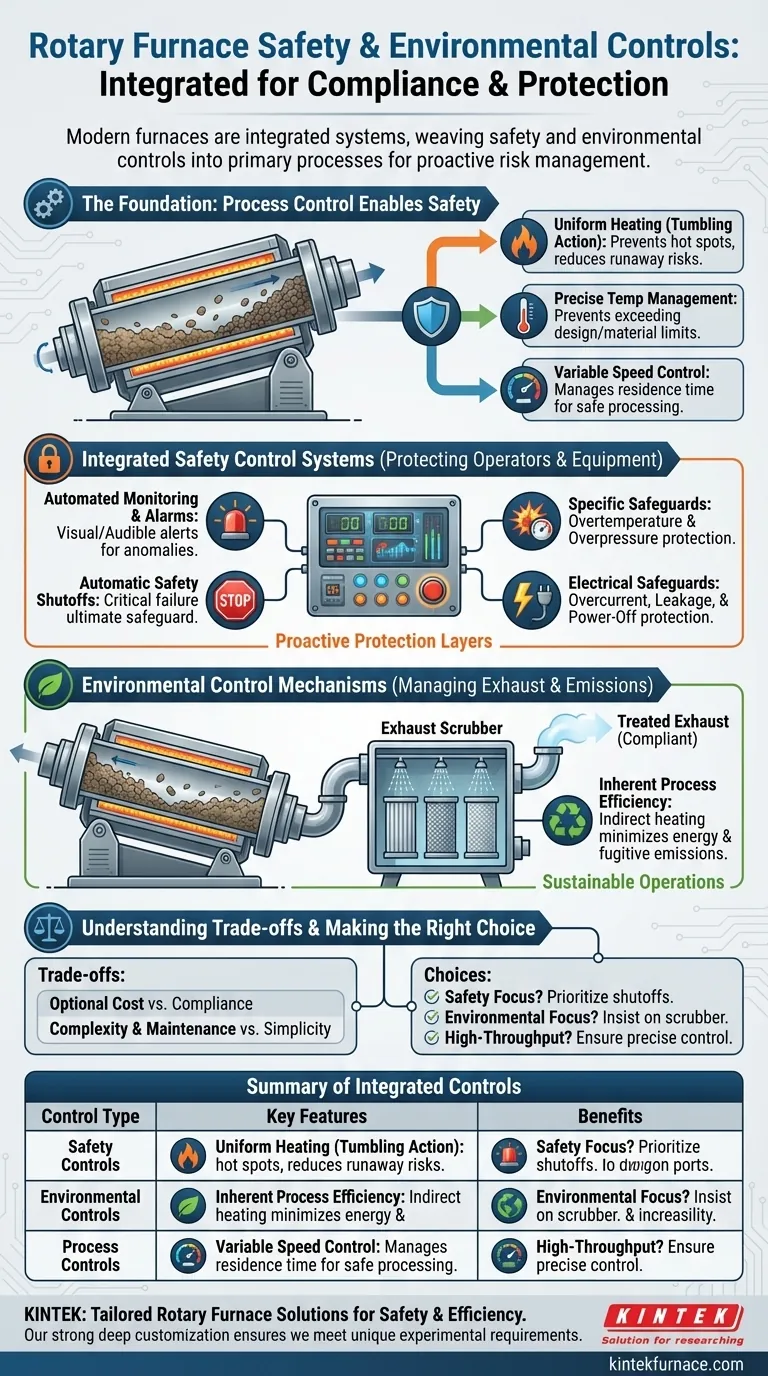
At their core, rotary furnaces integrate two key types of controls: automated safety systems that monitor operating conditions and optional environmental systems that treat exhaust gases. Advanced control systems provide a suite of safeguards, including automatic shutoffs for overtemperature, overpressure, or electrical faults, while exhaust scrubbers can be integrated to remove harmful particulates and gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
The crucial insight is that modern rotary furnaces are not merely heating devices; they are integrated systems where safety and environmental controls are woven into the primary process controls, ensuring that operational safety and regulatory compliance are managed proactively, not as an afterthought.

The Foundation: How Process Control Enables Safety
To understand the safety features, you must first understand the furnace's fundamental operation. A rotary furnace uses a slowly rotating, inclined tube to ensure materials are continuously mixed and exposed to uniform heat.
Uniform Heating as a Safety Feature
The constant rotation of the material is a primary form of process control. By preventing "hot spots" where material could overheat, this tumbling action inherently reduces the risk of runaway reactions or material degradation, which is a foundational safety benefit.
Precise Temperature Management
Modern rotary furnaces feature advanced temperature control systems. These systems are not just for process quality; they are a critical safety layer, preventing the furnace from exceeding its design limits or the safe processing temperature of the material inside.
Variable Speed Control
The ability to control the rotation speed of the furnace tube is another key process parameter. This allows operators to manage the residence time of the material, ensuring reactions proceed as expected and preventing unsafe conditions that could arise from processing material too quickly or too slowly.
Integrated Safety Control Systems
Beyond the inherent safety of controlled processing, rotary furnaces are equipped with multiple layers of dedicated safety systems designed to protect operators and equipment.
Automated System Monitoring and Alarms
The central control system continuously monitors all critical parameters. If any measurement deviates from the set safe operating window, the system will trigger an audible and visual alarm, alerting operators to the anomaly.
Automatic Safety Shutoffs
In the event of a critical failure, the control system is programmed to initiate an automatic shutdown sequence. This is the ultimate safeguard against catastrophic failure and protects against multiple hazards.
Specific Electrical and Mechanical Safeguards
These systems typically include a suite of specific protections:
- Overtemperature Protection: Shuts down heating elements if the temperature exceeds a critical setpoint.
- Overpressure Protection: Monitors internal pressure and activates safety protocols if it becomes too high.
- Overcurrent and Leakage Protection: Electrical switches safeguard against short circuits, current surges, or ground faults, preventing electrical shock and fire hazards.
- Disconnection and Power-Off Safeguards: Ensure the system defaults to a safe state in the event of a power interruption or component disconnection.
Environmental Control Mechanisms
Environmental controls in rotary furnaces are designed to manage and mitigate the impact of the exhaust stream generated during processing.
Exhaust Gas Treatment
The primary environmental control is an exhaust scrubber. Often offered as an optional but highly integrated component, the scrubber treats the furnace's off-gas before it is vented. This system effectively removes harmful particulates and neutralizes acidic or toxic gases, ensuring compliance with air quality regulations.
Inherent Process Efficiency
The efficient, indirect heating design of a rotary furnace minimizes energy consumption and waste. By containing the process within the tube and applying heat externally, these furnaces reduce the volume of fugitive emissions and maximize thermal energy, which is an inherent environmental benefit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced controls offer significant benefits, it is important to recognize the associated considerations.
Optional Features vs. Base Cost
Many of the most effective environmental controls, particularly exhaust scrubbers, are sold as optional add-ons. This creates a direct trade-off between the initial capital cost of the furnace and its level of environmental compliance.
System Complexity and Maintenance
Highly integrated control systems add complexity. While they enhance safety and precision, they also require more sophisticated operator training and a rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure the sensors and automated shutoffs remain reliable over time. A simpler system may be easier to maintain but lacks these critical protections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goals will determine which control features are most critical for your operation.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize a furnace with a comprehensive suite of automated shutoffs for overtemperature, overpressure, and electrical faults.
- If your primary focus is strict environmental compliance: Insist on a fully integrated exhaust scrubber system designed to handle the specific off-gases your process will generate.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous processing: Ensure the system has precise, reliable, and automated control over both temperature profiles and tube rotation speed to maintain safety and quality.
Ultimately, selecting the right controls transforms a rotary furnace from a simple heating tool into a safe, compliant, and highly efficient processing system.
Summary Table:
| Control Type | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Controls | Automated shutoffs for overtemperature, overpressure, electrical faults | Protects operators and equipment, prevents accidents |
| Environmental Controls | Exhaust scrubbers for gas and particulate removal | Ensures regulatory compliance, reduces emissions |
| Process Controls | Uniform heating, precise temperature, variable speed | Enhances safety, improves efficiency and product quality |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's safety and efficiency with tailored rotary furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering reliable performance and compliance. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















