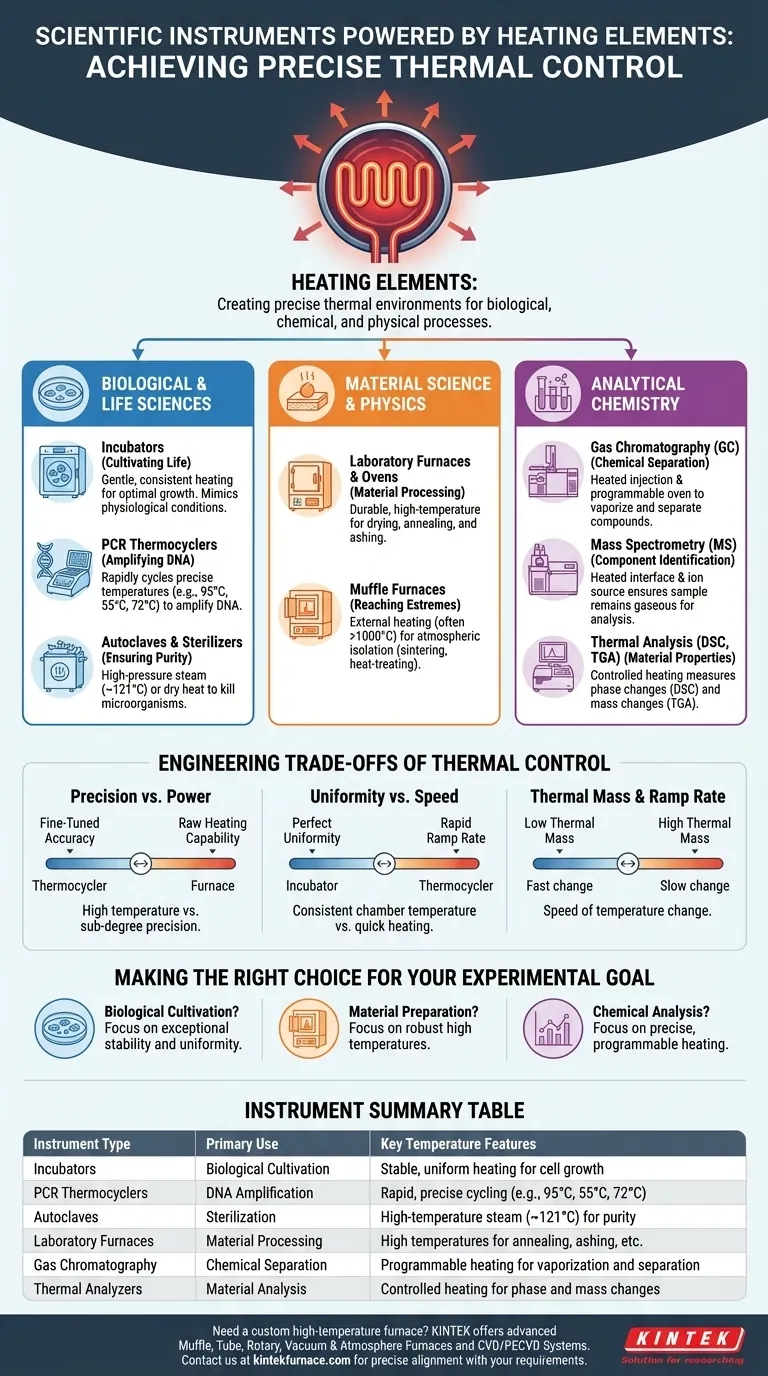
At its core, a vast array of scientific instruments rely on heating elements to function. These components are essential for creating the precise thermal environments needed for experiments, with common examples including laboratory incubators for growing cultures, high-temperature furnaces for material processing, and a wide range of analytical instruments that depend on controlled temperature for accurate measurements.
The use of a heating element in a scientific instrument is rarely about simply making something hot. It is about achieving precise, stable, and repeatable temperature control, which is a fundamental variable in countless biological, chemical, and physical processes.

The Role of Heat in Biological and Life Sciences
In biology, temperature is not just a setting; it is a critical parameter that dictates the viability and behavior of living systems. Instruments in this field use heating elements to create and maintain these specific conditions.
Incubators: Cultivating Life
Incubators use gentle, consistent heating to provide the optimal temperature for growing biological samples like cell cultures or microbial colonies. They essentially create a stable, artificial environment that mimics physiological conditions, allowing researchers to study cellular processes outside of a living organism.
PCR Thermocyclers: Amplifying DNA
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a cornerstone of molecular biology used to amplify DNA. A thermocycler contains a heating (and cooling) block that rapidly cycles through precise temperatures, typically 95°C, ~55°C, and 72°C, to denature DNA strands, anneal primers, and extend new strands.
Autoclaves and Sterilizers: Ensuring Purity
To prevent contamination, labs must sterilize equipment and media. Autoclaves use powerful heating elements to boil water, creating high-pressure steam (~121°C) that effectively kills all microorganisms. Dry heat sterilizers use heating elements without water to achieve similar results at higher temperatures.
High-Temperature Applications in Material Science
For physicists and material scientists, high temperatures are a tool for altering or analyzing the fundamental properties of a substance.
Laboratory Furnaces and Ovens
These are workhorse instruments used for a variety of tasks, from simply drying glassware to complex processes like annealing metals to increase their ductility or ashing samples to determine their inorganic content. The heating element is designed for durability and the ability to reach and hold very high temperatures.
Muffle Furnaces: Reaching Extremes
For applications requiring even higher temperatures (often >1000°C) and atmospheric isolation, muffle furnaces are used. Their internal chamber is heated externally, allowing for processes like gravimetric analysis, sintering ceramics, or heat-treating materials without direct exposure to the heating element.
Precision Heating in Analytical Chemistry
In chemical analysis, heat is often used to change the physical state of a sample or to drive separations, making it possible to identify and quantify its components.
Gas Chromatography (GC)
A GC instrument separates chemical compounds based on their boiling points and affinity for the column. It uses a heated injection port to instantly vaporize the sample and a programmable oven that ramps up the temperature of the column, causing compounds to travel through and elute at different, predictable times.
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Many mass spectrometers are connected to other instruments like a GC or liquid chromatograph. The interface and ion source of the MS are often heated to ensure the sample remains in a gaseous state as it enters the vacuum chamber for ionization and analysis.
Thermal Analysis (DSC, TGA)
Instruments like a Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) or Thermogravimetric Analyzer (TGA) use heating as the core of their measurement. A DSC precisely heats a sample and a reference to measure phase transitions (like melting), while a TGA measures changes in a sample's mass as it is heated, revealing information about its composition and thermal stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal Control
The design and implementation of a heating system in a scientific instrument involve critical engineering compromises that directly impact its performance.
Precision vs. Power
A high-power furnace designed to reach 1200°C does not need the same sub-degree precision as a PCR thermocycler that must hit 94.0°C exactly. The choice of element, sensor, and control logic is a trade-off between raw heating capability and fine-tuned accuracy.
Uniformity vs. Speed
Achieving a perfectly uniform temperature inside an oven or incubator chamber is a major challenge. Fans may be used to circulate air, but this can introduce other issues like sample dehydration. An instrument might be able to heat up quickly, but at the cost of creating "hot spots" that can ruin an experiment.
Thermal Mass and Ramp Rate
The speed at which an instrument can change temperature (its ramp rate) is limited by its thermal mass. A large, heavy furnace block will heat and cool much more slowly than the small, low-mass block in a modern thermocycler, whose entire function depends on rapid temperature changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting an instrument requires understanding how its heating system aligns with your experimental needs.
- If your primary focus is biological cultivation: You need an instrument with exceptional temperature stability and uniformity, like a high-quality incubator.
- If your primary focus is material preparation or testing: You require a robust furnace or oven capable of reaching and holding high temperatures reliably.
- If your primary focus is chemical separation and analysis: You need an instrument where heating is a precisely controlled and programmable variable, such as a gas chromatograph or thermal analyzer.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control through these instruments is fundamental to achieving reliable, reproducible, and meaningful scientific results.
Summary Table:
| Instrument Type | Primary Use | Key Temperature Features |
|---|---|---|
| Incubators | Biological cultivation | Stable, uniform heating for cell growth |
| PCR Thermocyclers | DNA amplification | Rapid, precise cycling (e.g., 95°C, 55°C, 72°C) |
| Autoclaves | Sterilization | High-temperature steam (~121°C) for purity |
| Laboratory Furnaces | Material processing | High temperatures for annealing, ashing, etc. |
| Gas Chromatography | Chemical separation | Programmable heating for vaporization and separation |
| Thermal Analyzers | Material analysis | Controlled heating for phase and mass changes |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements—enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your scientific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















