The precise control offered by a box furnace makes it the ideal tool for several demanding industrial and research applications.
Heat Treatment: Annealing and Hardening
Heat treatment is a broad category of processes used to alter the physical properties of a material. Annealing, for example, involves heating a metal and then cooling it slowly to reduce hardness and make it more workable.
Conversely, other heat treatments can be used to significantly increase the hardness and strength of an alloy. The box furnace ensures the material follows the exact temperature profile required for these transformations.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering is a core process in powder metallurgy. It involves heating compacted metal or ceramic powders to a temperature just below their melting point.
At this temperature, the particles bond together, creating a solid, dense object. The uniform heat distribution in a box furnace is essential for ensuring all parts of the component are sintered evenly, preventing weak spots.
Brazing and Alloy Melting
Brazing is a process for joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal that has a lower melting point. The box furnace provides controlled heat to melt the filler material and create a strong joint without melting or distorting the base components.
For alloy melting, the goal is to create a homogenous mixture of two or more metals. The stable, uniform heating of a box furnace ensures complete mixing and chemical purity.
Electronics Manufacturing
In the electronics industry, controlled heating is vital. Box furnaces are used for processes like solder reflow, hermetic packaging, and component welding. The clean, gentle, and precise heat ensures strong electrical connections without damaging sensitive microelectronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, the design of a box furnace introduces one primary trade-off that defines its ideal use case.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
A box furnace is, by its nature, a batch-processing tool. Materials are loaded, the door is closed, the thermal cycle is run, and the finished batch is then unloaded.
This makes it perfect for research and development, small-to-medium production runs, or manufacturing high-value parts where process control is more important than sheer volume. It is not suited for high-volume, continuous manufacturing lines where parts move constantly through a tunnel furnace.
Generalization vs. Specialization
While a box furnace can perform many tasks, highly specialized applications may benefit from furnaces designed for a single purpose. A box furnace offers excellent versatility, but it may not match the unique performance characteristics of a dedicated vacuum brazing furnace, for example.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a box furnace depends entirely on your intended application and production scale.
- If your primary focus is material research and development: The box furnace is an indispensable and versatile tool for testing how different thermal cycles affect material properties.
- If your primary focus is specialized, low-to-medium volume production: Its repeatability and process control make it ideal for creating high-quality components via sintering, brazing, or complex heat treatments.
- If your primary focus is delicate component assembly: Its ability to provide clean, uniform, and precisely controlled heat is perfect for electronics packaging and other sensitive manufacturing steps.
Ultimately, the box furnace is a powerful instrument for anyone who needs to do more than just heat a material, but to transform it.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening metals | Improves hardness, ductility, strength |
| Sintering | Powder metallurgy, ceramics | Creates dense, solid parts from powders |
| Brazing | Joining metals with filler | Strong joints without base metal distortion |
| Alloy Melting | Homogenizing metal mixtures | Ensures purity and uniform composition |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Solder reflow, packaging | Protects sensitive components with clean heat |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom box furnace solution?
KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs in heat treatment, sintering, brazing, and more.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior material transformations and enhance your research or production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















