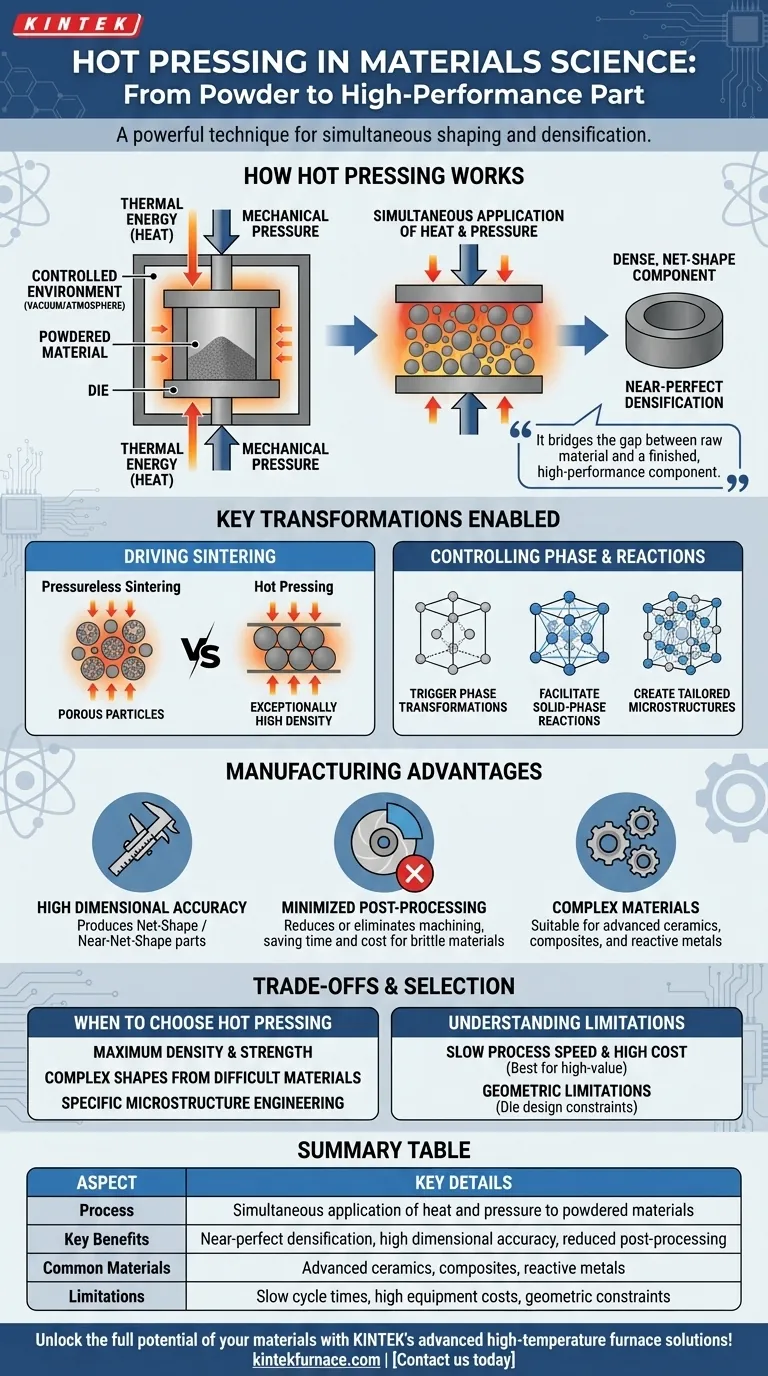
In materials science, hot pressing is a powerful technique that simultaneously shapes and densifies powdered materials into a solid component. It uses a combination of high temperature and mechanical pressure to transform loose powder into a dense, high-performance part with precise dimensions, often in a single step.
The essential role of hot pressing is to achieve near-perfect densification and superior material properties that are often impossible with pressureless or room-temperature methods. It bridges the gap between raw material and a finished, high-performance component.
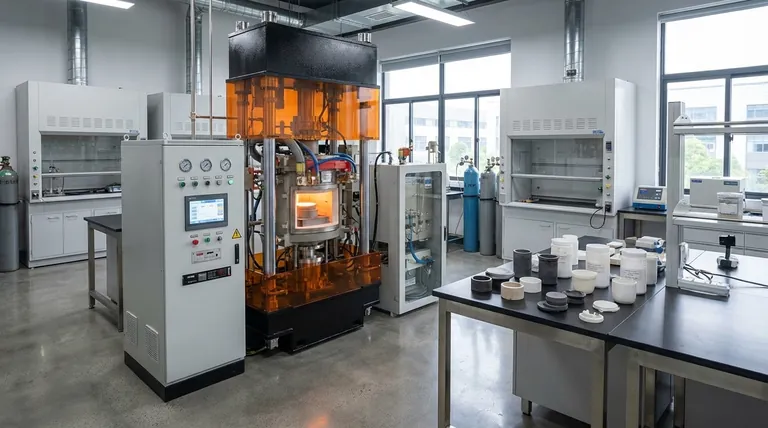

How Hot Pressing Fundamentally Works
Hot pressing is an elegant synergy of thermal and mechanical energy, applied within a highly controlled environment to achieve a specific outcome.
The Power of Heat and Pressure
Heat is applied to the material powder, but not enough to melt it completely. This thermal energy makes the material particles more pliable and increases the rate of atomic diffusion.
Simultaneously, a strong external pressure is applied. This force pushes the softened particles together, collapsing the empty spaces (or porosity) between them and promoting strong bonds to form where they touch.
A Controlled Environment for Precision
This entire process occurs inside a specialized press, often with a controlled atmosphere or vacuum. This prevents oxidation or contamination, which is critical when working with reactive, high-performance materials.
The Key Transformations It Enables
The combination of heat and pressure drives fundamental changes within the material, which is the true source of its power.
Driving Sintering to Its Limit
Sintering is the process of bonding particles together into a solid mass using heat alone. Hot pressing dramatically accelerates this process.
The external pressure physically forces particles into contact, eliminating pores much more effectively than heat alone. This is the mechanism responsible for creating materials with exceptionally high density, which directly correlates to improved strength and durability.
Controlling Phase and Reactions
The precise temperature and pressure allow engineers to trigger specific phase transformations—changes in the material's internal crystal structure. This is used to create a final material with desired properties like enhanced hardness or thermal stability.
It also facilitates solid-phase reactions, where different powdered materials can react to form new compounds or composites directly within the press.
The Manufacturing Advantage: From Powder to Part
Beyond improving material properties, hot pressing offers significant practical advantages in the manufacturing workflow.
High Dimensional Accuracy
Because the material is consolidated within a rigid die, the final component has excellent dimensional accuracy and can conform to complex geometries. This is often referred to as producing a "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" part.
Minimizing Post-Processing
The ability to produce a finished part with tight tolerances directly from powder dramatically reduces or eliminates the need for subsequent machining or grinding. For hard, brittle materials like advanced ceramics, avoiding machining is a massive saving in time, cost, and complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Process Speed and Cost
Hot pressing cycles can be slow due to the time required for heating and cooling. The equipment needed to generate high temperatures and pressures is also expensive, making this process best suited for high-value components rather than mass production.
Geometric Limitations
The shape of the final part is limited by the design of the die. Extremely complex internal features or very large components can be challenging or impossible to produce with this method.
When to Choose Hot Pressing
Your specific goal will determine if hot pressing is the right approach for your project.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: Hot pressing is the superior choice for creating components with minimal porosity and exceptional mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is producing a complex shape from a difficult-to-machine material: The near-net-shape capability of hot pressing can bypass costly and challenging machining steps, saving significant resources.
- If your primary focus is engineering a specific microstructure: The precise control over temperature and pressure allows you to guide phase transformations and create materials with tailored performance characteristics.
Ultimately, hot pressing empowers you to transform raw powders into finished, high-performance parts by controlling their form and function in a single, decisive step.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous application of heat and pressure to powdered materials |
| Key Benefits | Near-perfect densification, high dimensional accuracy, reduced post-processing |
| Common Materials | Advanced ceramics, composites, reactive metals |
| Limitations | Slow cycle times, high equipment costs, geometric constraints |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored hot pressing systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, from achieving maximum density to producing complex shapes efficiently. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength



















